Abstract
Three sizes of CuO nanosheets were synthesized by hydrothermal method. The structure and morphology of CuO nanosheets were characterized by X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy. Dielectrophoresis nano-manipulation technique was employed to arrange the materials on pre-designed Ti/Au electrodes to fabricate the three humidity sensors, and the sensing properties were then tested. The experimental results show that the sensitivity greatly increases with the decreasing size of CuO nanosheets, the sensitivity of sensor a, b, c are 369%, 3278%, 22,611% in 97.3% RH, respectively. The smaller sized CuO nanomaterials have better response characteristic, the response time of sensor a, b, c under 11.3–97.3% RH are 53 s, 49 s, 32 s, respectively. And correspondingly, hysteresis properties and the repeatability are also a little influenced. In addition, based on complex impedance spectroscopy and multilayer adsorption theory, the impact of size on humidity sensing property was discussed. The results indicated the feasibility to obtain higher performance of humidity sensor, especially the higher sensitivity, via employment the smaller size sensing nanomaterials.
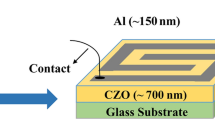
Graphic Abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hong, S., Shin, J., Hong, Y., Wu, M., Jeong, Y., Jang, D., Jung, G., Bae, J.H., Lee, J.H.: Humidity-sensitive field effect transistor with In(2)O(3) nanoparticles as a sensing layer. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 19, 6656–6662 (2019)
Gupta, S.P., Pawbake, A.S., Sathe, B.R., Late, D.J., Walke, P.S.: Superior humidity sensor and photodetector of mesoporous ZnO nanosheets at room temperature. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 293, 83–92 (2019)
Lin, C., Zhang, H., Zhang, J., Chen, C.: Enhancement of the humidity sensing performance in Mg-doped hexagonal ZnO microspheres at room temperature. Sens. (Basel) 19, 519 (2019)
Li, H., Zhang, J., Tao, B., Wan, L., Gong, W.: Investigation of capacitive humidity sensing behavior of silicon nanowires. Phys. E 41, 600–604 (2009)
Yeo, T.L., Sun, T., Grattan, K.T.V.: Fibre-optic sensor technologies for humidity and moisture measurement. Sens. Actuators A 144, 280–295 (2008)
Shelke, N.T., Karle, S.C., Karche, B.R.: Hydrothermal growth and humidity-dependent electrical properties of molybdenum disulphide nanosheets. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 19, 5158–5166 (2019)
Zhang, H., Yu, S., Chen, C., Zhang, J., Liu, J., Li, P.: Effects on structure, surface oxygen defects and humidity performance of Au modified ZnO via hydrothermal method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 486, 482–489 (2019)
Nunes, D., Pimentel, A., Gonçalves, A., Pereira, S., Branquinho, R., Barquinha, P., Fortunato, E., Martins, R.: Metal oxide nanostructures for sensor applications. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 34, 043001 (2019)
Zhu, Y., Wang, Y., Duan, G., Zhang, H., Li, Y., Liu, G., Xu, L., Cai, W.: In situ growth of porous ZnO nanosheet-built network film as high-performance gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 221, 350–356 (2015)
Kim, H., Park, S., Park, Y., Choi, D., Yoo, B., Lee, C.S.: Fabrication of a semi-transparent flexible humidity sensor using kinetically sprayed cupric oxide film. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 274, 331–337 (2018)
Li, D., Hu, J., Wu, R., Lu, J.G.: Conductometric chemical sensor based on individual CuO nanowires. Nanotechnology 21, 485502 (2010)
Ko, Y.H., Nagaraju, G., Lee, S.H., Yu, J.S.: Facile preparation and optoelectronic properties of CuO nanowires for violet light sensing. Mater. Lett. 117, 217–220 (2014)
Hien, V.X., Minh, V.D., Phuoc, L.H., Vuong, D., Dang, Y.-W., Heo, N.D.Chien: Synthesis of high-density poinsettia-like microstructure of CuO by the hydrothermal method and its ethanol sensing properties. J. Electron. Mater. 46, 3445–3452 (2017)
Umar, A., Alshahrani, A.A., Algarni, H., Kumar, R.: CuO nanosheets as potential scaffolds for gas sensing applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 250, 24–31 (2017)
Can, N.: Electrospun CuO nanofibers for room temperature volatile organic compound sensing applications. Mater. Chem. Phys. 213, 6–13 (2018)
Li, D., Zu, X., Ao, D., Tang, Q., Fu, Y., Guo, Y., Bilawal, K., Faheem, M.B., Li, L., Li, S., Tang, Y.: High humidity enhanced surface acoustic wave (SAW) H2S sensors based on sol–gel CuO films. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 294, 55–61 (2019)
Liu, A., Nie, S., Liu, G., Zhu, H., Zhu, C., Shin, B., Fortunato, E., Martins, R., Shan, F.: In situ one-step synthesis of p-type copper oxide for low-temperature, solution-processed thin-film transistors. J. Mater. Chem. C 5, 2524–2530 (2017)
Ashokan, S., Jayamurugan, P., Ponnuswamy, V.: Effects of CuO and oxidant on the morphology and conducting properties of PANI:CuO hybrid nanocomposites for humidity sensor application. Polym. Sci. Ser. B 61, 86–97 (2019)
Chani, M.T.S.: Impedimetric sensing of temperature and humidity by using organic-inorganic nanocomposites composed of chitosan and a CuO-Fe3O4 nanopowder. Microchim. Acta 184, 2349–2356 (2017)
Wang, Z., Xiao, Y., Cui, X., Cheng, P., Wang, B., Gao, Y., Li, X., Yang, T., Zhang, T., Lu, G.: Humidity-sensing properties of urchinlike CuO nanostructures modified by reduced graphene oxide. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 3888–3895 (2014)
Wang, S.-B., Hsiao, C.-H., Chang, S.-J., Lam, K.-T., Wen, K.-H., Young, S.-J., Hung, S.-C., Huang, B.-R.: CuO nanowire-based humidity sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 12, 1884–1888 (2012)
Krcmar, P., Kuritka, I., Maslik, J., Urbanek, P., Bazant, P., Machovsky, M., Suly, P., Merka, P.: Fully inkjet-printed CuO sensor on flexible polymer substrate for alcohol vapours and humidity sensing at room temperature. Sens. (Basel) 19, 3068 (2019)
Holzki, M., Fouckhardt, H., Klotzbücher, T.: Evanescent-field fiber sensor for the water content in lubricating oils with sensitivity increase by dielectrophoresis. Sens. Actuators A 184, 93–97 (2012)
Kiasari, N.M., Servati, P.: Dielectrophoresis-assembled ZnO nanowire oxygen sensors. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 32, 982–984 (2011)
Chen, L., Zhang, J.: Capacitive humidity sensors based on the dielectrophoretically manipulated ZnO nanorods. Sens. Actuators A 178, 88–93 (2012)
Kim, W., Choi, M., Yong, K.: Generation of oxygen vacancies in ZnO nanorods/films and their effects on gas sensing properties. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 209, 989–996 (2015)
Agarwal, S., Sharma, G.L.: Humidity sensing properties of (Ba, Sr) TiO3 thin films grown by hydrothermal–electrochemical method. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 85, 205–211 (2002)
Matsuguchi, M., Umeda, S., Sadaoka, Y., Sakai, Y.: Characterization of polymers for a capacitive-type humidity sensor based on water sorption behavior. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 49, 179–185 (1998)
Qi, Q., Zhang, T., Wang, S., Zheng, X.: Humidity sensing properties of KCl-doped ZnO nanofibers with super-rapid response and recovery. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 137, 649–655 (2009)
Sharma, A., Kumar, Y., Mazumder, K., Rana, A.K., Shirage, P.M.: Controlled Zn1–xNixO nanostructures for an excellent humidity sensor and a plausible sensing mechanism. New J. Chem. 42, 8445–8457 (2018)
Agmon, N.: The Grotthuss mechanism. Chem. Phys. Lett. 244, 456–462 (1995)
Zhao, L.-X., Song, S.-E., Du, N., Hou, W.-G.: A sorbent concentration-dependent Freundlich isotherm. Colloid Polym. Sci. 291, 541–550 (2012)
Xia, L.X., Shen, Z., Vargas, T., Sun, W.J., Ruan, R.M., Xie, Z.D., Qiu, G.Z.: Attachment of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans onto different solid substrates and fitting through Langmuir and Freundlich equations. Biotechnol. Lett. 35, 2129–2136 (2013)
Yang, T., Yu, Y.Z., Zhu, L.S., Wu, X., Wang, X.H., Zhang, J.: Fabrication of silver interdigitated electrodes on polyimide films via surface modification and ion-exchange technique and its flexible humidity sensor application. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 208, 327–333 (2015)
Tomer, V.K., Thangaraj, N., Gahlot, S., Kailasam, K.: Cubic mesoporous Ag@CN: a high performance humidity sensor. Nanoscale 8, 19794–19803 (2016)
Passe-Coutrin, N., Altenor, S., Gaspard, S.: Assessment of the surface area occupied by molecules on activated carbon from liquid phase adsorption data from a combination of the BET and the Freundlich theories. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 332, 515–519 (2009)
Nounou, M.N., Nounou, H.N.: Multiscale estimation of the Freundlich adsorption isotherm. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 7, 509–518 (2010)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos.61674058, 61604002,), Open Fund of Shanghai Key Laboratory of Multidimensional Information Processing, East China Normal University (Grant No. 2019MIP002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, Y., Jiang, H., Ye, Z. et al. Impact of Size on Humidity Sensing Property of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles. Electron. Mater. Lett. 16, 61–71 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-019-00181-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-019-00181-4