Abstract
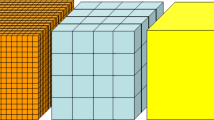
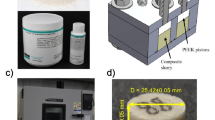
A method based on X-ray micro-CT was introduced to create realistic representative volume elements (RVE) for particulate-filled composite materials. The method is applicable to most composite systems, and can be utilized to improve artificial computer algorithms by presenting the number, the dimension, and the orientation of filler particles inside the RVEs. Three different shapes of glass fillers (spherical, flake, and fiber) and filler mass fractions (5%, 10%, and 15%) were introduced to epoxy resin to demonstrate the capability of micro-CT to create RVEs. Two kind of RVEs were created; voxel-based and geometry-based. Voxel-based RVEs were created from binary segmentation of images taken from micro-CT. Geometry-based RVEs were created after reconstruction of voxel-based RVEs to eliminate the stepped-like appearance of non-orthogonal interfaces. These RVE’s were then used in the finite element analysis to find the effective mechanical properties such as Young’s modulus, shear modulus, Poisson’s ratio of the samples. In order to assess the numerical findings, compression tests were performed according to ASTM D695. Also, spherical fillers were distributed inside a volume artificially using an algorithm and RVEs were created. The number and the dimension of the spherical fillers were supplied from X-ray micro-CT and optical microscopy, respectively. The elastic moduli found using RVEs created from the algorithm is close to the elastic moduli found using RVEs created from X-ray micro-CT.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
ABAQUS 6.12 Online documentation, Dassault Systemes, Providence, RI, USA (2012)
ASTM. D695.36782. Standard test method for compressive properties of rigid plastics (2015)
Badel, P., Vidal-Salle, E., Maire, E., Boisse, P.: Simulation and tomography analysis of textile composite reinforcement deformation at the mesoscopic scale. Compos. Sci. Technol. 68(12), 2433–2440 (2008)
Beran, M.J., Molyneux, J.: Use of classical variational principles to determine bounds for the effective bulk modulus in heterogeneous media. Q. Appl. Math. 24, 107–118 (1966)
Bernasconi, A., Cosmi, F., Hine, P.J.: Analysis of fibre orientation distribution in short fibre reinforced polymers: a comparison between optical and tomographic methods. Compos. Sci. Technol. 72, 2002–2008 (2012)
Blacklock, M., Bale, H., Begley, M., Cox, B.: Generating virtual textile composite specimens using statistical data from micro-computed tomography: 1D tow representations for the Binary Model. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 60, 451–470 (2012)
Bohm, H.J., Eckschlager, A., Han, W.: Multi-inclusion unit cell models for metal matrix composites with randomly oriented discontinuous reinforcements. Comput. Mater. Sci. 25(1–2), 42–53 (2002)
Chauhan, S.R., Thakur, S.: Effects of particle size, particle loading and sliding distance on the friction and wear properties of cenosphere particulate filled vinylester composites. Mater. Des. 51, 398–408 (2013)
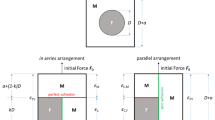
Cinar, K., Guven, I.: Micro-computed tomography as a tool to investigate the deformation behavior of particulate-filled composite materials. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 140(2), 1–17 (2018)
Djebara, Y., El Moumen, A., Kanit, T., Madani, S., Imad, A.: Modeling of the effect of particles size, particles distribution and particles number on mechanical properties of polymer–clay nanocomposites: numerical homogenization versus experimental results. Compos. B Eng. 86, 135–142 (2016)
Drach, B., Tsukrov, I., Trofimov, A.: Comparison of full field and single pore approaches to homogenization of linearly elastic materials with pores of regular and irregular shapes. Int. J. Solids Struct. 96, 48–63 (2016)
El Moumen, A., Kanit, T., Imad, A., El Minor, H.: Effect of reinforcement shape on physical properties and representative volume element of particles-reinforced composites: statistical and numerical approaches. Mech. Mater. 83, 1–16 (2015)
Halphin, J.C., Tsai, S.W.: Environmental factors in composite materials. AFML TR 67-423, Air Force Materials Laboratory Report (1967)
Harraez, M., Gonzales, C., Lopes, C.S., Guzman de Villoria, R., Lorca, J., Varela, T., Sanchez, J.: Computational micromechanics evaluation of the effect of fibre shape on the transverse strength of unidirectional composites: an approach to virtual materials design. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 91(2), 484–492 (2016)
Hashin, Z., Shtrikman, S.: A variational approach to the theory of the elastic behavior of multiphase materials. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 11, 127–140 (1963)
Hbaieb, K., Wang, Q.X., Chia, Y.H.J., Cotterell, B.: Modelling stiffness of polymer/clay nanocomposites. Polymer 48(3), 901–909 (2007)
Kanit, T., Forest, S., Galliet, I., Mounoury, V., Jeulin, D.: Determination of the size of the representative volume element for random composites: statistical and numerical approach. Int. J. Solids Struct. 40(13–14), 3647–3679 (2003)
Kari, S., Berger, H., Rodriguez-Ramos, R., Gabbert, U.: Computational evaluation of effective material properties of composites reinforced by randomly distributed spherical particles. Compos. Struct. 77, 223–231 (2007a)
Kari, S., Berger, H., Gabbert, U.: Numerical evaluation of effective material properties of randomly distributed short cylindrical fibre composites. Comput. Mater. Sci. 39(1), 198–204 (2007b)
Kushvaha, V., Tippur, H.: Effect of filler shape, volume fraction and loading rate on dynamic fracture behavior of glass-filled epoxy. Compos. B Eng. 64, 126–137 (2014)
Mori, T., Tanaka, K.: Average stress in matrix and average elastic energy of materials with misfitting inclusions. Acta Mater. 21(5), 571–574 (1973)
Mortazavi, B., Baniassadi, M., Bardon, J., Ahzi, S.: Modeling of two-phase random composite materials by finite element, Mori–Tanaka and strong contrast methods. Compos. B Eng. 45(1), 1117–1125 (2013)
Naouar, N., Vidal-Salle, E., Schneider, J., Maire, E., Boisse, P.: 3D composite reinforcement meso F.E. analyses based on X-ray computed tomography. Compos. Struct. 132, 1094–1104 (2015)
Panda, S.P., Panda, S.: Micromechanical finite element analysis of effective properties of a unidirectional short piezoelectric fiber reinforced composite. Int. J. Mech. Mater. Des. 11(1), 41–57 (2015)
Qi, L., Tian, W., Zhou, J.: Numerical evaluation of effective elastic properties of composites reinforced by randomly distributed short fibers with certain aspect ratio. Compos. Struct. 131, 843–851 (2015)
Rask, M., Madsen, B., Sorensen, B.F., Fife, J.L., Martyniuk, K., Lauridsen, E.M.: In situ observations of microscale damage evolution in unidirectional natural fibre composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 43(10), 1639–1649 (2012)
Reuss, A.: Berechnung der fliegrenze von mischkristallen auf grund der plastizittsbedingung fr einkristalle. J. Appl. Math. Mech. 9(1), 49–58 (1929)
Sab, K.: On the homogenization and the simulation of random materials. Eur. J. Mech. Solids. 11, 585–607 (1992)
Shedbale, A.S., Singh, I.V., Mishra, B.K.: Heterogeneous and homogenized models for predicting the indentation response of particle reinforced metal matrix composites. Int. J. Mech. Mater. Des. 13, 531–552 (2017)
Shen, H., Nutt, S., Hull, D.: Direct observation and measurement of fiber architecture in short fiber-polymer composite foam through micro-CT imaging. Compos. Sci. Technol. 64, 2113–2120 (2004)
Sheng, N., Boyce, M.C., Parks, D.M., Rutledge, G.C., Abes, J.I., Cohen, R.E.: Multiscale micromechanical modeling of polymer/clay nanocomposites and the effective clay particle. Polymer 45(2), 487–506 (2004)
Straumit, I., Lomov, S.V., Wevers, M.: Quantification of the internal structure and automatic generation of voxel models of textile composites from X-ray computed tomography data. Compos. Part A-Appl. Sci. Manuf. 69, 150–158 (2015)
Sun, T.C., Vaidya, S.R.: Prediction of composite properties from a representative volume element. Compos. Sci. Technol. 56, 171–179 (1996)
Tebmann, M., Mohr, S., Gayetskyy, S., Habler, U., Hanke, R., Greiner, G.: Automatic determination of fiber-length distribution in composite material using 3D CT data. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. (2010). https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/545030
Tian, W., Qi, L., Su, C., Zhou, J., Jing, Z.: Numerical simulation on elastic properties of short-fiber-reinforced metal matrix composites: effect of fiber orientation. Compos. Struct. 152, 408–417 (2016)
Tian, W., Qi, L., Zhou, J., Liang, J., Ma, Y.: Representative volume element for composite reinforced by spatially randomly distributed discontinuous fibers and its applications. Compos. Struct. 131, 366–373 (2015)
Voight, W.: Ueber die beziehung zwischen den beiden elasticitatsconstanten isotroper korper. Ann. Phys. 274, 573–587 (1889)
Xu, L.M., Fan, H., Sze, K.Y., Li, C.: Elastic property prediction by finite element analysis with random distribution of materials for heterogeneous solids. Int. J. Mech. Mater. Des. 3(4), 319–327 (2006)
Zhang, M., Jivkov, A.P.: Micromechanical modelling of deformation and fracture of hydrating cement paste using X-ray computed tomography characterization. Compos. B Eng. 88, 64–72 (2016)
Acknowledgement
This paper is based on the work supported partially by the VCU Presidential Research Quest Fund (Grant No. 295082).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guven, I., Cinar, K. Micromechanical modeling of particulate-filled composites using micro-CT to create representative volume elements. Int J Mech Mater Des 15, 695–714 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10999-018-09438-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10999-018-09438-6