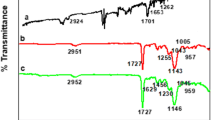
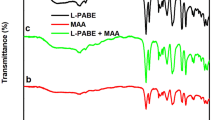
Abstract
Computational strategies have been employed to investigate the influence of the nature of monomers and cross-linker in order to design three dimensional imprinted polymers with selective recognition sites for L-phenylalanine benzyl ester (L-PABE) molecule. Here, computational chemistry methods were applied to screen the molar quantity of functional monomers that interact with one mole of the template molecule. Effects of the nature of functional monomer, cross-linker, and molar ratio were determined computationally using density functional calculations with B3LYP functional and generic 6–31G basis set. Methacrylic acid (MAA) and ethylene glycol dimethacrylate (EGDMA) were used as the functional monomer and crosslinking agent, respectively. L-PABE imprinted polymer layered on multiwalled carbon nanotube (MWCNT) and conventional bulk MIP were synthesised and characterized as well. To investigate the influence of pre-organization of binding sites on the selectivity of L-PABE, respective non-imprinted polymers were also synthesised. MWCNT-MIPs and MIPs exhibited the highest adsorption capacity towards L-PABE. The synthesized polymers revealed characteristic adsorption features and selectivity towards L-PABE in comparison with those of its enantiomer analogues.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ertürk, G.; Mattiasson, B. Molecular imprinting techniques used for the preparation of biosensors. Sensors2017, 288, 1–17.
Shah, N; Haneef, M; Park, J; Ul-Islam, M. A brief overview of molecularly imprinted polymers: From basics to applications. J. Pharm. Res.2012, 5, 3309–3317.
Ou, J.; Dong, J.; Tian, T.; Hu, J.; Ye, M.; Zou, H. Enantioseparation of tetrahydropalmatine and Tröger’s base by molecularly imprinted monolith in capillary electrochromatography. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods2007, 70, 71–76.
Lu, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X. Study on the mechanism of chiral recognition with molecularly imprinted polymers. Anal. Chim. Acta2003, 489, 33–43.
Mahony, J. O.; Karlsson, B. C. G.; Nicholls, I. A. Correlated theoretical, spectroscopic and X-ray crystallographic studies of a non-covalent molecularly imprinted polymerisation system. Analyst2007, 132, 1161–1168.
Sajini, T.; Gigimol, M. G.; Mathew, B. A brief overview of molecularly imprinted polymers supported on titanium dioxide matrices. Mater. Today Chem.2019, 11, 283–295.
Zhong, C.; Yang, B.; Jiang, X.; Li, J. Critical reviews in analytical chemistry current progress of nanomaterials in molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensing current progress of nanomaterials in molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensing. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem.2018, 48, 15–32.
Rezaei, B.; Rahmanian, O. Direct nanolayer preparation of molecularly imprinted polymers immobilized on multiwalled carbon nanotubes as a surface-recognition sites and their characterization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci.2012, 125, 798–803.
Jacobs, C. Nanotube based electrochemical sensors for biomolecules. Anal. Chim. Acta2010, 662, 105–127.
Anirudhan, T. S.; Alexander, S. Synthesis and characterization of vinyl-functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotubes based molecular imprinted polymer for the separation of chlorpyrifos from aqueous solutions. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol.2013, 88, 1847–1858.
Xu, L.; Xu, Z. Molecularly imprinted polymer based on multiwalled carbon nanotubes for ribavirin recognition. J. Polym. Res.2012, 19, 1–6.
Kan, X.; Zhao, Y.; Geng, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, J. Composites of multiwalled carbon nanotubes and molecularly imprinted polymers for dopamine recognition. J. Phys. Chem. C2008, 112, 4849–4854.
Scida, K.; Stege, P. W.; Haby, G.; Messina, G. A.; García, C. D. Recent applications of carbon-based nanomaterials in analytical chemistry. Anal. Chim. Acta2011, 691, 6–17.
Prasad, B. B.; Srivastava, A.; Pandey, I.; Tiwari, M. P. Electrochemically grown imprinted polybenzidine nanofilm on multiwalled carbon nanotubes anchored pencil graphite fibers for enantioselective micro-solid phase extraction coupled with ultratrace sensing of D- and L-methionine. J. Chromatogr. B2013, 912, 65–74.
Datsyuk, V.; Kalyva, M.; Papagelis, K.; Parthenios, J.; Tasis, D.; Siokou, A.; Kallitsis, I.; Galiotis, C. Chemical oxidation of multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Carbon2008, 6, 2–9.
Nicholls, I. A.; Andersson, H. S.; Golker, K.; Henschel, H.; Karlsson, B. C. G.; Olsson, G. D.; Rosengren, A. M.; Shoravi, S.; Suriyanarayanan, S.; Wiklander, J. G.; Wikman, S. Rational design of biomimetic molecularly imprinted materials: Theoretical and computational strategies for guiding nanoscale structured polymer development. Anal. Bioanal. Chem.2011, 400, 1771–1786.
Meier, F.; Schott, B.; Riedel, D.; Mizaikoff, B. Computational and experimental study on the influence of the porogen on the selectivity of 4-nitrophenol molecularly imprinted polymers. Anal. Chim. Acta2012, 744, 68–74.
Riahi, S.; Edris-Tabrizi, F.; Javanbakht, M.; Ganjali, M. R.; Norouzi, P. A computational approach to studying monomer selectivity towards the template in an imprinted polymer. J. Mol. Model.2009, 15, 829–836.
Cowen, T.; Karim, K.; Piletsky, S. Computational approaches in the design of synthetic receptors—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta2016, 936, 62–74.
Nicholls, I. A.; Chavan, S.; Golker, K.; Karlsson, C. G.; Olsson, G. D.; Rosengren, A. M. Theoretical and computational strategies for the study of the molecular imprinting process and polymer performance. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol.2015, 150, 25–50.
Batra, D.; Shea, K. J. Combinatorial methods in molecular imprinting. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol.2003, 7, 434–442.
Sajini, T.; Aravind, K.; Mathew, B. Theoretical and computational strategies for the fabrication of enantioselective recognition site on molecularly imprinted polymers. Int. J. Curr. Adv. Res.2017, 6, 6334–6336.
Nicholls, I. A.; Andersson, H. S.; Charlton, C.; Henschel, H.; Karlsson, B. C. G.; Karlsson, J. K.; Mahony, J. O.; Rosengren, A. M.; Rosengren, K. J.; Wikman, S. Theoretical and computational strategies for rational molecularly imprinted polymer design. Biosens. Bioelectron.2009, 25, 543–552.
Tadi, K. K.; Motghare, R. V. Computational and experimental studies on oxalic acid imprinted polymer. J. Chem. Sci.2013, 125, 413–418.
Riahi, S.; Eynollahi, S.; Ganjali, M. R.; Norouzi, P. Computational approach to investigation of template/monomer complex in imprinted polymers; dinitrobenzene sensor. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci.2010, 5, 509–516.
Khan, M. S.; Wate, P. S.; Krupadam, R. J. Combinatorial screening of polymer precursors for preparation of benzo. J. Mol. Model.2012, 18, 1969–1981.
Nicholls, I. A.; Karlsson, C. G.; Olsson, G. D.; Rosengren, A. M. Computational strategies for the design and study of molecularly imprinted materials. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res.2018, 10, 27.
McCormick, T. M.; Bridges, C. R.; Carrera, E. I.; Dicarmine, P. M.; Gibson, G. L.; Hollinger, J.; Kozycz, L. M.; Seferos, D. S. Conjugated polymers: Evaluating DFT methods for more accurate orbital energy modeling. Macromolecules2013, 46, 3879–3886.
Singh, A. K.; Singh, M. Designing L-serine targeted molecularly imprinted polymer via theoretical investigation. J. Theor. Comput. Chem.2016, 15
Mojica, E. R. E. Screening of different computational models for the preparation of sol-gel imprinted materials. J. Mol. Model.2013, 19, 3911–3923.
Silva, C. F.; Borges, K. B.; Soares, C. Rational design of a molecularly imprinted polymer for dinotefuran: Theoretical and experimental studies aimed at the development of an efficient adsorbent for microextraction by packed sorbent. Analyst2018, 143, 141–149.
Pardeshi, S.; Patrikar, R.; Dhodapkar, R.; Kumar, A. Validation of computational approach to study monomer selectivity toward the template Gallic acid for rational molecularly imprinted polymer design. J. Mol. Model.2012, 18, 4797–4810.
Acquaye, C. T. A.; Gorecki, M.; Wilchek, M.; Votano, J. R.; Rich, A. Antisickling activity of amino acid benzyl esters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.1980, 77, 181–185.
Acquaye, C. T. A.; Young, J. D.; Ellory, J. C.; Gorecki, M.; Wilchek, M. Mode of transport and possible mechanism of action of L-phenylalanine benzyl ester as an anti-sickling agent. Biochim. Biophys. Acta1982, 693, 407–416.
Frisch, G. E. S. M. J.; Trucks, G. W.; Schlegel, H. B.; Robb, B. M. M. A.; Cheeseman, J. R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, H. P. H. G. A.; Nakatsuji, H.; Caricato, M.; Li, X.; Izmaylov, M. H. A. F.; Bloino, J.; Zheng, G.; Sonnenberg, J. L.; Ehara, T. N. M.; Toyota, K.; Fukuda, R.; Hasegawa, J.; Ishida, M.; Honda, J. Y.; Kitao, O.; Nakai, H.; Vreven, T.; Montgomery, J. A.; Peralta, E. B. J. E.; Ogliaro, F.; Bearpark, M.; Heyd, J. J.; Kudin, J. N. K. N.; Staroverov, V. N.; Keith, T.; Kobayashi, R.; Raghavachari, J. T. K.; Rendell, A.; Burant, J. C.; Iyengar, S. S.; Cossi, J. B. C. M.; Rega, N.; Millam, J. M.; Klene, M.; Knox, J. E.; Bakken, R. E. S. V.; Adamo, C.; Jaramillo, J.; Gomperts, R.; Yazyev, J. W. O. O.; Austin, A. J.; Cammi, R.; Pomelli, C.; Martin, G. A. V. R. L.; Morokuma, K.; Zakrzewski, V. G.; Salvador, A. D. D. P.; Dannenberg, J. J.; Dapprich S.; Farkas, D. J. F. O.; Foresman, J. B.; Ortiz, J. V.; Cioslowski, J. Gaussian 09 Revis. D.01, 2013.
Dennington, R.; Keith, T.; Millam, J. Semichem Inc. Shawnee Mission. KS, 2016.
Polimer, P.; Molekul, C. Synthesis and characterization of a molecularly imprinted polymer for Pb2+ uptake using 2-vinylpyridine as the complexing monomer. Sains. Malaysiana2010, 39, 829–835.
Zakaria, N. D.; Yusof, N. A.; Haron, J.; Abdullah, A. H. Synthesis and evaluation of a molecularly imprinted polymer. Int. J. Mol. Sci.2009, 10, 354–365.
Zhang, W.; Li, Q.; Cong, J.; Wei, B.; Wang, S. Mechanism analysis of selective adsorption and specific recognition by molecularly imprinted polymers of Ginsenoside Re. Polymers2018, 10.
Yuan, H.; Ma, X.; Xu, Z. Pore structure analysis of PFSA/SiO2 composite catalysts from nitrogen adsorption isotherms. Sci. China Chem.2011, 54, 257–262.
Li, S.; Huang, X.; Zheng, M.; Li, W.; Tong, K. Molecularly imprinted polymers: Thermodynamic and kinetic considerations on the specific sorption and molecular recognition. Sensors2008, 8, 2854–2864.
Karim, K.; Breton, F.; Rouillon, R.; Piletska, E. V.; Guerreiro, A.; Chianella, I.; Piletsky, S. A. How to find effective functional monomers for effective molecularly imprinted polymers? Adv. Drug Deliver. Rev.2005, 57, 1795–1808.
Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Tang, S. Theoretical guidance for experimental research of the dicyandiamide and methacrylic acid molecular imprinted polymer. New J. Chem.2017, 41, 13370–13376.
Muhammad, T.; Nur, Z.; Piletska, E. V.; Piletsky, S. A. Rational design of molecularly imprinted polymer: The choice of cross-linker. Analyst2012, 137, 2623–2628.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sajini, T., Thomas, R. & Mathew, B. Computational Design and Fabrication of Enantioselective Recognition Sorbents for L-phenylalanine Benzyl Ester on Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes Using Molecular Imprinting Technology. Chin J Polym Sci 37, 1305–1318 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-019-2282-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-019-2282-4