Abstract
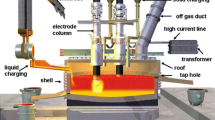
To increase the utilization fraction of vanadium titano-magnetite in the blast furnace burden to > 80 pct, a new slag zone with high MgO was found. The effect of the TiO2 content and MgO/CaO mass ratio on the viscosity and liquidus temperature of the high TiO2-bearing blast furnace slag was investigated in the present work. The results indicated that at a fixed CaO/SiO2 ratio of 1.1, the viscosity decreases with increasing TiO2 content at a range of 20 to 34 mass pct. Conversely, increasing the MgO/CaO ratio from 0.32 to 0.65 causes a slight increase in the slag viscosity. The activation energy may show a concomitant variation corresponding to the viscosity of slag. The liquidus temperature first increases and then slightly decreases with TiO2 content. However, the liquidus temperature first decreases and then increases with the MgO/CaO ratio, similar to the variation of the thermodynamic calculation using FactSage software. Various viscosity models were employed to predict the viscosity, and Yan’s model was found to be the most reliable in predicting the viscosity in the present study. In addition, the iso-viscosity distribution diagram was obtained using Yan’s model calculation. It may have potential for application in the blast furnace ironmaking process with super-high (> 80 pct) vanadium titano-magnetite. A suitable slag composition was found to satisfy the smelting process in a blast furnace with super-high TiO2 content at low temperature by using more MgO and less CaO content.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Chen, B. Song, L.N. Wang, T. Qi, Y. Wang, and W.J. Wang: Miner. Eng., 2011, vol. 24 (8), pp. 864-69.
L. Zhang, L. Zhang, M. Wang, G. Li and Z. Sui: Min. Eng., 2007, vol. 20, pp. 684-93.
R. Moskalyk and A. Alfantazi: Miner. Eng., 2003, vol. 16, pp. 793-805.
J. Xiang, Q. Huang, X. Lv, C. Bai: J. Hazard. Mater., 2017, vol. 336, pp.1-7.
F. Valighazvini, F. Rashchi, R Khayyam Nekouei: Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2013, vol. 52, pp. 1723-30.
X. Zou, X. Lu: Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, vol. 20, pp. 1829-35.
Z. Yuan, X. Wang, C. Xu, W. Li and M. Kwauk: Minerals Engineering, 2006, vol. 19, pp. 975-78.
T. Nagasaka, M. Hino, S. Ban-ya, Met. Trans. B, 2000, vol. 31B, pp. 945.
N. Saito, N. Hori, K. Nakashima and K. Mori: Metall. Materi. Trans. B, 2003, vol. 34, pp. 509-16.
A. Shankar, M. Gornerup, A. K. Lahiri and S. Seetharaman: Materi. Trans. B, 2007, vol. 38, pp. 911-15.
G. Li, J. Ma, H. Ni, Q. Shen, F. Tsukihashi, ISIJ Int. 2006, vol. 46, pp. 981.
I. Sohn, W. Wang, H. Matsuura, F. Tsukihashi, D. J. Min: ISIJ Int., 2012, vol. 52, pp. 158-60.
A. Ohno and H. Ross: Can. Metall. Q., 1963, vol. 2, pp. 259-79.
H. Park, J. Y. Park, H. Kim and I. Sohn: Steel Res. Int., 2012, vol. 83, pp. 150-56.
J. L. Liao, J. Li, X. D. Wang and Z. T. Zhang: Ironmak. Steelmak., 2012, vol. 39, pp. 133.
N. Saito, N. Hori, K. Nakashima, K. Mori: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2003, vol. 34B, pp. 509-16.
Z. Yan, X. Lv, W. He and J. Xiang: ISIJ Int., 2017, vol. 52, pp. 31-36.
Z. Yan, X. Lv, D. Liang, J. Zhang and C. Bai: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2017, vol. 48, pp. 1092-99.
S. Seftharaman, D. Sichen, S. SridharK, and C. Mills: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2000, vol. 31B, pp. 111-19.
K. Hu, X. Lv, S. Li, W. Lv, B. Song and K. Han: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2018, vol. 49, pp. 1963-73.
R.G. Duan, K.M. Liang, and G.U. Shouren: Mater. Trans. JIM, 1998, vol. 39, pp. 1162-63.
B.O. Mysen, F. J. Ryerson, D. Virgo, and F.A. Seifert: Am. Miner.,1980, vol. 65, pp. 1150-65.
S. Zhang, X. Zhang, H. Peng, L. Wen, G. Qiu, M. Hu and C. Bai: ISIJ Int., 2014, vol. 54, pp. 734-42.
D. J. Kim, Y.S. Lee, D. J. Min, S. M. Jung and S. H. Yi: ISIJ Int.,2004, vol. 44, pp. 1291-97.
H. Kim, W. H. Kim, I. Sohn and D. J. Min: Steel Res. Int., 2010, vol. 81, pp. 261-64.
Z. Yan, R. G. Reddy, X. Lv, Z. Pang and W. He: Ironmak. Steelmak., 2018, vol. 81, pp. 1-7.
P.V. Riboud, Y. Roux, L.D. Lucas, and H. Gaye: Fachber. Huttenpraxis Met., 1981, vol. 19, pp. 859-69.
G.H. Zhang and K.C. Chou: J. Min. Metall. B, 2012, vol. 48, pp. 433-42.
Mills, K.C. and S. Sridhar: Ironmak. Steelmak., 1999, vol. 26, pp. 262-8.
G. Urbain: Steel Res. Int., 1987, vol. 58, pp. 111-16.
Z. Yan, X. Lv, J. Zhang, Y. Qin and C. Bai: Can. Metall. Q., 2016, vol. 55, pp. 186-94.
Acknowledgment
We thank the National Key R&D Program of China (no. 2018YFC1900500) for the financial support of this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Manuscript submitted 26 August, 2019.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pang, Z., Lv, X., Jiang, Y. et al. Blast Furnace Ironmaking Process with Super-High TiO2 in the Slag: Viscosity and Melting Properties of the Slag. Metall Mater Trans B 51, 722–731 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-019-01756-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-019-01756-0