Abstract
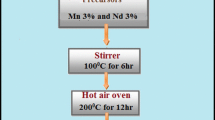
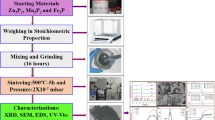
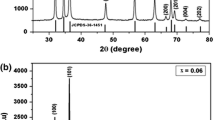
Zinc stannate has attracted substantial interest owing to its unique properties making it a suitable ternary oxide for numerous applications. One of the most promising ternary semiconducting oxides, zinc stannate (Zn2SnO4) is more stable than binary semiconducting oxides such as ZnO and SnO2 because of its attractive physical properties and very high electrical conductivity. Nanoparticles of pure and doped Zn2SnO4 were synthesized via facile hydrothermal technique. Characterization methods such as XRD, FTIR, SEM, UV and VSM were carried out to study the behaviour of zinc stannate. X-ray diffraction analysis confirmed the phase purity and high crystalline nature of the synthesized sample. Scanning electron micrography illustrated its spherical morphology. The increment of bandgap was observed for the doped zinc stannate. The presence of functional groups was confirmed using FTIR spectrum. The magnetic property of the material was analysed using vibrational sample magnetometer and found to exhibit diamagnetic behaviour for pure zinc stannate and weak ferromagnetic property for Co- and Fe-doped Zn2SnO4. The attained results depict the excellent and exceptional structural, optical and magnetic properties which establish the use of Zn2SnO4 nanoparticles in a wide range of applications especially in the field of optoelectronic devices and spintronics.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Senna, Dekker encyclopedia of nanoscience and nanotechnology, 2nd edn. (Taylor and Francis CRC Press, Florida, 2009)
K. Ahalya, N. Suriyanarayanan, S. Sangeetha, Mater. Sci. Semi. Processing. 27, 672–681 (2014)
N. Tiwari, S. Doke, A. Lohar, S. Mahamuni, C. Kamal, A. Chakrabarti, R.J. Choudhary, P. Mondal, S.N. Jha, D. Bhattacharyya, J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 90, 100–113 (2016)
J. Kennedy, J. Leveneur, Y. Takeda, G.V.M. Williams, S. Kupke, D.R.G. Mitchell, A. Markwitz, J.B. Metson, J. Mat. Sci. 47(3), 1127–1134 (2012)
T.L. Villarreal, G. Boschloo, A. Hagfeldt, J. Phys. Chem. C. 111, 5549 (2007)
M. Mary Jaculine, S.J. Das, H.J. Kim, B.C. Kim, K.H. Yu, C. JustinRaj, Mater. Lett. 111, 28–31 (2013)
M. Fakhrzad, A.H. Navidpour, M. Tahari, S. Abbasi, Mater. Res. Express. 6, 095037 (2019)
S. Sumithra, N.V. Jaya, J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Electron. 29, 4048 (2018)
A.R. Fattahi, M. Asemi, M. Ghanaatshoar, J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Electron. 30, 13525 (2019)
K. Srinivas, S. Manjunath Rao, P. Venugopal Reddy, Nanoscale. 3, 642 (2011)
W. Yu, K. Jiang, J. Wu, J. Gan, M. Zhu, Z. Hu, J. Chu, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 13, 6211 (2011)
S. Sumithra, N.V. Jaya, J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 30, 1883 (2017)
C.G. Anchieta, D. Sallet, E.L. Foletto, S.S. DaSilva, O. Chiavone-Filho, C.A.O. Nascimento, Ceram. Int. 40, 4173–4178 (2014)
W. Cun, W. Xinming, J. Mater. Sci. 37, 2989 (2002)
L. Allwin Joseph, J. EmimaJ eronsia, M. Mary Jaculine, S. Jerome Das, Phys. Res. Int. 2016, 6 (2016)
D.W. Kim, S.S. Shin, I.S. Cho, S. Lee, D.H. Kim, C.W. Lee, H.S. Jung, K.S. Hong, Nanoscale. 4, 557 (2012)
S. Sumithra, N. Victor Jaya, Physica. 493, 35–42 (2016)
N.D. Thien, L.M. Quynh, L. Van Vu et al., J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Electron. 30, 1813 (2019)
C. Chao, G. Li, J. Li, Y. Liu, Ceram. Int. 41, 1857–1862 (2015)
W. Wang, H. Chai, X. Wang, X. Hu, X. Li, App. Surf. Sci. 341, 43–47 (2015)
M. Mary Jaculine, C. JustinRaj, H.-J. Kim, A. Jeya Rajendran, S. Jerome Das, Mater. Sci. Semi. Processing. 25, 52–58 (2014)
Z. Li, Y. Zhou, H. Yang, R. Huang, Z. Zou, Electrochim. Acta. 152, 25–30 (2015)
P. Jayabal, V. Sasirekha, J. Mayandi, V. Ramakrishnan, SuperlatticesMicrostruct. 75, 775–784 (2014)
M.B. Ali, F. Barka-Bouaifel, H. Elhouichet, B. Sieber, A. Addad, L. Boussekey, M. Férid, R. Boukherroub, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 457, 360–369 (2015)
X. Zhu, L. Geng, F. Zhang, L. Liu, L. Cheng, J. Power Source. 189, 828–831 (2009)
J.E. Jeronsia, L.A. Joseph, M.M. Jaculine, P.A. Vinosha, S.J. Das, J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 10, 601 (2016)
V. Gandhi, R. Ganesan, H.H. AbdulrahmanSyedahamed, M. Thaiyan, J. Phys. Chem. C. 118, 9715–9725 (2014)
B. Cullity, Elements of X-ray diffraction, 2nd edn. (Adisson-Wesley Publishing, Boston, 1978)
H.P. Klug, L.E. Alexander, X-ray diffraction procedures for polycrystalline and amorphous materials (Wiley, New York, 1962)
G.K. Williamson, R.E. Smallman, Phil. Mag. 1, 34 (1956)
J. Tauc, Amorphousand liquid semiconductors (Plenum, New York, 1974)
R. Yousefi, J. Beheshtian, S.M. Seyed-Talebi, H.R. Azimi, F.J. Sheini, Chem An Asian J. 13(9), 1228–1228 (2018)
R.F. Dezfuly, R. Yousefi, F. Jamali-Sheini, Ceram. Int. 42, 7455–7746 (2016)
A. Saáedi, R. Yousefi, F. Jamali-Sheini, A.K. Zak, M. Cheraghizade, M.R. Mahmoudian, M.A. Baghchesara, A.S. Dezaki, Physica E. 79, 113–118 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joseph, L.A., Ragu, R., Akilan, M. et al. Structural, optical and magnetic behaviour of cobalt- and ferrous-doped zinc stannate nanoparticles synthesized by hydrothermal method. Appl. Phys. A 126, 43 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-3220-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-3220-6