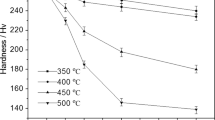
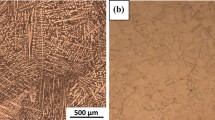
Abstract
Two different thermo-mechanical processing routes, single-cold-rolling and double-cold-rolling, are adopted to process a Cu-Ni-Si alloy, and their effects on the microstructure and properties of the alloys are investigated. While keeping identical aging treatments and equivalent total cold-rolling deformation, 45-minute final aging at 450 °C endows the double-cold-rolling-processed alloys with a tensile strength of 754 ± 12 MPa, higher than 691 ± 3 MPa for the single-cold-rolling-processed alloys, whereas their electrical conductivities are close (~ 39 pct IACS). The final aging at 450 °C for 4 hours, on the other hand, renders the double-cold-rolling-processed alloy an electrical conductivity of 52.6 pct IACS, greater than 43.7 pct IACS for the single-cold-rolling-processed alloy, whereas their strengths are approximately identical (~ 705 MPa). The superior mechanical and electrical properties in the double-cold-rolling-processed alloy with the final aging time from 45 minutes to 4 hours are attributed to the dissolution of large precipitates during the second cold rolling followed by the acceleration of fine and uniformly dispersed precipitates in the final aging. Finally, the effects of dislocations, grain boundaries, solute atoms, and precipitates on the mechanical and electrical properties of the examined Cu-Ni-Si alloy are discussed on the theoretical basis, which can provide guidelines to further processing optimization.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
K. Ziewiec, K. Bryła, A. Błachowski, K. Ruebenbauer and D. Mucha: J. Alloys Compd., 2009, vol. 483, pp. 585-88.
J. Yi, Y.L. Jia, Y.Y. Zhao, Z. Xiao, K.J. He, Q. Wang, M.P. Wang and Z. Li: Acta Mater., 2019, vol. 166, pp. 261-70.
Q. Liu, Z. Xiang, Y. Ge, J. Wang and J.Z. Cui: Metall. Mater. Trans. A., 2006, vol. 37, pp. 3233-38.
Y. Zhang, B.H. Tian, A.A. Volinsky, H.L. Sun, Z. Chai, P. Liu, X.H. Chen and Y. Liu: J Mater Eng Perform., 2016, vol. 25, pp. 1336-41.
W. Wang, H. Kang, Z. Chen, Z.J. Chen, C.L. Zou, R.G. Li, G.M. Yin and T.M. Wang: Mater. Sci. Eng A., 2016, vol. 673, pp. 378-90.
E. Lee, S. Han, K. Euh, S.H. Lim and S.S. Kim: Met. Mater. Int., 2011, vol. 17, pp. 569-76.
C. Watanabe, S. Takeshita and R Monzen: Metall. Mater. Trans. A., 2015, vol. 46, pp. 2469-75.
J.Y. Cheng, B.B. Tang, F.X. Yu and B Shen: J. Alloys Compd., 2014, vol. 614, pp. 189-95.
F.L. Hadj, H. Azzeddine, T. Baudin, M.H. Mathon, F. Brisset, A.L. Helbert, M. Kawasaki, D. Bradai and T.G. Langdon: J. Alloys Compd., 2015, vol. 638, pp. 88-94.
A.Y. Khereddine, F.L. Hadj, H. Azzeddine, T. Baudin, F. Brisset, A.L. Helbert, M.H. Mathon, M. Kawasaki, D. Bradai and T.G. Langdon: J. Alloys Compd., 2013, vol. 574, pp. 361-67.
A.Y. Khereddine, F.L. Hadj, M. Kawasaki, T. Baudin, D. Bradai and T.G. Langdon: Mater. Sci. Eng A., 2013, vol. 576, pp. 149-55.
S. Suzuki, N. Shibutani, K. Mimura, M. Isshiki and Y. Waseda: J. Alloys Compd., 2006, vol. 417, pp. 116-20.
Q. Lei, Z. Li, Y. Gao, X. Peng and B.J. Derby: J. Alloys Compd., 2017, vol. 695, pp. 2413-23.
A. Ventura, C. Marvel, G. Pawlikowski, M. Bayes, M. Watanabe, R. Vinci and W. Misiolek: Metall. Mater. Trans. A., 2017, vol. 48, pp. 6070-6082.
G.M. Stoica, D.E. Fielden, R. McDaniels, Y. Liu, B. Huang, P. K. Liaw, C. Xu and T.G. Langdon: Mater. Sci. Eng A., 2005, vol. 410, pp. 239-42.
T. Tsuchiyama, S. Yamamoto, S. Hata, M. Murayama, S. Morooka, D. Akama and S. Takaki: Acta Mater., 2016, vol. 113, pp. 48-55.
M. Gholami, J. Vesely, I. Altenberger, H.A. Kuhn, M. Janecek, M. Wollmann and L. Wagner: J. Alloys Compd., 2017, vol. 696, pp. 201-12.
Williamson GK, Hall WH: Acta Metal., 1953, vol. 1, pp. 22-22.
S. Brandstetter, P.M. Derlet, S. Van Petegem and H, Van Swygenhoven: Acta Mater., 2008, vol. 56, pp. 165-76.
Avrami, M.: J CHEM PHYS., 1939, vol. 7, pp.1103-12.
J.R. Davis: Copper and Copper Alloys, ASM international, New York, NY, 2001.
K. Ma, H. Wen, T. Hu, T.D. Topping, D. Isheim, D.N. Seidman, E.J. Lavernia and J.M. Schoenung: Acta Mater, 2014, vol. 62, pp. 141-155.
R. Labusch: Phys. Status Solidi B., 1970, vol. 41, pp. 659-69.
L. Balogh, T. Ungár, Y.H. Zhao, Y.T. Zhu, Z. Horita, C. Xu and T.G. Langdon: Acta Mater., 2008, vol. 56, pp. 809-20.
J. Miyake, G. Ghosh and M.E. Fine: MRS BULL., 1996, vol. 21, pp. 13-18.
S. A. Lockyer and F. W. Noble: J MATER SCI., 1994, vol. 29, pp. 218-26
Argon A S, Orowan E: Phy Today., 1971, vol. 24, pp. 60-60.
T. Gladman: Met. Sci. J., 1999, vol. 15, pp. 30-36.
Y. Wu, Y. Li, J.Y. Liu, S. Tan, F. Jiang and J Sun: Mater. Sci. Eng A., 2018, vol. 731, pp. 403-12.
N. J. Petch: J. Iron Steel Inst., 1953, vol. 174, pp. 25–28.
N. Hansen: Scr. Mater., 2004, vol. 51, pp. 801-06.
V. Verma, V. Pandey, V.N. Shukla, S. Annapoorni and R.K. Kotnala: Solid State Commun., 2009, vol. 149, pp. 1726-30.
L. Tian, I. Anderson, T. Riedemann and A. Russell: Acta Mater., 2014, vol. 77, pp. 151-61.
G. Ghosh, J. Miyake and M. Fine: JOM., 1997, vol. 49, pp. 56-60.
H. Xie, L. Jia and Z. Lu: Mater. Charact., 2009, vol. 60, pp. 114-18.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2016YFB0301300) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51974028, 51504023 and U1602271).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Manuscript submitted March 7, 2019.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, L., Fu, H., Wang, C. et al. Enhanced Mechanical and Electrical Properties of a Cu-Ni-Si Alloy by Thermo-mechanical Processing. Metall Mater Trans A 51, 331–341 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-019-05507-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-019-05507-3