Abstract
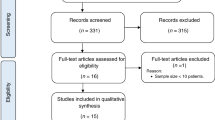
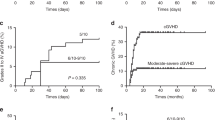
In the absence of an HLA-matched donor, the best treatment for acquired aplastic anemia patients refractory to immunosuppression is unclear. We collected and analyzed data from all acquired aplastic anemia patients who underwent a haploidentical transplantation with posttransplant cyclophosphamide in Europe from 2011 to 2017 (n = 33). The cumulative incidence of neutrophil engraftment was 67% (CI95%: 51–83%) at D +28 and was unaffected by age group, stem cell source, ATG use, or Baltimore conditioning regimen. The cumulative incidence of grades II–III acute GvHD was 23% at D +100, and limited chronic GvHD was 10% (0–20) at 2 years, without cases of grade IV acute or extensive chronic GvHD. Two-year overall survival was 78% (64–93), and 2-year graft-versus-host disease-free survival was 63% (46–81). In univariate analysis, the 2-year OS was higher among patients who received the Baltimore conditioning regimen (93% (81–100) versus 64% (41–87), p = 0.03), whereas age group, stem cell source, and ATG use had no effect. Our results using unmanipulated haploidentical transplantation and posttransplant cyclophosphamide for treating refractory AA patients are encouraging, but warrant confirmation in a prospective study with a larger number of patients and longer follow-up.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Young NS. Aplastic anemia. N. Engl J Med. 2018;379:1643–56.
Bacigalupo A. How I treat acquired aplastic anemia. Blood. 2017;129:1428–36.
Peffault de Latour R. Transplantation for bone marrow failure: current issues. Hematology. 2016;90–8.
Scheinberg P, Cooper JN, Sloand EM, Wu CO, Calado RT, Young NS. Association of telomere length of peripheral blood leukocytes with hematopoietic relapse, malignant transformation, and survival in severe aplastic anemia. JAMA. 2010;304:1358–64.
Olnes MJ, Scheinberg P, Calvo KR, Desmond R, Tang Y, Dumitriu B, et al. Eltrombopag and improved hematopoiesis in refractory aplastic anemia. N. Engl J Med. 2012;367:11–9.
Townsley DM, Olnes MJ, Broder K, Scheinberg P, Desmond R, Bevans M, et al. Eltrombopag restores trilineage hematopoiesis in refractory severe aplastic anemia that can be sustained on discontinuation of drug. Blood. 2013;123:1818–25.
Lengline E, Drenou B, Peterlin P, Tournilhac O, Abraham J, Berceanu A, et al. Nationwide survey on the use of eltrombopag in patients with severe aplastic anemia: a report on behalf of the french reference center for aplastic anemia. Haematologica. 2018;103:212–20.
Cle DV, Atta EH, Dias DSP, Lima CBL, Bonduel M, Sciuccati G, et al. Repeat course of rabbit antithymocyte globulin as salvage following initial therapy with rabbit antithymocyte globulin in acquired aplastic anemia. Haematologica. 2015;100:e345–7.
Trcuelu A, Passweg J, Nissen C, Bargetzi M, Hoffmann T, Signer E, et al. Repeated treatment with horse antilymphocyte globulin for severe aplastic anaemia. Br J Haematol. 1998;100:393–400.
Yoshizato T, Dumitriu B, Hosokawa K, Makishima H, Yoshida K, Townsley D, et al. Somatic mutations and clonal hematopoiesis in aplastic anemia. N. Engl J Med. 2015;373:35–47.
Scheinberg P, Young NS. How I treat acquired aplastic anemia. Blood. 2014;120:1185–96.
Bacigalupo A. Alternative donor transplants for severe aplastic anemia. Hematology. 2018;467–73.
Luznik L, Donnell PVO, Symons HJ, Chen AR, Susan M, Zahurak M, et al. HLA-haploidentical bone marrow transplantation for hematologic malignancies using nonmyeloablative conditioning and high-dose, posttransplantation cyclophosphamide. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2008;14:641–50.
European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. MED-AB forms manual a guide to the completion of the EBMT HSCT Med-AB forms [Internet]. 2018. p. 1–152. https://www.ebmt.org/sites/default/files/2018-03/MED-AB Forms Manual.pdf.
Battipaglia G, Ruggeri A, Labopin M, Volin L, Blaise D, Socie G, et al. Refined graft-versus-host disease/relapse-free survival in transplant from HLA-identical related or unrelated donors in acute myeloid leukemia. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2018;53:1295–303.
Iacobelli S. Suggestions on the use of statistical methodologies in studies of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2013;48:S1–37.
Valdez JM, Scheinberg P, Nunez O, Wu CO, Young NS, Walsh TJ. Decreased infection-related mortality and improved survival in severe aplastic anemia in the past two decades. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;52:726–35.
Devillier R, Dalle J-HH, Kulasekararaj A, D’aveni M, Clément L, Chybicka A, et al. Unrelated alternative donor transplantation for severe acquired aplastic anemia: a study from the french society of bone marrow transplantation and cell therapies and the EBMT severe aplastic anemia working party. Haematologica. 2016;101:884–90.
Maury S, Chir Z, Boiron J, Galambrun C, Yakouben K, Bordigoni P, et al. Unrelated stem cell transplantation for severe acquired aplastic anemia: improved outcome in the era of high-resolution HLA matching between donor and recipient. Haematologica. 2007;92:589–96.
Socie G, Henry-Amar M, Bacigalupo A, Hows J, Tichelli A, Ljungman P, et al. Malignant tumors occurring after treatment of aplastic anemia. European Bone Marrow Transplantation-Severe Aplastic Anaemia Working Party. N. Engl J Med. 1993;329:1152–7.
Peffault de Latour R, Purtill D, Ruggeri A, Sanz G, Michel G, Gandemer V, et al. Influence of nucleated cell dose on overall survival of unrelated cord blood transplantation for patients with severe acquired aplastic anemia: a study by eurocord and the aplastic anemia working party of the european group for blood and marrow transplant. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2011;17:78–85.
Peffault de Latour R, Chevret S, Jubert C, Sirvent A, Galambrun C, Ruggeri A, et al. Unrelated cord blood transplantation in patients with idiopathic refractory severe aplastic anemia: a nationwide phase 2 study. Blood. 2018;132:750–4.
Horan J, Wang T, Haagenson M, Ayas M, Baxter-Lowe LA, Bielorai B, et al. Evaluation of HLA matching requirements in unrelated hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for nonmalignant disorders. Blood. 2012;120:2918–24.
Yagasaki H, Kojima S, Yabe H, Kato K, Kigasawa H, Sakamaki H, et al. Acceptable HLA-mismatching in unrelated donor bone marrow transplantation for patients with acquired severe aplastic anemia. Blood. 2011;118:3186–90.
Passweg JR, Përez WS, Eapen M, Camitta BM, Gluckman E, Hinterberger W, et al. Bone marrow transplants from mismatched related and unrelated donors for severe aplastic anemia. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2006;37:641–9.
Kim H, Im HJ, Koh K-N, Kang SH, Yoo JW, Choi ES, et al. Comparable outcome with a faster engraftment of optimized haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation compared with transplantations from other donor types in pediatric acquired aplastic anemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2019;25:965–74.
Im HJ, Koh KN, Seo JJ, Choi ES, Jang S, Kwon SW, et al. Excellent outcome of haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in children and adolescents with acquired severe aplastic anemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2013;19:754–9.
Gao L, Li Y, Zhang Y, Chen X, Gao L, Zhang C, et al. Long-term outcome of HLA-haploidentical hematopoietic SCT without in vitro T-cell depletion for adult severe aplastic anemia after modified conditioning and supportive therapy. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2014;49:519–24.
Li XH, Gao CJ, Da WM, Bin CaoY, Wang ZH, Xu LX, et al. Reduced intensity conditioning, combined transplantation of haploidentical hematopoietic stem cells and mesenchymal stem cells in patients with severe aplastic anemia. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:1–7.
Yamei W, Rongmu L, Yongbin C, Yingjian S, Xiaohong L. Improved outcome of haploidentical transplantation in severe aplastic anemia using reduced-intensity fludarabine-based conditioning. Oncotarget. 2017;8:83817–30.
Xu ZL, Zhou M, Jia JS, Mo WJ, Zhang XH, Zhang YP, et al. Immunosuppressive therapy versus haploidentical transplantation in adults with acquired severe aplastic anemia. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2019;54:1319–26.
Zhu H, Luo RM, Luan Z, Lee V, Zhu YP, Luo CJ, et al. Unmanipulated haploidentical haematopoietic stem cell transplantation for children with severe aplastic anaemia. Br J Haematol. 2016;174:799–805.
Yang S, Yuan X, Ma R, Jiang L, Guo J, Zang Y, et al. Comparison of outcomes of frontline immunosuppressive therapy and frontline haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for children with severe aplastic anemia who lack an HLA-matched sibling donor. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2019;25:975–80.
Xu LP, Jin S, Wang SQ, Xia LH, Bai H, Gao SJ, et al. Upfront haploidentical transplant for acquired severe aplastic anemia: registry-based comparison with matched related transplant. J Hematol Oncol. 2017;10:1–10.
Xu L-PP, Wang S-QQ, Wu D-PP, Wang J-MM, Gao S-JJ, Jiang M, et al. Haplo-identical transplantation for acquired severe aplastic anaemia in a multicentre prospective study. Br J Haematol. 2016;175:265–74.
Esteves I, Bonfim C, Pasquini R, Funke V, NF P, Rocha V, et al. Haploidentical BMT and post-transplant Cy for severe aplastic anemia: a multicenter retrospective study. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2015;50:685–9.
Clay J, Kulasekararaj AG, Potter V, Grimaldi F, McLornan D, Raj K, et al. Nonmyeloablative peripheral blood haploidentical stem cell transplantation for refractory severe aplastic anemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2014;20:1711–6.
DeZern AE, Zahurak M, Symons H, Cooke K, Jones RJ, Brodsky RA. Alternative donor transplantation with high-dose post-transplantation cyclophosphamide for refractory severe aplastic anemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2017;23:498–504.
Anderlini P, Wu J, Gersten I, Ewell M, Tolar J, Antin JH, et al. Cyclophosphamide conditioning in patients with severe aplastic anaemia given unrelated marrow transplantation: a phase 1–2 dose de-escalation study. Lancet Haematol. 2015;2:e367–75.
Deeg HJ, Amylon ID, Harris RE, Collins R, Beatty PG, Feig S, et al. Marrow transplants from unrelated donors for patients with aplastic anemia: minimum effective dose of total body irradiation. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2001;7:208–15.
Bacigalupo A, Socie G, Hamladji RM, Aljurf M, Maschan A, Kyrcz-Krzemien S, et al. Current outcome of HLA identical sibling versus unrelated donor transplants in severe aplastic anemia: An EBMT analysis. Haematologica. 2015;100:696–702.
Giammarco S, Peffault de Latour R, Sica S, Dufour C, Socie G, Passweg J, et al. Transplant outcome for patients with acquired aplastic anemia over the age of 40: has the outcome improved? Blood. 2018;131:blood-2018-01-826495.
Bacigalupo A, Socié G, Schrezenmeier H, Tichelli A, Locasciulli A, Fuehrer M, et al. Bone marrow versus peripheral blood as the stem cell source for sibling transplants in acquired aplastic anemia: Survival advantage for bone marrow in all age groups. Haematologica. 2012;97:1142–8.
Schrezenmeier H, Passweg JR, Marsh JCW, Bacigalupo A, Bredeson CN, Bullorsky E, et al. Worse outcome and more chronic GVHD with peripheral blood progenitor cells than bone marrow in HLA-matched sibling donor transplants for young patients with severe acquired aplastic anemia. Blood. 2007;110:1397–400.
Gorin C. Bone marrow harvesting for HSCT. In: Carreras E, Dufour C, Mohty M, Kröger N, editors. The EBMT handbook. Cham, Switzerland: Springer Open; 2019. p. 109–16.
Hübel K. Mobilization and collection of HSC. In: Carreras E, Dufour C, Mohty M, Kröger N, editors. The EBMT handbook. Cham, Switzerland: Springer Open; 2019. p. 117–24.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Fondation HPN France—Aplasie Médullaire (Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria—Aplastic Anemia Foundation in France) for helping fund this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Contributions
PHP, RPL, CD and AR planned this study. PHP, DJE and RPL wrote the paper with support of GS. PB was responsible for data collection and processing. DJE performed statistical analyses. All authors provided critical feedback and helped shape the research, analyses, and paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prata, P.H., Eikema, DJ., Afansyev, B. et al. Haploidentical transplantation and posttransplant cyclophosphamide for treating aplastic anemia patients: a report from the EBMT Severe Aplastic Anemia Working Party. Bone Marrow Transplant 55, 1050–1058 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-019-0773-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-019-0773-0
This article is cited by
-
Second haploidentical bone marrow transplantation with antithymocyte antibody-containing conditioning regimen for graft failure in eight patients with severe aplastic anemia
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Addition of ruxolitinib to standard graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis for allogeneic stem cell transplantation in aplastic anemia patients
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2024)
-
Recent advances in the diagnosis and treatment of pediatric acquired aplastic anemia
International Journal of Hematology (2024)
-
Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for aplastic anemia
International Journal of Hematology (2024)
-
Thiotepa-based reduced toxicity conditioning in combination with post-transplant cyclophosphamide and mTOR inhibitor for heavily transfused acquired severe aplastic anemia in children and young adults: encouraging outcomes of a pilot study
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2023)