Abstract
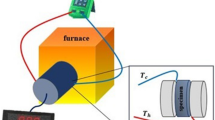
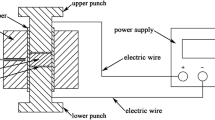
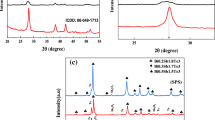
Bi-Te is a thermoelectric material used at room temperature. It is typically fabricated as a single-crystal ingot, making processing difficult and material loss very high. Pressureless sintering processes have been studied to address these issues; however, they typically result in lower-density material. Methods such as hot isostatic pressing and spark plasma sintering have mainly been studied. However, there has been limited research on pressureless sintering without additional steps such as pressurization or charging. The aim of this study is to obtain a dense Bi2Te2.7Se0.3 sintered body by combining rapid sintering with air sintering by modifying a typical sintering furnace. The effect of heating rate on densification and phase change was also investigated. Bi2Te2.7Se0.3 powder was first synthesized by the mechanochemical method. The synthesized powder was then heated at a rate of 5°C/s to 20°C/s and finally sintered at a temperature of 570°C for 10 min in H2/N2 mixture under Te-rich conditions. These conditions produced a sintered body with relative density of at least 90% of the theoretical density, and a bulk density of 6.98 g/cm3 was obtained when temperature was increased at a rate of 20°C/s. Observation of the microstructure showed that porosity decreased as the heating rate was increased. The results of this study confirm that the heating rate during rapid sintering can affect the density of the sintered body.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.S. Dresselhaus, G. Chen, M.Y. Tang, R.G. Yang, H. Lee, D.Z. Wang, Z.F. Ren, J.P. Fleurial, and P. Gogna, Adv. Mater. 19, 1043–1053 (2007).
G.S. Nolas, D.T. Morelli, and T.M. Tritt, Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 29, 89–116 (1999).
J. Seo, K. Park, D. Lee, and C. Lee, Mater. Sci. Eng. B 49, 247–250 (1997).
H.C. Kim, T.S. Oh, and D.B. Hyun, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 61, 743–749 (2000).
S. Miura, Y. Sato, K. Fukuda, K. Nishimura, and K. Ikeda, J. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 277, 244–249 (2000).
G. Delaizir, G. Bernard-Granger, J. Monnier, R. Grodzki, O. Kim-Hak, P.-D. Szkutnik, M. Soulier, S. Saunier, D. Goeuriot, O. Rouleau, J. Simon, C. Godart, and C. Navone, Mater. Res. Bull. 47, 1954–1960 (2012).
J. Arreguin-Zavala, D. Vasilevskiy, S. Turenne, and R.A. Masut, J. Electron. Mater. 42, 1992–1998 (2013).
L.D. Zhao, B.-P. Zhang, J.-F. Li, M. Zhou, and W.S. Liu, Phys. B 400, 11–15 (2007).
M. Scheele, N. Oeschler, K. Meier, A. Kornowski, C. Kinke, and H. Weller, Adv. Funct. Mater. 19, 3476–3483 (2009).
G. Molenat, L. Durand, J. Galy, and A. Couret, J. Metall. 2010, 9 (2010).
K. Hasezaki, M. Nishimura, M. Umata, H. Tsukuda, and M. Araoka, Mater. Trans. JIM 35, 428–432 (1994).
M. Zakeri, M. Allahkarami, Gh Kavei, A. Khanmohammadian, and M.R. Rahimipour, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 209, 96–101 (2009).
C.H. Lee, Y.W. Shin, H.S. Shin, D.H. Yeo, and S. Nahm, Nanosci. Nanotechnol. Lett. 9, 40–44 (2017).
O. Falkenbach, M.O. Loeh, C.W. Wiegand, A. Schmitz, D. Dartung, G. Koch, P.J. Klar, E. Mueller, and S. Schlecht, J. Electron. Mater. 46, 5781–5791 (2017).
A. Soni, Y. Shen, M. Yin, Y. Zhao, L. Yu, X. Hu, Z. Dong, K.A. Khor, M.S. Dresselhaus, and Q. Xiong, Nano Lett. 12, 4305–4310 (2012).
L.D. Zhao, B.P. Zhang, J.F. Le, H.L. Zhang, and W.S. Liu, Solid State Sci. 10, 651 (2008).
J. Bruchon, D.P. Munoz, F. Valdivieso, and S. Drapier, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 85, 2398–2405 (2012).
M.Y. Kim, S.I. Kim, H.J. Cho, H.A. Mun, H.S. Kim, J.H. Lim, S.W. Kim, and K.H. Lee, Scr. Mater. 167, 120–125 (2019).
Y. Pan, T.R. Wei, Q. Cao, and J.F. Li, Mater. Sci. Eng. B 197, 75–81 (2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, C.H., Shin, H.S., Yeo, D.H. et al. Effect of Heating Rate on Bulk Density and Microstructure in Bi2Te2.7Se0.3 Sintering. J. Electron. Mater. 49, 736–742 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-019-07750-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-019-07750-1