Abstract
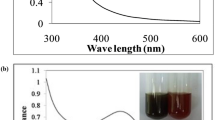
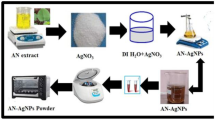
Synthesis of metallic nanoparticles using secondary metabolites present in plant extracts has attracted attention. In this study, Lantana trifolia aqueous extracts were used to synthesize silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) which were then screened for their antimicrobial activity. The morphology, size and functional groups present in AgNPs was evaluated using electron microscopy and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR). The role of temperature, reaction time and concentration of precursor ion were evaluated by measuring the surface plasmon resonance of AgNPs using UV–Vis spectroscopy. The crystal structure, hydrodynamic diameters and redox potential were evaluated using powder X-ray diffractometer (PWXRD), dynamic light scattering (DLS) and cyclic voltammetry respectively. The data obtained in this study revealed that increase in the reaction time led to an increase in surface plasmon resonance of AgNPs while the increase in temperature from 20 to 35 ℃ increased the rate of AgNPs synthesis. The XRD diffractogram revealed that the particles were composed of silver with 2θ = 38.36, 44.428, 54.89, and 57.87, corresponding to the silver crystal planes of (111), (200), (220), and (311). The diameters of the nanoparticles were between 35 and 70 nm, and they had moderate antimicrobial activity against E. coli, P. aeruginosa, C. albicans, S. aureus and B. subtilis.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. van Duin, D.L. Paterson, Multidrug-resistant bacteria in the community trends and lessons learned. Infect. Dis. Clin. North Am. 30, 377–390 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idc.2016.02.004
S. Shaikh, N. Nazam, S.M.D. Rizvi, K. Ahmad, M.H. Baig, E.J. Lee, I. Choi, Mechanistic insights into the antimicrobial actions of metallic nanoparticles and their implications for multidrug resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102468
O. Lushchak, A. Zayachkivska, A. Vaiserman, Metallic nanoantioxidants as potential therapeutics for type 2 diabetes a hypothetical background and translational perspectives. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/3407375
L. Wang, C. Hu, L. Shao, The antimicrobial activity of nanoparticles present situation and prospects for the future. Int. J. Nanomed. 12, 227–1249 (2017). https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S121956
T.C. Dakal, A. Kumar, R.S. Majumdar, V. Yadav, Mechanistic basis of antimicrobial actions of silver nanoparticles. Front Microbiol. (2016). https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.01831
R. Behra, L. Sigg, M.J.D. Clift, F. Herzog, M. Minghetti, B. Johnston, A. Petri-Fink, B. Rothen-Rutishauser, Bioavailability of silver nanoparticles and ions from a chemical and biochemical perspective. J. R. Soc. Interface. 10, 20130396 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1098/rsif.2013.0396
I.-M. Chung, I. Park, K. Seung-Hyun, M. Thiruvengadam, G. Rajakumar, Plant-Mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles their characteristic properties and therapeutic applications. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 11, 40 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-016-1257-4
S. Ahmed, M. Ahmad, B.L. Swami, S. Ikram, A review on plants extract mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications a green expertise. J. Adv. Res. 7, 17–28 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2015.02.007
A. Martínez-Abad, Multifunctional and nanoreinforced polymers for food packaging, (Elsevier. New York (2011). https://doi.org/10.1533/9780857092786.3.347
S.-L. Abram, J. Gagnon, M. Priebe, N. Hérault, K.M. Fromm, Ag nanoencapsulation for antimicrobial applications. Chimia (Aarau). 72, 49–252 (2018). https://doi.org/10.2533/chimia.2018.249
M. Priebe, J. Widmer, N. Suhartha Löwa, S.L. Abram, I. Mottas, A.K. Woischnig, P.S. Brunetto, N. Khanna, C. Bourquin, K.M. Fromm, Antimicrobial silver-filled silica nanorattles with low immunotoxicity in dendritic cells, Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 13, 11–22 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2016.08.002.
Q.B. Xu, L.J. Xie, H. Diao, F. Li, Y.Y. Zhang, F.Y. Fu, X.D. Liu, Antibacterial cotton fabric with enhanced durability prepared using silver nanoparticles and carboxymethyl chitosan. Carbohydr Polym. 177, 187–193 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.08.129
T.I. Shaheen, A.A.A. El Aty, In-situ green myco-synthesis of silver nanoparticles onto cotton fabrics for broad spectrum antimicrobial activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 118, 2121–2130 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.07.062
S. Kaul, N. Gulati, D. Verma, S. Mukherjee, U. Nagaich, Role of nanotechnology in cosmeceuticals a review of recent. Adv. J. Pharm. 2018, 1–19 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/3420204
E.O. Sousa, J.G.M. Costa, Genus lantana Chemical aspects and biological activities. Brazilian J Pharmacogn. 22, 1155–1180 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1590/S0102-695X2012005000058
S.S. Azam, A. Habib, A.S. Memic, M. Ahmed, M. Oves, M.S. Khan, Antimicrobial activity of metal oxide nanoparticles against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria a comparative study. Int. J. Nanomed. 7, 6003–6009 (2012). https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S35347
M.I. Masum, M.M. Siddiqa, K.A. Ali, Y. Zhang, Y. Abdallah, E. Ibrahim, W. Qiu, C. Yan, B. Li, Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles using phyllanthus emblicafruit extract and its inhibitory action against the pathogen acidovorax oryzaestrain RS-2 of rice bacterial brown stripe. Front Microbiol. (2019). https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.00820
C. Ponce, J. Chanona, V. Garibay, E. Palacios, G. Calderon, R. Sabo, Functionalization of agave cellulose nanoparticles and its characterization by microscopy and spectroscopy techniques, microsc microanal. 19, 200–201 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1017/S1431927613002997.
E.S. Madivoli, E.G. Maina, P.K. Kairigo, M.K. Murigi, J.K. Ogilo, J.O. Nyangau, P.K. Kimani, C. Kipyegon, In vitro antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of Prunus africana (Hook. f.) Kalkman (bark extracts) and Harrisonia abyssinica Oliv. extracts (bark extracts) a comparative study, J. Med. Plants Econ. Dev. (2018). https://doi.org/10.4102/jomped.v2i1.39.
L. Katata-Seru, T. Moremedi, O.S. Aremu, I. Bahadur, Green synthesis of iron nanoparticles using Moringa oleifera extracts and their applications removal of nitrate from water and antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Liq. 256, 296–304 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.11.093
D. Ciolacu, F. Ciolacu, P.V. Popa, Amorphous cellulose—structure and characterization, Cellul. Chem. Technol. 45, 3–21
Z. Wang, C. Fang, M. Megharaj, Characterization of iron-polyphenol nanoparticles synthesized by three plant extracts and their fenton oxidation of azo dye. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2(2014), 1022–1025 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/sc500021n
Y.Y. Loo, Y. Rukayadi, M.-A.-R. Nor-Khaizura, C.H. Kuan, B.W. Chieng, M. Nishibuchi, S. Radu, In vitro antimicrobial activity of green synthesized silver nanoparticles against selected gram-negative foodborne pathogens. Front Microbiol. 9, 1555 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01555
J. Olson, S. Dominguez-Medina, A. Hoggard, L.Y. Wang, W.S. Chang, S. Link, Optical characterization of single plasmonic nanoparticles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 44, 40–57 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/c4cs00131a
S.I. Vasylevskyi, S. Kracht, P. Corcosa, K.M. Fromm, B. Giese, M. Füeg, Formation of silver nanoparticles by electron transfer in peptides and c-cytochromes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56, 5926–5930 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201702621
M. Ndikau, N.M. Noah, D.M. Andala, E. Masika, Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using citrullus lanatus fruit rind extract. Int. J. Anal. Chem. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8108504
X.C. Jiang, W.M. Chen, C.Y. Chen, S.X. Xiong, A.B. Yu, Role of temperature in the growth of silver nanoparticles through a synergetic reduction approach. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 6, 1–9 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11671-010-9780-1
N. Ahmad, B.C. Ang, M.A. Amalina, C.W. Bong, Influence of precursor concentration and temperature on the formation of nanosilver in chemical reduction method, Sains Malaysiana. 47, 57–168 (2018). https://doi.org/10.17576/jsm-2018-4701-19.
M. Vanaja, K. Paulkumar, M. Baburaja, S. Rajeshkumar, G. Gnanajobitha, C. Malarkodi, M. Sivakavinesan, G. Annadurai, Degradation of methylene blue using biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/742346
G. Socrates, Infrared and Raman Characteristic Group Frequencies, 3rd edition, 2001. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrs.1238.
C. Levard, S. Mitra, T. Yang, A.D. Jew, A.R. Badireddy, G. V. Lowry, G.E. Brown, Effect of chloride on the dissolution rate of silver nanoparticles and toxicity to E. coli, Environ. Sci. Technol. 47, 5738–5745 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/es400396f.
J. Hoyos-Arbeláez, M. Vázquez, J. Contreras-Calderón, Electrochemical methods as a tool for determining the antioxidant capacity of food and beverages a review. Food Chem. 221, 1371–1381 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.11.017
M. José Jara-Palacios, M. Luisa Escudero-Gilete, J. Miguel Hernández-Hierro, F.J. Heredia, D. Hernanz, Cyclic voltammetry to evaluate the antioxidant potential in winemaking by-products, Talanta. 165, 211–215 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2016.12.058.
L.C. Yun’an Qing, R. Li, G. Liu, Y. Zhang, X. Tang, J. Wang, H. Liu, Y. Qin, Potential antibacterial mechanism of silver nanoparticles and the optimization of orthopedic implants by advanced modification technologies, Int. J. Nanomed. 13, 3311–3327 (2018). https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S165125.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Department of Chemistry, Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology and Sino Africa Joint Research Centre (SAJOREC) for provision of facilities where part of the work was done. The authors also acknowledge the financial support of the National research fund, AFRICA-ai-JAPAN Project JFY 2018/2019 and Research Production and Extension division, Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology (JKUAT-RPE) for their financial support. The authors also acknowledge the financial support of the Federal Commission of Scholarships for a one-year PhD research stay at the University of Fribourg under Prof. Katharina M. Fromm.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Madivoli, E.S., Kareru, P.G., Gachanja, A.N. et al. Facile Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Lantana trifolia Aqueous Extracts and Their Antibacterial Activity. J Inorg Organomet Polym 30, 2842–2850 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-019-01432-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-019-01432-5