Abstract
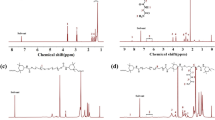
Given its thermal reversibility, high yield, and minimal side reactions, the Diels–Alder (DA) reaction is a particularly desirable technique for the preparation of polymeric materials with heat-stimulated self-healing properties. A linear self-healing polyurethane containing thermally reversible DA bonds (PU-DA) was developed in this study. Results revealed that the introduction of DA bonds conferred outstanding mechanical property and thermal reversibility to PU-DA films. Thus, the as-prepared PU-DA films demonstrated excellent self-healing performance. The self-healing behavior of the PU-DA films under various heat treatments was examined through qualitative observation and quantitative measurements. The PU-DA underwent self-repair through the combination of two healing actions, i.e., the thermal movement of molecular chains and the thermally reversible DA reaction. Moreover, the self-healing behavior of the PU-DA was repeatable, and the PU-DA continued to present high strength even after undergoing three damage–repair cycles at the same site. In addition, the as-prepared PU-DA exhibited excellent macro-scale self-healing behavior, and it endowed the PU-DA presented reprocessing performance. The PU-DA can be recycled given its excellent self-healing and outstanding reprocessing performances.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gojzewski H, Imre B, Check C et al (2016) J Polym Sci Polym Phys 54:2298
Kasprzyk P, Sadowska E, Datta J (2019) J Polym Environ 27(11):2588
Zimmer B, Nies C, Schmitt C et al (2017) Polymer 115:77
Krol P (2007) Prog Mater Sci 52(6):915
Tsou CH, Lee HT, Tsai HA et al (2013) Polym Degrad Stab 98:643
Galhano R, Acero NF, Matos S et al (2018) J Polym Environ 26(1):91
Holder KM, Cain AA, Plummer MG et al (2016) Macromol Mater Eng 301:665
Yu ZY, Feng LB, Chai CS et al (2016) Acta Polym Sin 11:1579
Du P, Wu M, Liu X et al (2014) New J Chem 38:770
Wu DY, Meure S, Solomon D (2008) Prog Polym Sci 33:479
Burattini S, Greenland BW, Chappell D et al (2010) Chem Soc Rev 39:1973
Blaiszik BJ, Kramer SLB, Olugebefola SC et al (2010) Annu Rev Mater Res 40:179
Youngblood JP, Sottos NR (2008) MRS Bull 33:732
Liu C, Ma C, Xie Q et al (2017) J Mater Chem A 5:15855
Daicho H (2012) Nat Commun 3:1132
Peterson AM, Jensen RE, Palmese GR (2010) ACS Appl Mater Inter 2:1141
Liu YL, Hsieh CY (2006) J Polym Sci Polym Chem 44:905
Duval A, Couture G, Caillol S et al (2017) ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5:1199
Cheng X, Peng C, Zhang D et al (2013) J Polym Sci A 51:1205
Liu YL, Chuo TW (2013) Polym Chem 4:2194
Boufi S, Belgacem MN, Quillerou J et al (1993) Macromolecules 26:6706
Feng LB, Yu ZY, Bian YH et al (2017) Polym 124:48
Nandivada H, Jiang X, Lahann J (2007) Adv Mater 19:2197
Feng LB, Zhao HW, He X et al (2019) Polym Eng Sci 59:1603
Gandini A (2010) Polym Chem 1:245
Gandini A (2013) Prog Polym Sci 38:1
Du P, Liu X, Zheng Z et al (2013) RSC Adv 3:15475
Feng LB, Yu ZY, Bian YH et al (2018) Constr Build Mater 186:1212
Zhong Y, Wang X, Zheng Z et al (2015) J Appl Polym Sci 132:41944
Fang YL, Li JC, Du XS et al (2018) Polym 158:166
Fang YL, Du XS, Du ZL et al (2017) J Mater Chem A 5:8010
FangY L, Du XS, Jiang YX et al (2018) ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6(11):14490
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51463010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors claim there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, L., Bian, Y., Chai, C. et al. Effect of Heat-Treatment on Self-healing and Processing Behavior of Thermally Reversible Polyurethanes. J Polym Environ 28, 647–656 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-019-01633-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-019-01633-6