Abstract
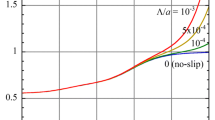
General expressions of the electrophoretic mobility-zeta potential relationship for a cylindrical colloidal particle with a hydrodynamically slipping surface in an aqueous electrolyte solution under a transverse or tangential electric field are obtained on the basis of the Navier boundary condition. Approximate expressions for the electrophoretic mobility of cylindrical particles carrying a low zeta potential are derived. As in the case of a sphere, the electrophoretic mobility of a cylinder increases with increasing slip length, which characterizes the hydrophobicity of the particle surface.

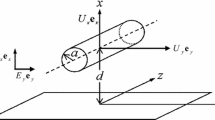
Electrophoretic mobility of a cylinder with a slip surface in a transverse electric filed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Derjaguin BV, Landau DL (1941) Theory of the stability of strongly charged lyophobic sols and of the adhesion of strongly charged particles in solutions of electrolytes. Acta Physicochim USSR 14:633–662
Verwey EJW, Overbeek JTG (1948) Theory of the stability of lyophobic colloids. Elsevier/Academic Press, Amsterdam
von Smoluchowski M (1921) Elektrische endosmose und strömungsströme. In: Greatz E (ed) Handbuch der Elektrizität und des Magnetismus, Band II Stationäre ströme. Barth, Leipzig, pp 366–428
Hückel E (1924) Die Kataphorese der Kugel. Phys Z 25:204–210
Henry DC (1931) The cataphoresis of suspended particles. Part I. The equation of cataphoresis. Proc Roy Soc London Ser A 133:106–129
Abramson HA, Gorin MH, Moyer LS (1939) The polar groups of protein and amino acid surfaces in liquids. Chem Rev 24:345–366
Overbeek JTG (1943) Theorie der Elektrophorese. Kolloid-Beihefte 54:287–364
Booth F (1950) The cataphoresis of spherical, solid non-conducting particles in a symmetrical electrolyte. Proc Roy Soc London Ser A 203:514–533
Wiersema PH, Loeb AL, Overbeek JTG (1966) Calculation of the electrtophoretic mobility of a spherical colloid particle. J Colloid Interface Sci 22:78–99
Dukhin SS, Semenikhin NM (1970) Theory of double layer polarization and its influence on the electrokinetic and electrooptical phenomena and the dielectric permeability of disperse systems. Calculation of the electrophoretic and diffusiophoretic mobility of solid spherical particles. Kolloid Zh 32:360–368
Dukhin SS, Derjaguin BV (1974) Nonequilibrium double layer and electrokinetic phenomena. In: Matievic E (ed) Surface and colloid science, vol 2. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, pp 273–336
de Keizer A, van der Drift WPJT, Overbeek JTG (1975) Electrophoresis of randomly oriented cylindrical particles. Biophys Chem 3:107–108
O’Brien RW, White LR (1978) Electrophoretic mobility of a spherical colloidal particle. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans II 74:1607–1626
Stigter D (1978) Electrophoresis of highly charged colloidal cylinders in univalent salt solutions. 1. Mobility in transverse field. J Phys Chem 82:1417–1423
Stigter D (1978) Electrophoresis of highly charged colloidal cylinders in univalent salt solutions. 2. Random orientation in external field and application to polyelectrolytes. J Phys Chem 82:1424–1429
van der Drift WPJT, de Keizer A, Overbeek JTG (1979) Electrophoretic mobility of a cylinder with high surface charge density. J Colloid Interface Sci 71:67–78
Hunter RJ (1981) Zeta Potential in Colloid Science. Academic Press, New York
Sherwood JD (1982) Electrophoresis of rods. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans II 78:1091–1100
Van de Ven TGM (1989) Colloid hydrodynamics. Academic Press, New York
Hunter RJ (1989) Foundations of colloid science, vol 2. Oxford University Press, London/New York
Dukhin SS (1993) Non-equilibrium electric surface phenomena. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 44:1–134
Ohshima H (1994) A simple expression for Henry’s function for the retardation effect in electrophoresis of spherical colloidal particles. J Colloid Interface Sci 168:269–271
Lyklema J (1995) Fundamentals of interface and colloid science, solid-liquid interfaces, vol 2. Academic Press, New York
Ohshima H (1996) Henry’s function for electrophoresis of a cylindrical colloidal particle. J Colloid Interface Sci 180:299–301
Delgado AV (ed) (2000) Electrokinetics and electrophoresis. Dekker, New York
Dukhin AS, Goetz PJ (2002) Ultrasound for characterizing colloids: particle sizing, zeta potential, rheology. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Spasic A, Hsu J-P (eds) (2005) Finely dispersed particles. Micro-. Nano-, Atto-Engineering, CRC Press, Boca Raton
Masliyah JH, Bhattacharjee S (2006) Electrokinetic and colloid transport phenomena. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken
Ohshima H (2006) Theory of colloid and interfacial electric phenomena. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Ohshima H (2010) Biophysical chemistry of biointerfaces. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken
Ohshima H (2014) Approximate analytic expression for the electrophoretic mobility of a cylindrical colloidal particle. Relaxation effect. Colloid Polym Sci 292:1227–1233
Ohshima H (2015) Approximate analytic expression for the electrophoretic mobility of moderately charged cylindrical colloidal particles. Langmuir 31:13633–13638
Lamb H. Hydrodynamics, Cambridge University Press; 1975
Khair AS, Squires TM (2009) The influence of hydrodynamic slip on the electrophoretic mobility of a spherical colloidal particle. Phys Fluids 21:042001
Park HM (2013) Electrophoresis of particles with Navier velocity slip. Electrophoresis 34:651–661
Bhattacharyya S, Majee PS (2017) Electrophoresis of a polarizable charged colloid with hydrophobic surface: a numerical study. Phys Rev E 95:042605
Gopmandal PP, Bhattacharyya S, Ohshima H (2017) On the similarity between the electrophoresis of a liquid drop and a spherical hydrophobic particle. Colloid Polym Sci 295:2077–2082
Kumar B, Gopmandal PP, Sinha RK, Ohshima H (2019) Electrophoresis of hydrophilic/hydrophobic rigid colloid with effects of relaxation and ion size. Electrophoresis 40:1282–1292
Ohshima H (2019) Electrokinetic phenomena in a dilute suspension of spherical solid colloidal particles with a hydrodynamically slipping surface in an aqueous electrolyte solution. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 272:101996
Acknowledgments
I thank Dr. Partha P. Gopmandal of National Institute of Technology Durgapru and Prof. Somnath Bhattacharyya of Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur for introducing me in the field of electrokinetics of a colloidal particle with a slip surface.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohshima, H. Electrophoretic mobility of a cylindrical colloidal particle with a slip surface. Colloid Polym Sci 298, 151–156 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-019-04586-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-019-04586-3