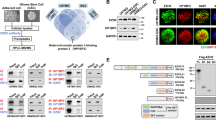
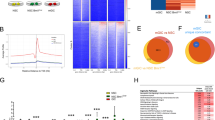
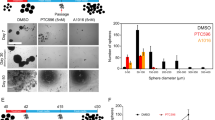
Abstract
High-grade gliomas (HGG) afflict both children and adults and respond poorly to current therapies. Epigenetic regulators have a role in gliomagenesis, but a broad, functional investigation of the impact and role of specific epigenetic targets has not been undertaken. Using a two-step, in vitro/in vivo epigenomic shRNA inhibition screen, we determine the chromatin remodeler BPTF to be a key regulator of adult HGG growth. We then demonstrate that BPTF knockdown decreases HGG growth in multiple pediatric HGG models as well. BPTF appears to regulate tumor growth through cell self-renewal maintenance, and BPTF knockdown leads these glial tumors toward more neuronal characteristics. BPTF’s impact on growth is mediated through positive effects on expression of MYC and MYC pathway targets. HDAC inhibitors synergize with BPTF knockdown against HGG growth. BPTF inhibition is a promising strategy to combat HGG through epigenetic regulation of the MYC oncogenic pathway.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A, et al. The 2007 WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathologica. 2007;114:97–109.
Wen PY, Kesari S. Malignant gliomas in adults. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:492–507. (Research support, N.I.H., extramural research support, Non-U.S. Gov’t Review).
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:987–96.
Fangusaro J. Pediatric high-grade gliomas and diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas. J Child Neurol. 2009;24:1409–17.
Rodriguez-Paredes M, Esteller M. Cancer epigenetics reaches mainstream oncology. Nat Med. 2011;17:330–9.
Clarke J, Penas C, Pastori C, Komotar RJ, Bregy A, Shah AH, et al. Epigenetic pathways and glioblastoma treatment. Epigenetics. 2013;8:785–95.
Maleszewska M, Kaminska B. Is glioblastoma an epigenetic malignancy? Cancers. 2013;5:1120–39.
Ferreira WA, Pinheiro Ddo R, Costa Junior CA, Rodrigues-Antunes S, Araujo MD, Leao Barros MB, et al. An update on the epigenetics of glioblastomas. Epigenomics. 2016;8:1289–305.
Touat M, Idbaih A, Sanson M, Ligon KL. Glioblastoma targeted therapy: updated approaches from recent biological insights. Ann Oncol. 2017;28:1457–72.
Lulla RR, Saratsis AM, Hashizume R. Mutations in chromatin machinery and pediatric high-grade glioma. Sci Adv. 2016;2:e1501354.
Schwartzentruber J, Korshunov A, Liu XY, Jones DT, Pfaff E, Jacob K, et al. Driver mutations in histone H3.3 and chromatin remodelling genes in paediatric glioblastoma. Nature. 2012;482:226–31.
Ghantous A, Hernandez-Vargas H, Byrnes G, Dwyer T, Herceg Z. Characterising the epigenome as a key component of the fetal exposome in evaluating in utero exposures and childhood cancer risk. Mutagenesis. 2015;30:733–42.
Miozzo M, Vaira V, Sirchia SM. Epigenetic alterations in cancer and personalized cancer treatment. Future Oncol. 2015;11:333–48.
Lee P, Murphy B, Miller R, Menon V, Banik NL, Giglio P, et al. Mechanisms and clinical significance of histone deacetylase inhibitors: epigenetic glioblastoma therapy. Anticancer Res. 2015;35:615–25.
Morales La Madrid A, Hashizume R, Kieran MW. Future clinical trials in DIPG: bringing epigenetics to the clinic. Front Oncol. 2015;5:148.
Mottamal M, Zheng S, Huang TL, Wang G. Histone deacetylase inhibitors in clinical studies as templates for new anticancer agents. Molecules. 2015;20:3898–941.
Herms JW, von Loewenich FD, Behnke J, Markakis E, Kretzschmar HA. c-myc oncogene family expression in glioblastoma and survival. Surg Neurol. 1999;51:536–42.
Wang J, Wang H, Li Z, Wu Q, Lathia JD, McLendon RE, et al. c-Myc is required for maintenance of glioma cancer stem cells. PloS ONE. 2008;3:e3769.
Broad D DepMap Achilles 19Q1 Public. Broad Institute, Cambridge, MA, 2019.
Ghandi M, Huang FW, Jané-Valbuena J, Kryukov GV, Lo CC, McDonald ER, et al. Next-generation characterization of the Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia. Nature. 2019;569:503–8.
Meyers RM, Bryan JG, McFarland JM, Weir BA, Sizemore AE, Xu H, et al. Computational correction of copy number effect improves specificity of CRISPR-Cas9 essentiality screens in cancer cells. Nat Genet. 2017;49:1779–84.
Xie Q, Wu QL, Kim L, Miller TE, Liau BB, Mack SC, et al. RBPJ maintains brain tumor-initiating cells through CDK9-mediated transcriptional elongation. J Clin Investig. 2016;126:2757–72.
Bao SD, Wu QL, McLendon RE, Hao YL, Shi Q, Hjelmeland AB, et al. Glioma stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA damage response. Nature. 2006;444:756–60.
Urick AK, Hawk LM, Cassel MK, Mishra NK, Liu S, Adhikari N, et al. Dual screening of BPTF and Brd4 using protein-observed fluorine NMR uncovers new bromodomain probe molecules. ACS Chem Biol. 2015;10:2246–56.
Li H, Ilin S, Wang W, Duncan EM, Wysocka J, Allis CD, et al. Molecular basis for site-specific read-out of histone H3K4me3 by the BPTF PHD finger of NURF. Nature. 2006;442:91–5.
Stankiewicz P, Khan TN, Szafranski P, Slattery L, Streff H, Vetrini F, et al. Haploinsufficiency of the chromatin remodeler BPTF causes syndromic developmental and speech delay, postnatal microcephaly, and dysmorphic features. Am J Hum Genet. 2017;101:503–15.
Bekpen C, Tastekin I, Siswara P, Akdis CA, Eichler EE. Primate segmental duplication creates novel promoters for the LRRC37 gene family within the 17q21.31 inversion polymorphism region. Genome Res. 2012;22:1050–8.
Ma Y, Liu X, Liu Z, Wei S, Shang H, Xue Y, et al. The chromatin remodeling protein Bptf promotes posterior neuroectodermal fate by enhancing Smad2-activated wnt8a expression. J Neurosci. 2015;35:8493–506.
Gong YC, Liu DC, Li XP, Dai SP. BPTF biomarker correlates with poor survival in human NSCLC. Eur Rev Med Pharm Sci. 2017;21:102–7.
Buganim Y, Goldstein I, Lipson D, Milyavsky M, Polak-Charcon S, Mardoukh C, et al. A novel translocation breakpoint within the BPTF gene is associated with a pre-malignant phenotype. PloS ONE. 2010;5:e9657.
Lee JH, Kim MS, Yoo NJ, Lee SH. BPTF, a chromatin remodeling-related gene, exhibits frameshift mutations in gastric and colorectal cancers. APMIS. 2016;124:425–7.
Xiao S, Liu L, Fang M, Zhou X, Peng X, Long J, et al. BPTF associated with EMT indicates negative prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci. 2015;60:910–8.
Richart L, Carrillo-de Santa Pau E, Rio-Machin A, de Andres MP, Cigudosa JC, Lobo VJ, et al. BPTF is required for c-MYC transcriptional activity and in vivo tumorigenesis. Nat Commun. 2016;7:10153.
Dai M, Lu JJ, Guo W, Yu W, Wang Q, Tang R, et al. BPTF promotes tumor growth and predicts poor prognosis in lung adenocarcinomas. Oncotarget. 2015;6:33878–92.
Dar AA, Nosrati M, Bezrookove V, de Semir D, Majid S, Thummala S, et al. The role of BPTF in melanoma progression and in response to BRAF-targeted therapy. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2015;107:pii:djv034.
Xiao S, Liu L, Lu X, Long J, Zhou X, Fang M. The prognostic significance of bromodomain PHD-finger transcription factor in colorectal carcinoma and association with vimentin and E-cadherin. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2015;141:1465–74.
Frey WD, Chaudhry A, Slepicka PF, Ouellette AM, Kirberger SE, Pomerantz WCK, et al. BPTF maintains chromatin accessibility and the self-renewal capacity of mammary gland stem cells. Stem Cell Rep. 2017;9:23–31.
Kim J, Lo L, Dormand E, Anderson DJ. SOX10 maintains multipotency and inhibits neuronal differentiation of neural crest stem cells. Neuron. 2003;38:17–31.
Bramanti V, Tomassoni D, Avitabile M, Amenta F, Avola R. Biomarkers of glial cell proliferation and differentiation in culture. Front Biosci. 2010;2:558–70.
Person F, Wilczak W, Hube-Magg C, Burdelski C, Moller-Koop C, Simon R, et al. Prevalence of betaIII-tubulin (TUBB3) expression in human normal tissues and cancers. Tumour Biol. 2017;39:1010428317712166.
Su Z, Niu W, Liu ML, Zou Y, Zhang CL. In vivo conversion of astrocytes to neurons in the injured adult spinal cord. Nat Commun. 2014;5:3338.
Bouchard C, Thieke K, Maier A, Saffrich R, Hanley-Hyde J, Ansorge W, et al. Direct induction of cyclin D2 by Myc contributes to cell cycle progression and sequestration of p27. EMBO J. 1999;18:5321–33.
Kerosuo L, Piltti K, Fox H, Angers-Loustau A, Hayry V, Eilers M, et al. Myc increases self-renewal in neural progenitor cells through Miz-1. J Cell Sci. 2008;121:3941–50.
Nebbioso A, Carafa V, Conte M, Tambaro FP, Abbondanza C, Martens J, et al. c-Myc modulation and acetylation is a key HDAC inhibitor target in cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23:2542–55.
Grasso CS, Tang Y, Truffaux N, Berlow NE, Liu L, Debily MA, et al. Functionally defined therapeutic targets in diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma. Nat Med. 2015;21:827.
Lapin DH, Tsoli M, Ziegler DS. Genomic insights into diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma. Front Oncol. 2017;7:57.
Landry J, Sharov AA, Piao Y, Sharova LV, Xiao H, Southon E, et al. Essential role of chromatin remodeling protein Bptf in early mouse embryos and embryonic stem cells. PLoS Genet. 2008;4:e1000241.
Green AL, Ramkissoon SH, McCauley D, Jones K, Perry JA, Hsu JH, et al. Preclinical antitumor efficacy of selective exportin 1 inhibitors in glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 2015;17:697–707.
Baird NL, Bowlin JL, Cohrs RJ, Gilden D, Jones KL. Comparison of varicella-zoster virus RNA sequences in human neurons and fibroblasts. J Virol. 2014;88:5877–80.
Wu TD, Nacu S. Fast and SNP-tolerant detection of complex variants and splicing in short reads. Bioinformatics. 2010;26:873–81.
Trapnell C, Williams BA, Pertea G, Mortazavi A, Kwan G, van Baren MJ, et al. Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nat Biotechnol. 2010;28:511–5.
Arrigoni L, Richter AS, Betancourt E, Bruder K, Diehl S, Manke T, et al. Standardizing chromatin research: a simple and universal method for ChIP-seq. Nucleic acids Res. 2016;44:e67.
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B. Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics. 2014;30:2114–20.
Wu TD, Watanabe CK. GMAP: a genomic mapping and alignment program for mRNA and EST sequences. Bioinformatics. 2005;21:1859–75.
Ramirez F, Ryan DP, Gruning B, Bhardwaj V, Kilpert F, Richter AS, et al. deepTools2: a next generation web server for deep-sequencing data analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44:W160–5.
Ross-Innes CS, Stark R, Teschendorff AE, Holmes KA, Ali HR, Dunning MJ, et al. Differential oestrogen receptor binding is associated with clinical outcome in breast cancer. Nature. 2012;481:389–93.
Benjamini Y, Hochberg YJ. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc. 1995;B57:289–300.
Andrade JM, Estevez-Perez MG. Statistical comparison of the slopes of two regression lines: a tutorial. Anal Chim Acta. 2014;838:1–12.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr William Pomerantz for his expertize and discussion of BPTF small molecule inhibitors, and Drs Stuart Orkin, Mark Kieran, and Jay Bradner for their advice at early stages of the project. We also acknowledge the University of Colorado Denver Research Histology Shared Resource, supported by the Cancer Center Support Grant (P30CA046934), as well as the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus Advanced Light Microscopy Core Facility and Functional Genomics Core Facility, for their assistance. The Colorado Animal Imaging Shared Resource is supported by the NCI and the University of Colorado Cancer Center (P30CA046934).
Funding
This work was supported by the Luke’s Army Pediatric Cancer Research Fund St. Baldrick’s Scholar Award, a Hyundai Hope on Wheels Young Investigator award, a Morgan Adams Foundation grant, a Pedals for Pediatrics grant, and NICHD K12HD068372 (ALG).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Green, A.L., DeSisto, J., Flannery, P. et al. BPTF regulates growth of adult and pediatric high-grade glioma through the MYC pathway. Oncogene 39, 2305–2327 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-019-1125-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-019-1125-7
This article is cited by
-
BPTF in bone marrow provides a potential progression biomarker regulated by TFAP4 through the PI3K/AKT pathway in neuroblastoma
Biological Procedures Online (2023)
-
Hsa_circRNA_102051 regulates colorectal cancer proliferation and metastasis by mediating Notch pathway
Cancer Cell International (2023)
-
Targeting the epigenome of cancer stem cells in pediatric nervous system tumors
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2023)
-
Hypoxia-induced exosomal circPDK1 promotes pancreatic cancer glycolysis via c-myc activation by modulating miR-628-3p/BPTF axis and degrading BIN1
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2022)
-
The emerging role of ISWI chromatin remodeling complexes in cancer
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2021)