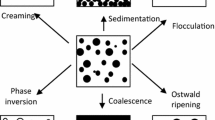
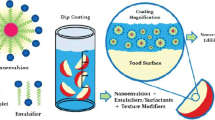
Abstract
Emulsion gels are widely used in food products, and they have the characteristics of both emulsions and biopolymer gels. When distributed in gels, functional ingredients are protected by the gels and immobilized by the gel network, and thus, they usually have improved physicochemical stability. Emulsion gels are generally prepared based on proteins, polysaccharides, or their mixtures, and characteristics of the oil droplets played essential roles in the properties and functions of the systems. Emulsion gels can be fabricated to behave differently when encountered with different environment by controlling the physical structures of the gels, including their digestion behaviors in the digestive tract, which allowed adjustment of the stability and releasing behaviors of the incorporated functional ingredients, contributing to their enhanced bioavailability. A lot of studies in the last 10 years have proved that emulsion gels can effectively deliver vitamins, carotenoids, minerals, phenolic bioactives, flavors, unsaturated fatty acids, and other functional ingredients, and they are also suitable for the development of fat-reduced food. This article systematically reviewed recent studies regarding the use of emulsion gels as delivery systems for various functional ingredients, trying to get an improved understanding of the structures and functionalities of emulsion gels, for the better design of functional foods.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abaee A, Mohammadian M, Jafari SM (2017) Whey and soy protein-based hydrogels and nano-hydrogels as bioactive delivery systems. Trends Food Sci Technol 70:69–81
Alejandre M, Ansorena D, Calvo MI, Cavero RY, Astiasarán I (2018) Influence of a gel emulsion containing microalgal oil and a blackthorn (Prunus spinosa L.) branch extract on the antioxidant capacity and acceptability of reduced-fat beef patties. Meat Sci in press
Allen TM, Cullis PR (2013) Liposomal drug delivery systems: from concept to clinical applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 65:36–48
Assadpour E, Jarafi SM (2018) A systematic review on nanoencapsulation of food bioactive ingredients and nutraceuticals by various nanocarriers. Crit Rev Food Sci in press
Bai L, Huan S, Li Z, McClements DJ (2017) Comparison of emulsifying properties of food-grade polysaccharides in oil-in-water emulsions: gum arabic, beet pectin, and corn fiber gum. Food Hydrocoll 66:144–153
Balakrishnan G, Nguyen BT, Schmitt C, Nicolai T, Chassenieux C (2017) Heat-set emulsion gels of casein micelles in mixtures with whey protein isolate. Food Hydrocoll 73:213–221
Bao Z (2015) Effects on the functional, structural and gelation property of soybean protein isolate treated by ultrasound. Nanchang University, China
Barbe F, Menard O, Le Gouar Y, Buffiere C, Famelart MH, Laroche B (2013) The heat treatment and the gelation are strong determinants of the kinetics of milk proteins digestion and of the peripheral availability of amino acids. Food Chem 136:1203–1212
Beaulieu L, Savoie L, Paquin P, Subirade M (2002) Elaboration and characterization of whey protein beads by an emulsification/cold gelation process: application for the protection of retinol. Biomacromolecules 3:239–248
Ben-Harb S, Panouille M, Huc-Mathis D, Moulin G, Saint-Eve A, Irlinger F, Bonnarme P, Michon C, Souchon I (2018) The rheological and microstructural properties of pea, milk, mixed pea-milk gels and gelled emulsions designed by thermal, acid, and enzyme treatments. Food Hydrocoll 77:75–84
Betz M, Kulozik U (2011) Microencapsulation of bioactive bilberry anthocyanins by means of whey protein gels. Procedia Food Sci 1:2047–2056
Betz M, Steiner B, Schantz M, Oidtmann J, Mäder K, Richling E, Kulozik U (2012) Antioxidant capacity of bilberry extract microencapsulated in whey protein hydrogels. Food Res Int 47:51–57
Bhattacharjee C, Das KP (2001) Characterization of microcapsules of β-lactoglobulin formed by chemical cross linking and heat setting. J Dispers Sci Technol 22:71–78
Brito-Oliveira TC, Bispo M, Moraes ICF, Campanella OH, Pinho SC (2017) Stability of curcumin encapsulated in solid lipid microparticles incorporated in cold-set emulsion filled gels of soy protein isolate and xanthan gum. Food Res Int 102:759–767
Cardoso CL, Mendes RO, Saraiva JA, Vazpires PR, Nunes ML (2010) Quality characteristics of high pressure-induced hake (Merluccius capensis) protein gels with and without MTGase. J Aquat Food Prod T 19:193–213
Chen X, McClements DJ, Wang J, Zou L, Deng S, Liu W (2018) Coencapsulation of (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate and quercetin in particle-stabilized W/O/W emulsion gels: controlled release and bioaccessibility. J Agric Food Chem 66:3691–3699
Chen X, McClements DJ, Zhu Y, Zou L, Li Z et al (2018) Gastrointestinal fate of fluid and gelled nutraceutical emulsions impact on proteolysis, lipolysis, and quercetin bioaccessibility. J Agric Food Chem 66:9087–9096
Chivero P, Gohtani S, Yoshii H, Nakamura A (2016) Assessment of soy soluble polysaccharide, gum arabic and OSA-starch as emulsifiers for mayonnaise-like emulsions. LWT Food Sci Technol 69:59–66
Dai L, Sun C, Wei Y, Mao L, Gao Y (2018) Characterization of Pickering emulsion gels stabilized by zein/gum Arabic complex colloidal nanoparticles. Food Hydrocoll 74:239–248
De Figueiredo FG, Pereira RNC, Vicente AA, Cunha RL (2018) Cold gel-like emulsions of lactoferrin subjected to ohmic heating. Food Res Int 103:371–379
Dickinson E (2012) Emulsion gels: the structuring of soft solids with protein-stabilized oil droplets. Food Hydrocoll 28:224–241
Dille MJ, Hattrem MN, Draget KI (2016) Bioactively filled gelatin gels; challenges and opportunities. Food Hydrocoll 76:17–29
Epstein J, Sanderson IR, Macdonald TT (2010) Curcumin as a therapeutic agent: the evidence from in vitro, animal and human studies. Brit J Nutr 103:1545–1557
Faridi EA, Jafari SM, Assadpour E (2017) Preparation of a multiple emulsion based on pectin-whey protein complex for encapsulation of saffron extract nanodroplets. Food Chem 221:1962–1969
Fathi M, Mozafari MR, Mohebbi M (2012) Nanoencapsulation of food ingredients using lipid based delivery systems. Trends Food Sci Technol 23:13–27
Feng W, Yue C, Wusigale NY, Liang L (2018) Preparation and characterization of emulsion-filled gel beads for the encapsulation and protection of resveratrol and α-tocopherol. Food Res Int 108:161–171
Freire M, Cofrades S, Pérez-Jiménez J, Goméz-Estaca J, Jiménez-Colmenero F (2018) Emulsion gels containing n-3 fatty acids and condensed tannins designed as functional fat replacers. Food Res Int 113:465–473
Freire M, Cofrades S, Serrano-Casas V, Pintado T, Jimenez MJ (2017) Gelled double emulsions as delivery systems for hydroxytyrosol and n-3 fatty acids in healthy pork patties. J Food Sci Technol 54:3959–3968
Ge W, Li D, Chen M, Wang X, Liu S, Sun R (2015) Characterization and antioxidant activity of β-carotene loaded chitosan-graft-poly(lactide) nanomicelles. Carbohydr Polym 117:169–176
Geremias-Andrade IM, Souki NPDBG, Moraes ICF, Pinho SC (2017) Rheological and mechanical characterization of curcumin-loaded emulsion-filled gels produced with whey protein isolate and xanthan gum. LWT Food Sci Technol 86:166–173
Ghorbanzade T, Jafari SM, Akhavan S, Hadavi R (2017) Nano-encapsulation of fish oil in nano-liposomes and its application in fortification of yogurt. Food Chem 216:146–152
Gómez-Mascaraque LG, Casagrande SC, De La Torre LG, Lópezrubio A (2017) Microencapsulation structures based on protein-coated liposomes obtained through electrospraying for the stabilization and improved bioaccessibility of curcumin. Food Chem 233:343–350
Guo Q, Bellissimo N, Rousseau D (2017) Role of gel structure in controlling in vitro intestinal lipid digestion in whey protein emulsion gels. Food Hydrocoll 69:264–272
Guo Q, Ye A, Bellissimo N, Singh H, Rousseau D (2017) Modulating fat digestion through food structure design. Prog Lipid Res 68:109–118
Guo Q, Ye A, Lad M, Dalgleish D, Singh H (2013) The breakdown properties of heat-set whey protein emulsion gels in the human mouth. Food Hydrocoll 33:215–224
Guo Q, Ye A, Lad M, Dalgleish D, Singh H (2014) Behavior of whey protein emulsion gel during oral and gastric digestion: effect of droplet size. Soft Matter 10:4173–4183
Guo Q, Ye A, Lad M, Dalgleish D, Singh H (2014) Effect of gel structure on the gastric digestion of whey protein emulsion gels. Soft Matter 10:1214–1223
Guo Q, Ye A, Lad M, Ferrua M, Dalgleish D, Singh H (2015) Disintegration kinetics of food gels during gastric digestion and its role on gastric emptying: an in vitro analysis. Food Funct 6:756–764
Harrison M, Hills BP (1996) A mathematical model to describe flavor release from gelatin gels. Int J Food Sci Technol 31:167–176
Hoffman AS (2012) Hydrogels for biomedical applications. Ann N Y Acad Sci 64:18–23
Hongsprabhas P, Barbut S (1997) Effect of gelation temperature on Ca2+ −induced gelation of whey protein isolate. LWT Food Sci Technol 30:45–49
Hou JJ, Guo J, Wang JM, Yang XQ (2016) Effect of interfacial composition and crumbliness on aroma release in soy protein/sugar beet pectin mixed emulsion gels. J Sci Food Agric 96:4449–4456
Huang J, Wang Q, Li T, Xia N, Xia Q (2018) Multilayer emulsions as a strategy for linseed oil and alpha-lipoic acid micro-encapsulation: study on preparation and in vitro characterization. J Sci Food Agric 98:3513–3523
Iwasaki T, Washio M, Yamamoto K, Nakamura K (2010) Rheological and morphological comparison of thermal and hydrostatic pressure-induced filamentous myosin gels. J Food Sci 70:432–436
Jiang Y, Liu L, Wang B (2019) Polysaccharide-based edible emulsion gel stabilized by regenerated cellulose. Food Hydrocoll 91:232–237
Jones OG, McClements DJ (2010) Functional biopolymer particles: design, fabrication, and applications. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 9:374–397
Karri VVSR, Raman SK, Kuppusamy G, Sanapalli BKR, Wadhwani A, Patel V, Malayandi R (2018) In vitro antifungal activity of a novel allylamine antifungal nanoemulsion gel. J Nanosci: Curr Res 3:1
Kruif CGD, Anema SG, Zhu C, Havea P, Coker C (2015) Water holding capacity and swelling of casein hydrogels. Food Hydrocoll 44:372–379
Kurt Ş, Ceylan HG (2018) Effects of flaxseed and pH on the emulsion properties of beef by using a model system. Turkish J Agr - Food Sci Technol 6:78–83
Kwan A, Davidov-Pardo G (2018) Controlled release of flavor oil nanoemulsions encapsulated in filled soluble hydrogels. Food Chem 250:46–53
Lamprecht A, Schafer U, Lehr CM (2001) Influences of process parameters on preparation of microparticle used as a carrier system for omega - 3 unsaturated fatty acid ethyl esters used in supplementary nutrition. J Microencapsul 18:347–357
Lee HA, Choi SJ, Moon TW (2006) Characteristics of sodium caseinate and soy protein isolate-stabilized emulsion-gels formed by microbial transglutaminase. J Food Sci 71:352–357
Leon AM, Medina WT, Park DJ, Aguilera JM (2018) Properties of microparticles from a whey protein isolate/alginate emulsion gel. Food Sci Technol Int 24:414–423
Li F, Kong X, Zhang C, Hua Y (2012) Gelation behavior and rheological properties of acid-induced soy protein-stabilized emulsion gels. Food Hydrocoll 29:347–355
Li H, Zhao L, Chen XD, Mercadéprieto R (2016) Swelling of whey and egg white protein hydrogels with stranded and particulate microstructures. Int J Biol Macromol 83:152–159
Liang L, Leung Sok Line V, Remondetto GE, Subirade M (2010) In vitro release of α-tocopherol from emulsion-loaded β-lactoglobulin gels. Int Dairy J 20:176–181
Liu F, Li R, Mao L, Gao Y (2018) Ethanol-induced composite hydrogel based on propylene glycol alginate and zein: formation, characterization and application. Food Chem 255:390–398
Lopes NA, Pinilla CMB, Brandelli A (2017) Pectin and polygalacturonic acid-coated liposomes as novel delivery system for nisin: preparation, characterization and release behavior. Food Hydrocoll 70:1–7
Lu Y, Qiu D, Cui M, Gao Y, Mao L (2018) Study on the effect of thermal treatment on the microstructures of emulsion gels and stability of different vitamins during storage. Food Sci, in press
Luo N, Ye A, Wolber F, Singh H (2019) Structure of whey protein emulsion gels containing capsaicinoids: impact on in-mouth breakdown behaviour and sensory perception. Food Hydrocoll 92:19–29
Luo Q, Borst JW, Westphal AH, Boom RM, Janssen AEM (2017) Pepsin diffusivity in whey protein gels and its effect on gastric digestion. Food Hydrocoll 66:318–325
Lupi FR, Gabriele D, Seta L, Baldino N, Cindio BD, Marino R (2015) Rheological investigation of pectin-based emulsion gels for pharmaceutical and cosmetic uses. Rheol Acta 54:41–52
Maldonado-Valderrama J, Wilde P, Macierzanka A, Mackie A (2011) The role of bile salts in digestion. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 165:36–46
Malone ME, Appelqvist IAM (2003) Gelled emulsion particles for the controlled release of lipophilic volatiles during eating. J Control Release 90:227–241
Maltais A, Remondetto GE, Subirade M (2010) Tableted soy protein cold-set hydrogels as carriers of nutraceutical substances. Food Hydrocoll 24:518–524
Mantovani RA, Cavallieri ALZ, Cunha RL (2016) Gelation of oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by whey protein. J Food Eng 175:108–116
Mao L, Miao S, Yuan F, Gao Y (2018) Study on the textural and volatile characteristics of emulsion filled protein gels as influenced by different fat substitutes. Food Res Int 103:1–7
Mao L, Roos YH, Miao S (2014) Study on the rheological properties and volatile release of cold-set emulsion-filled protein gels. J Agric Food Chem 62:11420–11428
Mao L, Roos YH, Biliaderis CG, Miao S (2017) Food emulsions as delivery systems for flavor compounds: a review. Crit Rev Food Sci 57:3173–3187
Matalanis A, Jones OG, McClements DJ (2011) Structured biopolymer-based delivery systems for encapsulation, protection, and release of lipophilic compounds. Food Hydrocoll 25:1865–1880
McClements DJ (2010) Emulsion design to improve the delivery of functional lipophilic components. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol 1:241–269
McClements DJ, Li Y (2010) Structured emulsion-based delivery systems: controlling the digestion and release of lipophilic food components. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 159:213–228
Mokhtari S, Jarafi SM, Assadpour E (2017) Development of a nutraceutical nano-delivery system through emulsification/internal gelation of alginate. Food Chem 229:286–295
Moschakis T, Panagiotopoulou E, Katsanidis E (2016) Sunflower oil organogels and organogel-in-water emulsions (part I): microstructure and mechanical properties. LWT Food Sci Technol 73:153–161
Mun S, Kim YR, McClements DJ (2015) Control of beta-carotene bioaccessibility using starch-based filled hydrogels. Food Chem 173:454–461
Mun S, Kim YR, Shin M, McClements DJ (2015) Control of lipid digestion and nutraceutical bioaccessibility using starch-based filled hydrogels: influence of starch and surfactant type. Food Hydrocoll 44:380–389
Mun S, Park S, Kim YR, McClements DJ (2016) Influence of methylcellulose on attributes of β-carotene fortified starch-based filled hydrogels: optical, rheological, structural, digestibility, and bioaccessibility properties. Food Res Int 87:18–24
Najet M, Soraya M, Taco N, Dominique DA, Riaublanc A (2007) Light-scattering study of the structure of aggregates and gels formed by heat-denatured whey protein isolate and β-lactoglobulin at neutral pH. J Agric Food Chem 55:3104–3111
Nourbehesht N, Shekarchizadeh H, Soltanizadeh N (2018) Investigation of stability, consistency, and oil oxidation of emulsion filled gel prepared by inulin and rice bran oil using ultrasonic radiation. Ultrason Sonochem 42:585–593
Nyemb K, Guérin-Dubiard C, Dupont D, Jardin J, Rutherfurd SM, Nau F (2014) The extent of ovalbumin in vitro digestion and the nature of generated peptides are modulated by the morphology of protein aggregates. Food Chem 157:429–438
Nyemb K, Guérin-Dubiard C, Pézennec S, Jardin J, Briard-Bion V, Cauty C, Rutherfurd SM, Dupont D, Nau F (2016) The structural properties of egg white gels impact the extent of in vitro protein digestion and the nature of peptides generated. Food Hydrocoll 54:315–327
O’Sullivan CM, Barbut S, Marangoni A (2016) Edible oleogels for the oral delivery of lipid soluble molecules: composition and structural design considerations. Trends Food Sci Technol 57:59–73
Okada KS, Lee Y (2017) Characterization of sodium mobility and binding by (23) Na NMR spectroscopy in a model lipoproteic emulsion gel for sodium reduction. J Food Sci 82:1563–1568
Öztürk B (2017) Nanoemulsions for food fortification with lipophilic vitamins: production challenges, stability, and bioavailability. Eur J Lipid Sci Technol 119:1500539
Paglarini CS, Furtado GF, Biachi JP (2018) Functional emulsion gels with potential application in meat products. J Food Eng 222:29–37
Pandey S, Senthilguru K, Uvanesh K, Sagiri SS, Behera B, Babu N, Bhattacharyya MK, Pal K, Banerjee I (2016) Natural gum modified emulsion gel as single carrier for the oral delivery of probiotic-drug combination. Int J Biol Macromol 92:504–514
Picone CSF, Bueno AC, Michelon M, Cunha RL (2017) Development of a probiotic delivery system based on gelation of water-in-oil emulsions. LWT Food Sci Technol 86:62–68
Qin XS, Zhao YY, Jiang ST, Luo ZG (2017) Colloidal and interfacial characteristics of transglutaminase-set soy protein isolate and wheat gluten mixture emulsion gels with ultrasound pretreatment: influence of the oil fraction. Food Hydrocolloid in press
Remondetto GE, Paquin P, Subirade M (2010) Cold gelation of beta-lactoglobulin in the presence of iron. J Food Sci 67:586–595
Ruffin E, Schmit T, Lafitte G, Dollat JM, Chambin O (2014) The impact of whey protein preheating on the properties of emulsion gel bead. Food Chem 151:324–332
Sala G, Vliet TV, Stuart MC, Velde FVD, Aken GAV (2009) Deformation and fracture of emulsion-filled gels: effect of gelling agent concentration and oil droplet size. Food Hydrocoll 23:1853–1863
Sarkar A, Juan JM, Kolodziejczyk E, Acquistapace S, Donatocapel L, Wooster TJ (2015) Impact of protein gel porosity on the digestion of lipid emulsions. J Agric Food Chem 63:8829–8837
Shakeel A, Lupi FR, Gabriele D, Baldino N, de Cindio B (2018) Bigels: a unique class of materials for drug delivery applications. Soft Mater 16:77–93
Shao P, Zhang H, Niu B, Jin W (2018) Physical stabilities of taro starch nanoparticles stabilized Pickering emulsions and the potential application of encapsulated tea polyphenols. Int J Biol Macromol 118:2032–2039
Shishir MRI, Xie L, Sun C, Zheng X, Chen W (2018) Advances in micro and nano-encapsulation of bioactive compounds using biopolymer and lipid-based transporters. Trends Food Sci Technol 78:34–60
Singh H, Ye A (2013) Structural and biochemical factors affecting the digestion of protein-stabilized emulsions. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 18:360–370
Sok Line VL, Remondetto GE, Subirade M (2005) Cold gelation of β-lactoglobulin oil-in-water emulsions. Food Hydrocoll 19:269–278
Soltani S, Madadlou A (2015) Gelation characteristics of the sugar beet pectin solution charged with fish oil-loaded zein nanoparticles. Food Hydrocoll 43:664–669
Tang C-H, Chen L, Foegeding EA (2011) Mechanical and water-holding properties and microstructures of soy protein isolate emulsion gels induced by CaCl2, glucono-delta-lactone (GDL), and transglutaminase: influence of thermal treatments before and/or after emulsification. J Agric Food Chem 59:4071–4077
Tang C-H, Luo L-J, Liu F, Chen Z (2013) Transglutaminase-set soy globulin-stabilized emulsion gels: influence of soy β-conglycinin/glycinin ratio on properties, microstructure and gelling mechanism. Food Res Int 51:804–812
Torchilin VP (2007) Micellar nanocarriers: pharmaceutical perspectives. Pharm Res 24:1–16
Torres O, Murray B, Sarkar A (2016) Emulsion microgel particles: novel encapsulation strategy for lipophilic molecules. Trends Food Sci Technol 55:98–108
Torres O, Tena NM, Murray B, Sarkar A (2017) Novel starch based emulsion gels and emulsion microgel particles: design, structure and rheology. Carbohydr Polym 178:86–94
Van de Velde F, de Hoog EH, Oosterveld A, Tromp RH (2015) Protein-polysaccharide interactions to alter texture. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol 6:371–388
Vélez MA, Perotti MC, Hynes ER, Gennaro AM (2019) Effect of lyophilization on food grade liposomes loaded with conjugated linoleic acid. J Food Eng 240:199–206
Velikov KP (2012) Colloidal emulsions and particles as micronutrient and nutraceutical delivery systems. Encapsulation Technologies and Delivery Systems for Food Ingredients and Nutraceuticals 319–391
Wan Z, Sun Y, Ma L, Yang X, Guo J, Yin S (2017) Responsive emulsion gels with tunable properties formed by self-assembled nanofibrils of natural saponin glycyrrhizic acid for oil structuring. J Agric Food Chem 65:2394–2405
Wang T, Bae M, Lee JY, Luo Y (2018) Solid lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles prepared with natural biomaterials: a new platform for oral delivery of lipophilic bioactives. Food Hydrocoll 84:581–592
Wang X, He Z, Zeng M, Qin F, Adhikari B, Chen J (2017) Effects of the size and content of protein aggregates on the rheological and structural properties of soy protein isolate emulsion gels induced by CaSO4. Food Chem 221:130–138
Wang X, Luo K, Liu S, Zeng M, Adhikari B, He Z, Chen J (2018) Textural and rheological properties of soy protein isolate tofu-type emulsion gels: influence of soybean variety and coagulant type. Food Biophys 13:324–332
Wang X, Zeng M, Qin F, Adhikari B, He Z, Chen J (2018) Enhanced CaSO4-induced gelation properties of soy protein isolate emulsion by pre-aggregation. Food Chem 242:459–465
Wijaya W, Patel AR, Setiowati AD, Meeren PVD (2017) Functional colloids from proteins and polysaccharides for food applications. Trends Food Sci Technol 68:376
Williams PA, Phillips GO, Matiamerino L, Dickinson E (2004) In: Phillips GO, Williams PA (ed) Gums and stabilisers for the food industry. Royal Society of Chemistry, London
Wu C, Navicha WB, Hua Y, Chen Y, Kong X, Zhang C (2018) Effects of removal of non-network protein on the rheological properties of heat-induced soy protein gels. LWT Food Sci Technol 95:193–199
Xianquan S, Shi J, Kakuda Y, Yueming J (2005) Stability of lycopene during food processing and storage. J Med Food 8:413–422
Xiao J, Shi C, Li Y, Pan Y, Huang Q (2017) Pickering emulsions immobilized within hydrogel matrix with enhanced resistance against harsh processing conditions and sequential digestion. Food Hydrocoll 62:35–42
Zhang Z, Zhang R, Zou L, McClements DJ (2016) Tailoring lipid digestion profiles using combined delivery systems: mixtures of nanoemulsions and filled hydrogel beads. RSC Adv 6:631–656
Zhang Z, Zhang R, Zou L, Chen L, Ahmed Y, Bishri WA, Balamash K, McClements DJ (2016) Encapsulation of curcumin in polysaccharide-based hydrogel beads: impact of bead type on lipid digestion and curcumin bioaccessibility. Food Hydrocoll 58:160–170
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31701648).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, Y., Mao, L., Hou, Z. et al. Development of Emulsion Gels for the Delivery of Functional Food Ingredients: from Structure to Functionality. Food Eng Rev 11, 245–258 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12393-019-09194-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12393-019-09194-z