Abstract
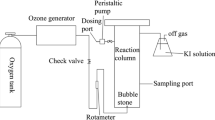
This study investigates the degradation and mineralization of BTEX by heterogeneous electro-Fenton process using GO/MWCNT/Fe3O4 as a catalyst and MWCNT-Ce/WO3/GF as an electrode. The nanoscale MWCNT-Ce/WO3 composite catalyst was distributed more evenly on GF surface to form a catalyst layer with higher oxygen reduction reaction performance. After optimization of pH and time variables, the Box–Behnken experimental design (BBD) and response surface methodology (RSM) were used to design and optimize the performance of proposed system and energy consumption. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) revealed that the quadratic model was adequately fitted to the experimental data with R2 (0.98) and adj-R2 (0.97). The significance levels of linear and interaction effects of the reaction parameters on process efficiency were obtained. Then, the optimization of the working conditions for the design of a sustainable treatment system with optimum efficiency was carried out using a response surface methodology. The experiment carried out in the calculated optimal conditions for the electro-Fenton degradation process (current intensity 300 mA, catalyst dosage of 0.6 g, initial BTEX concentration of 100 ppm, and electrode distance of 1 cm) showed a BTEX removal of 73.2% and energy consumption of 12.3 (kWh/m3) close to the theoretical value predicted by the model 73. 2% and 11.8 (kWh/m3), respectively. Furthermore, the reusability test of GO/MWCNT/Fe3O4 nanocomposite after several cycles confirmed the high catalytic activities of adsorbent. Comparing the proposed system with conventional GF electrode and Fe2+ catalyst showed that modification of cathode and catalyst led to increasing COD removal efficiency by around 36.6 and 31.6%, respectively. The findings of present study revealed that the proposed heterogeneous electro-Fenton process can be utilized as pre-treatment technology to improve the biodegradability and reduce the organic load of wastewater by combine oxidation and coagulation.

Graphical Abstract















Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Olvera-Vargas, X. Zheng, O. Garcia-Rodriguez, O. Lefebvre, Sequential “electrochemical peroxidation – Electro-Fenton” process for anaerobic sludge treatment. Water Res. 154, 277–286 (2019)
P.V. Nidheesh, R. Gandhimathi, Trends in electro-Fenton process for water and wastewater treatment: an overview. Desalination 299, 1–15 (2012)
J.C.G. Sousa, A.R. Ribeiro, M.O. Barbosa, M.F.R. Pereira, A.M.T. Silva, A review on environmental monitoring of water organic pollutants identified by EU guidelines. J. Hazard. Mater. 344, 146–162 (2018)
V. Poza-Nogueiras, M. Arellano, E. Rosales, M. Pazos, E. González-Romero, M.A. Sanromán, Heterogeneous electro-Fenton as plausible technology for the degradation of imidazolinium-based ionic liquids. Chemosphere 199, 68–75 (2018)
J.C. Murillo-Sierra, E. Ruiz-Ruiz, L. Hinojosa-Reyes, J.L. Guzmán-Mar, F. Machuca-Martínez, A. Hernández-Ramírez, Sulfamethoxazole mineralization by solar photo electro-Fenton process in a pilot plant. Catal. Today 313, 175–181 (2018)
R. Dewil, D. Mantzavinos, I. Poulios, M.A. Rodrigo, New perspectives for advanced oxidation processes. J. Environ. Manag. 195(Pt 2), 93–99 (2017)
C. Trellu, E. Mousset, Y. Pechaud, D. Huguenot, E.D. van Hullebusch, G. Esposito, M.A. Oturan, Removal of hydrophobic organic pollutants from soil washing/flushing solutions: a critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 306, 149–174 (2016)
S. Xavier, R. Gandhimathi, P.V. Nidheesh, S.T. Ramesh, Comparison of homogeneous and heterogeneous Fenton processes for the removal of reactive dye Magenta MB from aqueous solution. Desalin. Water Treat. 53(1), 109–118 (2015)
Y. Luo, W. Guo, H.H. Ngo, L.D. Nghiem, F.I. Hai, J. Zhang, S. Liang, X.C. Wang, A review on the occurrence of micropollutants in the aquatic environment and their fate and removal during wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 473-474, 619–641 (2014)
I. Sirés, E. Brillas, M.A. Oturan, M.A. Rodrigo, M. Panizza, Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes: today and tomorrow. A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 21(14), 8336–8367 (2014)
N. Klidi, F. Proietto, F. Vicari, A. Galia, S. Ammar, A. Gadri, O. Scialdone, Electrochemical treatment of paper mill wastewater by electro-Fenton process. J. Electroanal. Chem. 841, 166–171 (2019)
J. Meijide, M. Pazos, M.Á. Sanromán, Heterogeneous electro-Fenton catalyst for 1-butylpyridinium chloride degradation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 26(4), 3145–3156 (2019)
O. Ganzenko, C. Trellu, S. Papirio, N. Oturan, D. Huguenot, E.D. van Hullebusch, G. Esposito, M.A. Oturan, Bioelectro-Fenton: evaluation of a combined biological—advanced oxidation treatment for pharmaceutical wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 25(21), 20283–20292 (2018)
Y. Xiao, J.M. Hill, Mechanistic insights for the electro-Fenton regeneration of carbon materials saturated with methyl orange: dominance of electrodesorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 367, 59–67 (2019)
X. Huang, B. Feng, Y.N. Zhao, W. Hu, Fenton-reaction-derived Fe/N-doped graphene with encapsulated Fe3C nanoparticles for efficient photo-Fenton catalysis. Catal. Lett. 148(8), 2528–2536 (2018)
I. Ouiriemmi, A. Karrab, N. Oturan, M. Pazos, E. Rozales, A. Gadri, M.Á. Sanromán, S. Ammar, M.A. Oturan, Heterogeneous electro-Fenton using natural pyrite as solid catalyst for oxidative degradation of vanillic acid. J. Electroanal. Chem. 797, 69–77 (2017)
T.J. Al-Musawi, H. Kamani, E. Bazrafshan, A.H. Panahi, M.F. Silva, G. Abi, Optimization the effects of physicochemical parameters on the degradation of cephalexin in Sono-Fenton reactor by using Box-Behnken response surface methodology. Catal. Lett. 149(5), 1186–1196 (2019)
Y. Chen, H. Chen, J. Li, L. Xiao, Rapid and efficient activated sludge treatment by electro-Fenton oxidation. Water Res. 152, 181–190 (2019)
Nidheesh, P.V., H. Olvera-Vargas, N. Oturan, and M.A. Oturan, Heterogeneous electro-Fenton process: principles and applications, in Handbook of Environmental Chemistry. 2018, Springer Verlag. p. 85–110
Z. Es'haghzade, E. Pajootan, H. Bahrami, M. Arami, Facile synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles via aqueous based electro chemical route for heterogeneous electro-Fenton removal of azo dyes. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 71, 91–105 (2017)
A.G. Akerdi, Z. Es'Haghzade, S.H. Bahrami, M. Arami, Comparative study of GO and reduced GO coated graphite electrodes for decolorization of acidic and basic dyes from aqueous solutions through heterogeneous electro-Fenton process. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering 5(3), 2313–2324 (2017)
H. Dong, H. Su, Z. Chen, H. Yu, H. Yu, Fabrication of electrochemically reduced graphene oxide modified gas diffusion electrode for in-situ electrochemical advanced oxidation process under mild conditions. Electrochim. Acta 222, 1501–1509 (2016)
G. Gao, Q. Zhang, Z. Hao, C.D. Vecitis, Carbon nanotube membrane stack for flow-through sequential regenerative electro-Fenton. Environ. Sci. Technol. 49(4), 2375–2383 (2015)
Y. Liu, X. Quan, X. Fan, H. Wang, S. Chen, High-yield electrosynthesis of hydrogen peroxide from oxygen reduction by hierarchically porous carbon. Angewandte Chemie - International Edition 54(23), 6837–6841 (2015)
Y. Wang, Y. Liu, K. Wang, S. Song, P. Tsiakaras, H. Liu, Preparation and characterization of a novel KOH activated graphite felt cathode for the electro-Fenton process. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 165, 360–368 (2015)
Y. Gong, J. Li, Y. Zhang, M. Zhang, X. Tian, A. Wang, Partial degradation of levofloxacin for biodegradability improvement by electro-Fenton process using an activated carbon fiber felt cathode. J. Hazard. Mater. 304, 320–328 (2016)
Y. Wang, Y. Liu, X.Z. Li, F. Zeng, H. Liu, A highly-ordered porous carbon material based cathode for energy-efficient electro-Fenton process. Sep. Purif. Technol. 106, 32–37 (2013)
C. Flox, S. Ammar, C. Arias, E. Brillas, A.V. Vargas-Zavala, R. Abdelhedi, Electro-Fenton and photoelectro-Fenton degradation of indigo carmine in acidic aqueous medium. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 67(1–2), 93–104 (2006)
T.X.H. Le, M. Bechelany, S. Lacour, N. Oturan, M.A. Oturan, M. Cretin, High removal efficiency of dye pollutants by electron-Fenton process using a graphene based cathode. Carbon 94, 1003–1011 (2015)
H. Kaneko, K. Nozaki, Y. Wada, T. Aoki, A. Negishi, M. Kamimoto, Vanadium redox reactions and carbon electrodes for vanadium redox flow battery. Electrochim. Acta 36(7), 1191–1196 (1991)
W.H. Wang, X.D. Wang, Investigation of Ir-modified carbon felt as the positive electrode of an all-vanadium redox flow battery. Electrochim. Acta 52(24), 6755–6762 (2007)
M. Bartolozzi, Development of redox flow batteries. A historical bibliography. J. Power Sources 27(3), 219–234 (1989)
Y. Shen, H. Xu, P. Xu, X. Wu, Y. Dong, L. Lu, Electrochemical catalytic activity of tungsten trioxide-modified graphite felt toward VO2+/VO2+ redox reaction. Electrochim. Acta 132, 37–41 (2014)
P.M. Kadam, N.L. Tarwal, S.S. Mali, H.P. Deshmukh, P.S. Patil, Enhanced electrochromic performance of f-MWCNT-WO 3 composite. Electrochim. Acta 58(1), 556–561 (2011)
M.H. Chakrabarti, E.P.L. Roberts, C. Bae, M. Saleem, Ruthenium based redox flow battery for solar energy storage. Energy Convers. Manag. 52(7), 2501–2508 (2011)
S. Chandrabose Raghu, M. Ulaganathan, T.M. Lim, M. Skyllas Kazacos, Electrochemical behaviour of titanium/iridium(IV) oxide: tantalum pentoxide and graphite for application in vanadium redox flow battery. J. Power Sources 238, 103–108 (2013)
H. Zhou, Y. Shen, J. Xi, X. Qiu, L. Chen, ZrO2-nanoparticle-modified graphite felt: bifunctional effects on vanadium flow batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8(24), 15369–15378 (2016)
C. Yao, H. Zhang, T. Liu, X. Li, Z. Liu, Carbon paper coated with supported tungsten trioxide as novel electrode for all-vanadium flow battery. J. Power Sources 218, 455–461 (2012)
Y. Miseki, H. Kusama, H. Sugihara, K. Sayama, Cs-modified WO3 photocatalyst showing efficient solar energy conversion for O2 production and Fe (III) ion reduction under visible light. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 1(8), 1196–1200 (2010)
G.R. Bamwenda, T. Uesigi, Y. Abe, K. Sayama, H. Arakawa, Photocatalytic oxidation of water to O2 over pure CeO2, WO3, and TiO2 using Fe3+ and Ce4+ as electron acceptors. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 205(1–2), 117–128 (2001)
J. Friedl, C.M. Bauer, A. Rinaldi, U. Stimming, Electron transfer kinetics of the VO2+/VO2+—reaction on multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Carbon 63, 228–239 (2013)
H.Q. Zhu, Y.M. Zhang, L. Yue, W.S. Li, G.L. Li, D. Shu, H.Y. Chen, Graphite-carbon nanotube composite electrodes for all vanadium redox flow battery. J. Power Sources 184(2), 637–640 (2008)
E. Alfaya, O. Iglesias, M. Pazos, M.A. Sanromán, Environmental application of an industrial waste as catalyst for the electro-Fenton-like treatment of organic pollutants. RSC Adv. 5(19), 14416–14424 (2015)
S. Liu, Y. Gu, S.L. Wang, Y. Zhang, Y.F. Fang, D.M. Johnson, Y.P. Huang, Degradation of organic pollutants by a Co3O4-graphite composite electrode in an electro-Fenton-like system. Chin. Sci. Bull. 58(19), 2340–2346 (2013)
A. Babuponnusami, K. Muthukumar, A review on Fenton and improvements to the Fenton process for wastewater treatment. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering 2(1), 557–572 (2014)
W. He, X. Yan, H. Ma, J. Yu, J. Wang, X. Huang, Degradation of methyl orange by electro-Fenton-like process in the presence of chloride ion. Desalin. Water Treat. 51(34–36), 6562–6571 (2013)
N. Oturan, M. Zhou, M.A. Oturan, Metomyl degradation by electro-Fenton and electro-Fenton-like processes: a kinetics study of the effect of the nature and concentration of some transition metal ions as catalyst. J. Phys. Chem. A 114(39), 10605–10611 (2010)
P.V. Nidheesh, R. Gandhimathi, Comparative removal of rhodamine B from aqueous solution by electro-Fenton and electro-Fenton-like processes. Clean - Soil, Air, Water 42(6), 779–784 (2014)
B. Balci, M.A. Oturan, N. Oturan, I. Sires, Decontamination of aqueous glyphosate, (aminomethyl) phosphonic acid, and glufosinate solutions by electro-Fenton-like process with Mn2+ as the catalyst. J. Agric. Food Chem. 57(11), 4888–4894 (2009)
C. Wang, Y. Hua, Y. Tong, A novel electro-Fenton-like system using PW11O 39Fe(III)(H2O)4- as an electrocatalyst for wastewater treatment. Electrochim. Acta 55(22), 6755–6760 (2010)
Z.W. Cheng, S. Peng-fei, Y.F. Jiang, J.M. Yu, J.M. Chen, Ozone-assisted UV254nm photodegradation of gaseous ethylbenzene and chlorobenzene: effects of process parameters, degradation pathways, and kinetic analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 228, 1003–1010 (2013)
S. Gligorovski, R. Strekowski, S. Barbati, D. Vione, Environmental implications of hydroxyl radicals (•OH). Chem. Rev. 115(24), 13051–13092 (2015)
Dixon, W.T. and R.O.C. Norman, Electron spin resonance studies of oxidation. Part IV. Some benzenoid compounds. Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed), 1964: p. 4850–4856
E.T. Denisov, D.I. Metelitsa, Oxidation of benzene. Russ. Chem. Rev. 37, 1547–1566 (1968)
G.R. Peyton, The free-radical chemistry of persulfate-based total organic carbon analyzers. Mar. Chem. 41(1–3), 91–103 (1993)
R.A. Kenley, J.E. Davenport, D.G. Hendry, Gas-phase hydroxyl radical reactions. Products and pathways for the reaction of OH with aromatic hydrocarbons. J. Phys. Chem. 85(19), 2740–2746 (1981)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ranjbar, M., Majidian, N. & Samipourgiri, M. Heterogeneous Electro-Fenton Process by MWCNT-Ce/WO3 Nanocomposite Modified GF Cathode for Catalytic Degradation of BTEX: Process Optimization Using Response Surface Methodology. Electrocatalysis 10, 628–642 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12678-019-00550-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12678-019-00550-5