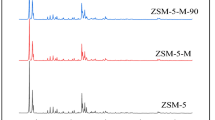
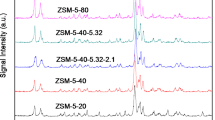
Abstract
Hierarchical ZSM-5 zeolite with radial mesopores is controllably synthesized using piperidine in a NaOH solution. The piperidine molecules enter the zeolite micropores and protect the zeolite framework from extensive desilication. The areas containing fewer aluminum atoms contain fewer piperidine protectant molecules and so they dissolve first. Small amounts of mesopores are then gradually generated in areas with more aluminum atoms and more piperidine protectant. In this manner, radial mesopores are formed in the ZSM-5 zeolite with a maximal preservation of the micropores and active sites. The optimal hierarchical ZSM-5 zeolite, prepared with a molar ratio of piperidine to zeolite of 0.03, had a mesopore surface area of 136 m2·g−1 and a solid yield of 80%. The incorporation of the radial mesopores results in micropores that are interconnected which shortened the average diffusion path length. Compared to the parent zeolite, the hierarchical ZSM-5 zeolite possesses more accessible acid sites and has a higher catalytic activity and a longer lifetime for the alkylation of benzene.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Corma A. Inorganic solid acids and their use in acid-catalyzed hydrocarbon reactions. Chemical Reviews, 1995, 95(3): 559–614
Cundy C S, Cox P A. The hydrothermal synthesis of zeolites: History and development from the earliest days to the present time. Chemical Reviews, 2003, 103(3): 663–702
Corma A. From microporous to mesoporous molecular sieve materials and their use in catalysis. Chemical Reviews, 1997, 97(6): 2373–2420
Tao Y S, Kanoh H, Abrams L, Kaneko K. Mesopore-modified zeolites: Preparation, characterization, and applications. Chemical Reviews, 2006, 106(3): 896–910
Zheng H, Zhai D, Zhao L, Zhang C, Yu S, Gao J, Xu C. Insight into the contribution of isolated mesopore on diffusion in hierarchical zeolites: The effect of temperature. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2018, 57(15): 5453–5463
Han J, Cho J, Kim J C, Ryoo R. Confinement of supported metal catalysts at high loading in the mesopore network of hierarchical zeolites, with access via the microporous windows. ACS Catalysis, 2018, 8(2): 876–879
Jia L Y, Raad M, Hamieh S, Toufaily J, Hamieh T, Bettahar M M, Mauviel G, Tarrighi M, Pinard L, Dufour A. Catalytic fast pyrolysis of biomass: Superior selectivity of hierarchical zeolites to aromatics. Green Chemistry, 2017, 19(22): 5442–5459
Groen J C, Bach T, Ziese U, Paulaime-van Donk A M, de Jong K P, Moulijn J A, Pérez-Ramírez J. Creation of hollow zeolite architectures by controlled desilication of Al-zoned ZSM-5 crystals. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2005, 127(31): 10792–10793
Zhang K, Ostraat M L. Innovations in hierarchical zeolite synthesis. Catalysis Today, 2016, 264: 3–15
Schmidt I, Boisen A, Gustavsson E, Stahl K, Pehrson S, Dahl S, Carlsson A, Jacobsen C J H. Carbon nanotube templated growth of mesoporous zeolite single crystals. Chemistry of Materials, 2001, 13(12): 4416–4418
Tao Y, Kanoh H, Kaneko K. ZSM-5 monolith of uniform mesoporous channels. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2003, 125(20): 6044–6045
Zhu K, Egeblad K, Christensen C H. Mesoporous carbon prepared from carbohydrate as hard template for hierarchical zeolites. European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2007, 2007(25): 3955–3960
Xiao F, Wang L, Yin C, Lin K, Di Y, Li J, Xu R, Su D, Schlögl R, Yokoi T, Tatsumi T. Catalytic properties of hierarchical mesoporous zeolites templated with a mixture of small organic ammonium salts and mesoscale cationic polymers. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2006, 45(19): 3090–3093
Zhao Z, Liu Y, Wu H, Li X, He M, Wu P. Hydrothermal synthesis of mesoporous titanosilicate with the aid of amphiphilic organosilane. Journal of Porous Materials, 2010, 17(4): 399–408
Liu H, Zhang S, Xie S, Zhang W, Xin W, Liu S, Xu L. Synthesis, characterization, and catalytic performance of hierarchical ZSM-11 zeolite synthesized via dual-template route. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2018, 39(1): 167–180
Wang X, Chen H, Meng F, Gao F, Sun C, Sun L, Wang S, Wang L, Wang Y. CTAB resulted direct synthesis and properties of hierarchical ZSM-11/5 composite zeolite in the absence of template. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2017, 243: 271–280
Groen J C, Jansen J C, Moulijn J A, Pérez-Ramírez J. Optimal aluminum-assisted mesoporosity development in MFI zeolites by desilication. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2004, 108(35): 13062–13065
Groen J C, Peffer L A A, Moulijn J A, Pérez-Ramírez J. Mechanism of hierarchical porosity development in MFI zeolites by desilication: The role of aluminium as a pore-directing agent. Chemistry (Weinheim an der Bergstrasse, Germany), 2005, 11(17): 4983–4994
Rutkowska M, Pacia I, Basąg S, Kowalczyk A, Piwowarska Z, Duda M, Tarach K A, Góra-Marek K, Michalik M, Díaz U, Chmielarz L. Catalytic performance of commercial Cu-ZSM-5 zeolite modified by desilication in NH3-SCR and NH3-SCO processes. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2017, 246: 193–206
Oruji S, Khoshbin R, Karimzadeh R. Preparation of hierarchical structure of Y zeolite with ultrasonic-assisted alkaline treatment method used in catalytic cracking of middle distillate cut: The effect of irradiation time. Fuel Processing Technology, 2018, 176: 283–295
Groen J C, Sano T, Moulijn J A, Pérez-Ramírez J. Alkalinemediated mesoporous mordenite zeolites for acid-catalyzed conversions. Journal of Catalysis, 2007, 251(1): 21–27
Pérez-Ramírez J, Abello S, Villaescusa L A, Bonilla A. Toward functional clathrasils: Size- and composition-controlled octadecasil nanocrystals by desilication. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2008, 47(41): 7913–7917
Verboekend D, Pérez-Ramírez J. Desilication mechanism revisited: Highly mesoporous all-silica zeolites enabled through pore-directing agents. Chemistry (Weinheim an der Bergstrasse, Germany), 2011, 17(4): 1137–1147
Sadowska K, Wach A, Olejniczak Z, Kustrowski P, Datka J. Hierarchic zeolites: Zeolite ZSM-5 desilicated with NaOH and NaOH/tetrabutylamine hydroxide. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2013, 167(3): 82–88
Groen J C, Peffer L A A, Moulijn J A, Pérez-Ramírez J. Mesoporosity development in ZSM-5 zeolite upon optimized desilication conditions in alkaline medium. Colloids and Surfaces. A, Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2004, 241(1–3): 53–58
Pérez-Ramírez J, Verboekend D, Bonilla A, Abello S. Zeolite catalysts with tunable hierarchy factor by pore-growth moderators. Advanced Functional Materials, 2009, 19(24): 3972–3979
Milina M, Mitchell S, Crivelli P, Cooke D, Pérez-Ramírez J. Mesopore quality determines the lifetime of hierarchically structured zeolite catalysts. Nature Communications, 2014, 5(1): 3922–3931
Wang D, Zhang L, Chen L, Wu H, Wu P. Postsynthesis of mesoporous ZSM-5 zeolite by piperidine-assisted desilication and its superior catalytic properties in hydrocarbon cracking. Journal of Materials Chemistry. A, Materials for Energy and Sustainability, 2015, 3(7): 3511–3521
Wang D, Xu L, Wu P. Hierarchical, core-shell meso-ZSM5@mesoporous aluminosilicate-supported Pt nanoparticles for bifunctional hydrocracking. Journal of Materials Chemistry. A, Materials for Energy and Sustainability, 2014, 2(37): 15535–15545
Kalipcilar H, Culfaz A. Influence of nature of silica source on template-free synthesis of ZSM-5. Crystal Research and Technology, 2001, 36(11): 1197–1207
Sing K S W, Everett D H, Haul R A W, Moscou L, Pierotti R A, Rouquerol J, Siemieniewska V T. Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 1985, 57(4): 603–619
Groen J C, Moulijn J A, Pérez-Ramírez J. Desilication: On the controlled generation of mesoporosity in MFI zeolites. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2006, 16(22): 2121–2131
Yoo W C, Zhang X, Tsapatsis M, Stein A. Synthesis of mesoporous ZSM-5 zeolites through desilication and re-assembly processes. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2012, 149(1): 147–157
Pérez-Ramírez J, Abelló S, Bonilla A, Groen J C. Tailored mesoporosity development in zeolite crystals by partial detemplation and desilication. Advanced Functional Materials, 2009, 19(1): 164–172
Gornicka E, Rode J E. Raczynska, E D, Dasiewicz B, Dobrowolski J C. Vibrational Spectroscopy, 2004, 36: 105–115
Kokotailo G T, Lawton S L, Olson D H, Meier W M. Structure of synthetic zeolite ZSM-5. Nature, 1978, 272(5652): 437–438
Zhu K, Sun J, Liu J, Wang L, Wan H, Hu J, Wang Y, Peden C H F, Nie Z. Solvent evaporation assisted preparation of oriented nanocrystalline mesoporous MFI zeolites. ACS Catalysis, 2011, 1(7): 682–690
Liu Y, Zhang W, Liu Z, Xu S, Wang Y, Xie Z, Han X, Bao X. Direct observation of the mesopores in ZSM-5 zeolites with hierarchical porous structures by laser-hyperpolarized 129Xe NMR. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2008, 112(39): 15375–15381
Schumacher R, Karge H G. Sorption kinetics study of the diethylbenzene isomers in MFI-type zeolites. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 1999, 30(2–3): 307–314
Zhou J, Liu Z, Wang Y, Gao H, Li L, Yang W, Xie Z, Tang Y. Enhanced accessibility and utilization efficiency of acid sites in hierarchical MFI zeolite catalyst for effective diffusivity improvement. RSC Advances, 2014, 4(82): 43752–43755
Yang W, Wang Z, Sun H, Zhang B. Advances in development and industrial applications of ethylbenzene processes. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2016, 37(1): 16–26
Saxena S K, Viswanadham N. Hierarchically nano porous nano crystalline ZSM-5 for improved alkylation of benzene with bioethanol. Applied Materials Today, 2016, 5: 25–32
Lei Z, Liu L, Dai C. Insight into the reaction mechanism and charge transfer analysis for the alkylation of benzene with propylene over H-β zeolite. Molecular Catalysis, 2018, 454: 1–11
Christensen C H, Johannsen K, Schmidt I, Christensen C H. Catalytic benzene alkylation over mesoporous zeolite single crystals: Improving activity and selectivity with a new family of porous materials. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2003, 125(44): 13370–13371
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2017YFB0702800) and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2016M600347).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
11705_2019_1853_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Hierarchical ZSM-5 zeolite with radial mesopores: Preparation, formation mechanism and application for benzene alkylation
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, D., Sun, H., Liu, W. et al. Hierarchical ZSM-5 zeolite with radial mesopores: Preparation, formation mechanism and application for benzene alkylation. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 14, 248–257 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-019-1853-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-019-1853-9