Abstract
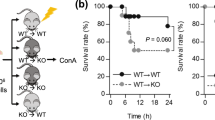
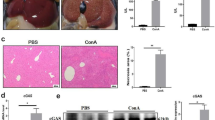
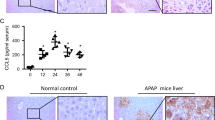
Fulminant hepatitis is a serious inflammatory condition of the liver characterized by massive necrosis of liver parenchyma following excessive immune cell infiltration into the liver, and possibly causing sudden hepatic failure and medical emergency. However, the underlying mechanisms are not fully understood. Here, we investigated the role of cyclic AMP-responsive element-binding protein, hepatocyte specific (CREBH) in concanavalin A (ConA)-driven hepatitis-evoked liver injury. C57BL/6J (WT) and Crebh knockout (KO) mice injected with ConA (7.5 or 25 mg/kg) and bone marrow (BM) chimeric mice, generated by injection of BM cells into sub-lethally irradiated recipients followed by ConA injection (22.5 or 27.5 mg/kg) 8 weeks later, were used for in vivo study. Primary mouse hepatocytes and HEK293T cells were used for a comparative in vitro study. Crebh KO mice are highly susceptible to ConA-induced liver injury and prone to death due to increased neutrophil infiltration driven by enhanced hepatic expression of neutrophil-attracting chemokines. Notably, BM chimera experiment demonstrated that Crebh-deficient hepatocytes have an enhanced ability of recruiting neutrophils to the liver, thereby promoting hepatotoxicity by ConA. Intriguingly, in vitro assays showed that p65, a subunit of NF-κB and common transcription factor for various chemokines, dependent transactivation was inhibited by CREBH. Furthermore, p65 expression was inversely correlated with CREBH level in ConA-treated mice liver and TNFα-stimulated primary mouse hepatocytes. This is the first demonstration that CREBH deficiency aggravates inflammatory liver injury following chemokine-dependent neutrophil infiltration via NF-κB p65 upregulation. CREBH is suggested to be a novel therapeutic target for treatment of fulminant hepatitis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams DH, Ju C, Ramaiah SK, Uetrecht J, Jaeschke H (2010) Mechanisms of immune-mediated liver injury. Toxicol Sci 115:307–321
Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O (2006) Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 124:783–801
Baggiolini M, Loetscher P (2000) Chemokines in inflammation and immunity. Immunol Today 21:418–420
Bajrami B, Zhu H, Kwak HJ, Mondal S, Hou Q, Geng G, Karatepe K, Zhang YC, Nombela-Arrieta C, Park SY et al (2016) G-CSF maintains controlled neutrophil mobilization during acute inflammation by negatively regulating CXCR2 signaling. J Exp Med 213:1999–2018
Balamayooran G, Batra S, Balamayooran T, Cai S, Jeyaseelan S (2011) Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 regulates pulmonary host defense via neutrophil recruitment during Escherichia coli infection. Infect Immun 79:2567–2577
Bernal W, Auzinger G, Dhawan A, Wendon J (2010) Acute liver failure. Lancet 376:190–201
Bonder CS, Ajuebor MN, Zbytnuik LD, Kubes P, Swain MG (2004) Essential role for neutrophil recruitment to the liver in concanavalin A-induced hepatitis. J Immunol 172:45–53
Chensue SW (2001) Molecular machinations: chemokine signals in host-pathogen interactions. Clin Microbiol Rev 14:821–835 (table of contents)
De Filippo K, Dudeck A, Hasenberg M, Nye E, van Rooijen N, Hartmann K, Gunzer M, Roers A, Hogg N (2013) Mast cell and macrophage chemokines CXCL1/CXCL2 control the early stage of neutrophil recruitment during tissue inflammation. Blood 121:4930–4937
De Plaen IG, Han XB, Liu X, Hsueh W, Ghosh S, May MJ (2006) Lipopolysaccharide induces CXCL2/macrophage inflammatory protein-2 gene expression in enterocytes via NF-kappaB activation: independence from endogenous TNF-alpha and platelet-activating factor. Immunology 118:153–163
Dienes HP, Hutteroth T, Hess G, Meuer SC (1987) Immunoelectron microscopic observations on the inflammatory infiltrates and HLA antigens in hepatitis B and non-A, non-B. Hepatology 7:1317–1325
Dominici S, Visvikis A, Pieri L, Paolicchi A, Valentini MA, Comporti M, Pompella A (2003) Redox modulation of NF-kappaB nuclear translocation and DNA binding in metastatic melanoma. The role of endogenous and gamma-glutamyl transferase-dependent oxidative stress. Tumori 89:426–433
Feng G, Ohmori Y, Chang PL (2006) Production of chemokine CXCL1/KC by okadaic acid through the nuclear factor-kappaB pathway. Carcinogenesis 27:43–52
Futosi K, Fodor S, Mocsai A (2013) Neutrophil cell surface receptors and their intracellular signal transduction pathways. Int Immunopharmacol 17:638–650
Gadjeva M, Tomczak MF, Zhang M, Wang YY, Dull K, Rogers AB, Erdman SE, Fox JG, Carroll M, Horwitz BH (2004) A role for NF-kappa B subunits p50 and p65 in the inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced shock. J Immunol 173:5786–5793
Gentile CL, Wang D, Pfaffenbach KT, Cox R, Wei Y, Pagliassotti MJ (2010) Fatty acids regulate CREBh via transcriptional mechanisms that are dependent on proteasome activity and insulin. Mol Cell Biochem 344:99–107
Jiang X, Takahashi N, Ando K, Otsuka T, Tetsuka T, Okamoto T (2003) NF-kappa B p65 transactivation domain is involved in the NF-kappa B-inducing kinase pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 301:583–590
Ke B, Zhao Z, Ye X, Gao Z, Manganiello V, Wu B, Ye J (2015) Inactivation of NF-kappaB p65 (RelA) in liver improves insulin sensitivity and inhibits cAMP/PKA pathway. Diabetes 64:3355–3362
Kim YH, Hwang JH, Kim KS, Noh JR, Choi DH, Kim DK, Tadi S, Yim YH, Choi HS, Lee CH (2015) Metformin ameliorates acetaminophen hepatotoxicity via Gadd45beta-dependent regulation of JNK signaling in mice. J Hepatol 63:75–82
Klein C, Wustefeld T, Heinrich PC, Streetz KL, Manns MP, Trautwein C (2003) ME3738 protects from concanavalin A-induced liver failure via an IL-6-dependent mechanism. Eur J Immunol 33:2251–2261
Knolle PA, Gerken G, Loser E, Dienes HP, Gantner F, Tiegs G, Meyer zum Buschenfelde KH, Lohse AW (1996) Role of sinusoidal endothelial cells of the liver in concanavalin A-induced hepatic injury in mice. Hepatology 24:824–829
Kolios G, Valatas V, Kouroumalis E (2006) Role of Kupffer cells in the pathogenesis of liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 12:7413–7420
Kremer M, Perry AW, Milton RJ, Rippe RA, Wheeler MD, Hines IN (2008) Pivotal role of Smad3 in a mouse model of T cell-mediated hepatitis. Hepatology 47:113–126
Lawrence T, Fong C (2010) The resolution of inflammation: anti-inflammatory roles for NF-kappaB. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 42:519–523
Lee JH, Giannikopoulos P, Duncan SA, Wang J, Johansen CT, Brown JD, Plutzky J, Hegele RA, Glimcher LH, Lee AH (2011) The transcription factor cyclic AMP-responsive element-binding protein H regulates triglyceride metabolism. Nat Med 17:812–815
Liu T, Zhang L, Joo D, Sun SC (2017) NF-kappaB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2:17023
Louis H, Le Moine O, Peny MO, Quertinmont E, Fokan D, Goldman M, Deviere J (1997) Production and role of interleukin-10 in concanavalin A-induced hepatitis in mice. Hepatology 25:1382–1389
Marra F, Tacke F (2014) Roles for chemokines in liver disease. Gastroenterology 147(577–594):e571
Martin T, Cardarelli PM, Parry GC, Felts KA, Cobb RR (1997) Cytokine induction of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 gene expression in human endothelial cells depends on the cooperative action of NF-kappa B and AP-1. Eur J Immunol 27:1091–1097
Misra J, Chanda D, Kim DK, Li T, Koo SH, Back SH, Chiang JY, Choi HS (2011) Curcumin differentially regulates endoplasmic reticulum stress through transcriptional corepressor SMILE (small heterodimer partner-interacting leucine zipper protein)-mediated inhibition of CREBH (cAMP responsive element-binding protein H). J Biol Chem 286:41972–41984
Mizuhara H, O'Neill E, Seki N, Ogawa T, Kusunoki C, Otsuka K, Satoh S, Niwa M, Senoh H, Fujiwara H (1994) T cell activation-associated hepatic injury: mediation by tumor necrosis factors and protection by interleukin 6. J Exp Med 179:1529–1537
Mulligan MS, Lentsch AB, Miyasaka M, Ward PA (1998) Cytokine and adhesion molecule requirements for neutrophil recruitment during glycogen-induced peritonitis. Inflamm Res 47:251–255
Nakagawa Y, Shimano H (2018) CREBH regulates systemic glucose and lipid metabolism. Int J Mol Sci 19:E1396
Noh JR, Kim YH, Kim DK, Hwang JH, Kim KS, Choi DH, Lee SJ, Lee HG, Lee TG, Weng HL et al (2018a) Small heterodimer partner deficiency increases inflammatory liver injury through C–X–C motif chemokine ligand 2-driven neutrophil recruitment in mice. Toxicol Sci 163:254–264
Noh JR, Kim YH, Kim DK, Hwang JH, Kim KS, Choi DH, Lee SJ, Lee HG, Lee TG, Weng HL et al (2018b) Small heterodimer partner negatively regulates C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 2 in hepatocytes during liver inflammation. Sci Rep 8:15222
Ottonello L, Montecucco F, Bertolotto M, Arduino N, Mancini M, Corcione A, Pistoia V, Dallegri F (2005) CCL3 (MIP-1alpha) induces in vitro migration of GM-CSF-primed human neutrophils via CCR5-dependent activation of ERK 1/2. Cell Signal 17:355–363
Penido C, Vieira-de-Abreu A, Bozza MT, Castro-Faria-Neto HC, Bozza PT (2003) Role of monocyte chemotactic protein-1/CC chemokine ligand 2 on gamma delta T lymphocyte trafficking during inflammation induced by lipopolysaccharide or Mycobacterium bovis bacille Calmette-Guerin. J Immunol 171:6788–6794
Reichel CA, Rehberg M, Lerchenberger M, Berberich N, Bihari P, Khandoga AG, Zahler S, Krombach F (2009) Ccl2 and Ccl3 mediate neutrophil recruitment via induction of protein synthesis and generation of lipid mediators. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 29:1787–1793
Rezzonico R, Imbert V, Chicheportiche R, Dayer JM (2001) Ligation of CD11b and CD11c beta(2) integrins by antibodies or soluble CD23 induces macrophage inflammatory protein 1alpha (MIP-1alpha) and MIP-1beta production in primary human monocytes through a pathway dependent on nuclear factor-kappaB. Blood 97:2932–2940
Richmond A (2002) Nf-kappa B, chemokine gene transcription and tumour growth. Nat Rev Immunol 2:664–674
Schreck R, Baeuerle PA (1990) NF-kappa B as inducible transcriptional activator of the granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor gene. Mol Cell Biol 10:1281–1286
Semerad CL, Liu F, Gregory AD, Stumpf K, Link DC (2002) G-CSF is an essential regulator of neutrophil trafficking from the bone marrow to the blood. Immunity 17:413–423
Smith JA (1994) Neutrophils, host defense, and inflammation: a double-edged sword. J Leukoc Biol 56:672–686
Sun SC, Chang JH, Jin J (2013) Regulation of nuclear factor-kappaB in autoimmunity. Trends Immunol 34:282–289
Tagawa Y, Matthys P, Heremans H, Dillen C, Zaman Z, Iwakura Y, Billiau A (2000) Bimodal role of endogenous interleukin-6 in concanavalin A-induced hepatitis in mice. J Leukoc Biol 67:90–96
Tiegs G, Hentschel J, Wendel A (1992) A T cell-dependent experimental liver injury in mice inducible by concanavalin A. J Clin Investig 90:196–203
Wang HX, Liu M, Weng SY, Li JJ, Xie C, He HL, Guan W, Yuan YS, Gao J (2012) Immune mechanisms of concanavalin A model of autoimmune hepatitis. World J Gastroenterol 18:119–125
Wu Z, Han M, Chen T, Yan W, Ning Q (2010) Acute liver failure: mechanisms of immune-mediated liver injury. Liver Int 30:782–794
Xu R, Huang H, Zhang Z, Wang FS (2014) The role of neutrophils in the development of liver diseases. Cell Mol Immunol 11:224–231
Xu C, Zhang C, Ji J, Wang C, Yang J, Geng B, Zhao T, Zhou H, Mu X, Pan J et al (2018) CD36 deficiency attenuates immune-mediated hepatitis in mice by modulating the proapoptotic effects of CXC chemokine ligand 10. Hepatology 67:1943–1955
Xue ML, Thakur A, Cole N, Lloyd A, Stapleton F, Wakefield D, Willcox MD (2007) A critical role for CCL2 and CCL3 chemokines in the regulation of polymorphonuclear neutrophils recruitment during corneal infection in mice. Immunol Cell Biol 85:525–531
Ye X, Jiang X, Guo W, Clark K, Gao Z (2013) Overexpression of NF-kappaB p65 in macrophages ameliorates atherosclerosis in apoE-knockout mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 305:E1375–1383
Ye T, Wang T, Yang X, Fan X, Wen M, Shen Y, Xi X, Men R, Yang L (2018) Comparison of concanavalin a-induced murine autoimmune hepatitis models. Cell Physiol Biochem 46:1241–1251
Zhang C, Wang G, Zheng Z, Maddipati KR, Zhang X, Dyson G, Williams P, Duncan SA, Kaufman RJ, Zhang K (2012) Endoplasmic reticulum-tethered transcription factor cAMP responsive element-binding protein, hepatocyte specific, regulates hepatic lipogenesis, fatty acid oxidation, and lipolysis upon metabolic stress in mice. Hepatology 55:1070–1082
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the KRIBB Research Initiative Program of the Republic of Korea, by the Development of Platform Technology for Innovative Medical Measurements Program (No. KRISS-2019-GP2019-0013) from the Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science and by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) and the Korean government (MSIP) (NRF-2019R1C1C1005319).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JRN, JHK, YHK and CHL designed the study, and drafted the manuscript. JRN, JHK, SYN, IBL, YJS, JHC, YS and YHK performed experiments, and collected and analyzed data for the study. TGL, HSC and CHL contributed to critical revisions of the text.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All animal experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the KRIBB.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noh, JR., Kim, JH., Na, SY. et al. Hepatocyte CREBH deficiency aggravates inflammatory liver injury following chemokine-dependent neutrophil infiltration through upregulation of NF-κB p65 in mice. Arch Toxicol 94, 509–522 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-019-02633-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-019-02633-0