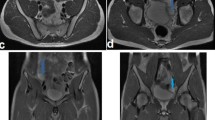
Abstract
Objectives
To measure the testicular volume and testicular fat deposition of middle-aged overweight men and to assess the utility of testicular fat deposition and testicular volume in determining and monitoring testicular infertility.
Materials and methods
Pelvic MRI with thin slice T2WI, T1WI and mDIXON Quant was performed on 30 middle-aged overweight patients in the treatment group and 30 middle-aged overweight men in the control group. Testicular volume and testicular fat deposition were measured separately based on thin slice T2WI and the fat fraction (FF) map of mDIXON Quant, and the testicular fat deposition observed with T1WI was used as a reference for qualitative diagnosis. Testicular volume and testicular fat deposition in middle-aged overweight individuals were compared using a t test with Bonferroni correction and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve.
Results
The testicular volumes (10.6–17.9 cm3) of individuals in the treatment group were smaller than those (12.6–19.0 cm3) of individuals in the control group (p < 0.05), and the average FF value (2.2–4.6%) of the testes in the treatment group was higher than that (1.5–3.1%) in the control group (p < 0.05). The ROC analysis showed that the area under the curve (AUC) of testicular fat deposition (0.899) was higher than that of testicular volume (0.777), and biopsy and sperm count were used as references to diagnose infertility. The diagnostic sensitivity (90.00%) of testicular fat deposition of the mDIXON Quant sequence was higher than that (50.00%) of the T1W sequence (p < 0.05). Testicular fat deposition was decreased after 6 months of active treatment with exercise weight loss and drug treatment, and no significant change in testicular volume was observed 6 months later.
Conclusion
The findings suggest that the proton density fat fraction (mDIXON Quant sequence in this study) approach is a novel tool for the quantitative and objective evaluation of testicular fat deposition. Testicular fat deposition measurement is more specific than testicular volume measurement in the diagnosis of male infertility, and the mDIXON Quant is more sensitive than T1WI in the diagnosis of testicular fat deposition. Furthermore, our findings may facilitate a more accurate diagnosis and monitoring of testicular infertility, therapeutic effect, and prognosis by measuring testicular fat deposition.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Best D, Avenell A, Bhattacharya S (2017) How effective are weight-loss interventions for improving fertility in women and men who are overweight or obese? A systematic review and meta-analysis of the evidence. Hum Reprod Update 23(6):681–705
Jelstad S, Ditta Valsdottir T, Johansen EI, Jensen JR (2019) Eight sessions of endurance training decrease fasting glucose and improve glucose tolerance in middle-aged overweight males. Arch Physiol Biochem 26:1–8
Aggerholm AS, Thulstrup AM, Toft G, Ramlau-Hansen CH, Bonde JP (2008) Is overweight a risk factor for reduced semen quality and altered serum sex hormone profile? Fertil Steril 90(3):619–626
Paasch U, Grunewald S, Kratzsch J, Glander HJ (2010) Obesity and age affect male fertility potential. Fertil Steril 94(7):2898–2901
Condorelli R, Calogero AE, La Vignera S (2013) Relationship between testicular volume and conventional or nonconventional sperm parameters. Int J Endocrinol 2013:145792
Ehala-Aleksejev K, Punab M (2018) Relationships between total testicular volume, reproductive parameters and surrogate measures of adiposity in men presenting for couple's infertility. Andrologia 50(4):e12952
López-Torres AS, Chirinos M (2017) Modulation of human sperm capacitation by progesterone, estradiol, and luteinizing hormone. Reprod Sci 24(2):193–201
Zeng Y, Hesketh T (2016) The effects of China’s universal two-child policy. Lancet 388(10054):1930–1938
Liu K, Case A, Reproductive Endocrinology, and Infertility Committee (2011) Advanced reproductive age and fertility. J Obstet Gynaecol Can 33(11):1165–1175
Mazaheri Y, Hricak H, Fine SW, Akin O, Shukla-Dave A, Ishill NM, Moskowitz CS, Grater JE, Reuter VE, Zakian KL, Touijer KA, Koutcher JA (2009) Prostate tumor volume measurement with combined T2-weighted imaging and diffusion-weighted MR: correlation with pathologic tumor volume. Radiology 252(2):449–457
Zhao SX, Xiao YH, Lv FR, Zhang ZW, Sheng B, Ma HL (2018) Lateral ventricular volume measurement by 3D MR hydrography in fetal ventriculomegaly and normal lateral ventricles. J Magn Reson Imaging 48(1):266–273
Zhang Y, Wang C, Duanmu Y, Zhang C, Zhao W, Wang L, Cheng X, Veronese N, Guglielmi G (2018) Comparison of CT and magnetic resonance mDIXON-Quant sequence in the diagnosis of mild hepatic steatosis. Br J Radiol 91(1091):20170587
Zhang Y, Zhou Z, Wang C, Cheng X, Wang L, Duanmu Y, Zhang C, Veronese N, Guglielmi G (2018) Reliability of measuring the fat content of the lumbar vertebral marrow and paraspinal muscles using MRI mDIXON-Quant sequence. Diagn Interv Radiol 24(5):302–307
Ford WC (2010) Comments on the release of the 5th edition of the WHO laboratory manual for the examination and processing of human semen. Asian J Androl 12(1):59–63
Corea M, Campagnone J, Sigman M (2015) The diagnosis of azoospermia depends on the force of centrifugation. Fertil Steril 83(4):920–922
Guo RM, Lin WS, Liu WM, Zhou WY, Cao SE, Wang J, Li QL (2018) Quantification of fat infiltration in the sacroiliac joints with ankylosing spondylitis using IDEAL sequence. Clin Radiol 73(3):231–236
Han BH, Park SB, Seo JT, Chun YK (2018) Usefulness of testicular volume, apparent diffusion coefficient, and normalized apparent diffusion coefficient in the MRI evaluation of infertile men with azoospermia. Am J Roentgenol 210(3):543–548
Guo RM, Zhao RZ, Zhang J, Yang F, Wen HQ, Wang J, Zhang Y, Li QL (2019) Quantification of fat deposition in the testis and epididymis using mDIXON Quant sequence: correlation with age and ejaculation. Abdom Radiol (NY) 44(4):1528–1534
Tsili AC, Ntorkou A, Astrakas L, Boukali E, Giannakis D, Maliakas V, Sofikitis N, Argyropoulou MI (2017) Magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging of the testis: preliminary observations. Eur J Radiol 95:265–270
Tsili AC, Astrakas LG, Ntorkou A, Giannakis D, Stavrou S, Maliakas V, Sofikitis N, Argyropoulou MI (2016) MR spectra of normal adult testes and variations with age: preliminary observations. Eur Radiol 26(7):2261–2267
Firat AK, Uğraş M, Karakaş HM, Erdem G, Kurus M, Ugras M, Celik T, Kahraman B, Doğanay S (2008) 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the normal testis: preliminary findings. Magn Reson Imaging 26(2):215–220
Chew WM, Hricak H, McClure RD, Wendland MF (1990) In vivo human testicular function assessed with P-31 MR spectroscopy. Radiology 177(3):743–747
Kise Y, Chikui T, Yamashita Y, Kobayashi K, Yoshiura K (2017) Clinical usefulness of the method for estimation of the salivary gland fat fraction: comparison with MR spectroscopy. Br J Radiol 90(1077):20160704
Serai SD, Dillman JR, Trout AT (2017) Proton density fat fraction measurements at 1.5- and 3-T hepatic MR imaging: same-day agreement among readers and across two imager manufacturers. Radiology 284(1):244–254
Guo RM, Li QL, Luo ZX, Tang W, Jiao J, Wang J, Kang Z, Chen SQ, Zhang Y (2018) In vivo assessment of neurodegeneration in type C Niemann-Pick disease by IDEAL-IQ. Korean J Radiol 19(1):93–100
Datar J, Regassa A, Kim WK, Taylor CG, Zahradka P, Suh M (2017) Lipid metabolism is closely associated with normal testicular growth based on global transcriptome profiles in normal and underdeveloped testis of obese Zucker (fa/fa) rats. Lipids 52(11):951–960
Akgul O, Gulkesen A, Akgol G, Ozgocmen S (2013) MR-defined fat infiltration of the lumbar paravertebral muscles differs between non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis and established ankylosing spondylitis. Mod Rheumatol 23(4):811–816
Carmona R, Harish S, Linda DD, Ioannidis G, Matsos M, Khalidi NA (2013) MR imaging of the spine and sacroiliac joints for spondyloarthritis: influence on clinical diagnostic confidence and patient management. Radiology 269(1):208–215
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 81801757), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (nos. 2018A030310322, 2019A1515012051), and the Guangdong Medical Research Foundation (no. A2018106).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We or our institution have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Institutional Research Ethics Committee of the Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen University.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all study participants.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Ql., Yang, F., Zhou, Wy. et al. Quantification of testicular fat deposition in the evaluation of middle-aged overweight male infertility. Magn Reson Mater Phy 33, 377–384 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-019-00803-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-019-00803-w