Abstract
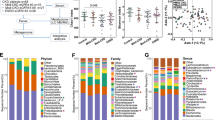
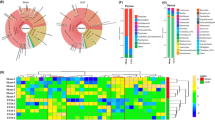
Dysbiosis of the gut microbiome and related metabolites in chronic kidney disease (CKD) have been intimately associated with the prevalence of cardiovascular diseases. Unfortunately, thus far, there is a paucity of sufficient knowledge of gut microbiome and related metabolites on CKD progression partly due to the severely limited investigations. Using a 5/6 nephrectomized (NX) rat model, we carried out 16S rRNA sequence and untargeted metabolomic analyses to explore the relationship between colon’s microbiota and serum metabolites. Marked decline in microbial diversity and richness was accompanied by significant changes in 291 serum metabolites, which were mediated by altered enzymatic activities and dysregulations of lipids, amino acids, bile acids and polyamines metabolisms. Interestingly, CCr was directly associated with some microbial genera and polyamine metabolism. However, SBP was directly related to certain microbial genera and glycine-conjugated metabolites in CKD rats. Administration of poricoic acid A (PAA) and Poria cocos (PC) ameliorated microbial dysbiosis as well as attenuated hypertension and renal fibrosis. In addition, treatments with PAA and PC lowered serum levels of microbial-derived products including glycine-conjugated compounds and polyamine metabolites. Collectively, the present study confirmed the CKD-associated gut microbial dysbiosis and identified a novel dietary and therapeutic strategy to improve the gut microbial dysbiosis and the associated metabolomic disorders and retarded the progression of kidney disease in the rat model of CKD.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Webster AC, Nagler EV, Morton RL, Masson P (2017) Chronic kidney disease. Lancet 389:1238–1252
Schmidt M, Mansfield KE, Bhaskaran K, Nitsch D, Sorensen HT, Smeeth L, Tomlinson LA (2017) Serum creatinine elevation after renin-angiotensin system blockade and long term cardiorenal risks: cohort study. BMJ 356:j791
Pickard JM, Zeng MY, Caruso R, Nunez G (2017) Gut microbiota: role in pathogen colonization, immune responses, and inflammatory disease. Immunol Rev 279:70–89
Schroeder BO, Backhed F (2016) Signals from the gut microbiota to distant organs in physiology and disease. Nat Med 22:1079–1089
Rooks MG, Garrett WS (2016) Gut microbiota, metabolites and host immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 16:341–352
Vaziri ND, Zhao YY, Pahl MV (2016) Altered intestinal microbial flora and impaired epithelial barrier structure and function in CKD: the nature, mechanisms, consequences and potential treatment. Nephrol Dial Transplant 31:737–746
Coppo R (2018) The gut-kidney axis in IgA nephropathy: role of microbiota and diet on genetic predisposition. Pediatr Nephrol 33:53–61
Chen YY, Chen DQ, Chen L, Liu JR, Vaziri ND, Guo Y, Zhao YY (2019) Microbiome-metabolome reveals the contribution of gut-kidney axis on kidney disease. J Transl Med 17:5
Vaziri ND, Wong J, Pahl M, Piceno YM, Yuan J, DeSantis TZ, Ni Z, Nguyen TH, Andersen GL (2013) Chronic kidney disease alters intestinal microbial flora. Kidney Int 83:308–315
Simoes-Silva L, Araujo R, Pestana M, Soares-Silva I, Sampaio-Maia B (2018) The microbiome in chronic kidney disease patients undergoing hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. Pharmacol Res 130:143–151
Anders HJ, Andersen K, Stecher B (2013) The intestinal microbiota, a leaky gut, and abnormal immunity in kidney disease. Kidney Int 83:1010–1016
Vaziri ND (2012) CKD impairs barrier function and alters microbial flora of the intestine: a major link to inflammation and uremic toxicity. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 21:587–592
Rossi M, Campbell KL, Johnson DW, Stanton T, Vesey DA, Coombes JS, Weston KS, Hawley CM, McWhinney BC, Ungerer JP, Isbel N (2014) Protein-bound uremic toxins, inflammation and oxidative stress: a cross-sectional study in stage 3-4 chronic kidney disease. Arch Med Res 45:309–317
Tang WH, Wang Z, Kennedy DJ, Wu Y, Buffa JA, Agatisa-Boyle B, Li XS, Levison BS, Hazen SL (2015) Gut microbiota-dependent trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) pathway contributes to both development of renal insufficiency and mortality risk in chronic kidney disease. Circ Res 116:448–455
Griffin KA, Picken M, Bidani AK (1994) Method of renal mass reduction is a critical modulator of subsequent hypertension and glomerular injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 4:2023–2031
Iyoda M, Shibata T, Hirai Y, Kuno Y, Akizawa T (2011) Nilotinib attenuates renal injury and prolongs survival in chronic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 22:1486–1496
Zhang ZH, Vaziri ND, Wei F, Cheng XL, Bai X, Zhao YY (2016) An integrated lipidomics and metabolomics reveal nephroprotective effect and biochemical mechanism of Rheum officinale in chronic renal failure. Sci Rep 6:22151
Zhang ZH, Wei F, Vaziri ND, Cheng XL, Bai X, Lin RC, Zhao YY (2015) Metabolomics insights into chronic kidney disease and modulatory effect of rhubarb against tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Sci Rep 5:14472
Wang M, Chen DQ, Chen L, Cao G, Zhao H, Liu D, Vaziri ND, Guo Y, Zhao YY (2018) Novel inhibitors of the cellular renin-angiotensin system components, poricoic acids, target Smad3 phosphorylation and Wnt/β-catenin pathway against renal fibrosis. Br J Pharmacol 175:2689–2708
Chen H, Yang T, Wang MC, Chen DQ, Yang Y, Zhao YY (2018) Novel RAS inhibitor 25-O-methylalisol F attenuates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and tubulo-interstitial fibrosis by selectively inhibiting TGF-β-mediated Smad3 phosphorylation. Phytomedicine 42:207–218
Bolger A, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014) Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30:2114–2120
Edgar RC, Flyvbjerg H (2015) Error filtering, pair assembly and error correction for next-generation sequencing reads. Bioinformatics 31:3476–3482
Edgar RC (2013) UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat Methods 10:996–998
Edgar R (2016) SINTAX: a simple non-Bayesian taxonomy classifier for 16S and ITS sequences. bioRxiv 074161. https://doi.org/10.1101/074161
Edgar RC (2010) Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26:2460–2461
Lozupone C, Knight R (2005) UniFrac: a new phylogenetic method for comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:8228–8235
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Peña AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7:335–336
Chen DQ, Cao G, Chen H, Argyopoulos CP, Yu H, Su W, Chen L, Samuels DC, Zhuang S, Bayliss GP, Zhao S, Yu XY, Vaziri ND, Wang M, Liu D, Mao JR, Ma SX, Zhao J, Zhang Y, Shang YQ, Kang H, Ye F, Cheng XH, Li XR, Zhang L, Meng MX, Guo Y, Zhao YY (2019) Identification of serum metabolites associating with chronic kidney disease progression and anti-fibrotic effect of 5-methoxytryptophan. Nat Commun 10:1476
Chen DQ, Cao G, Chen H, Liu D, Su W, Yu XY, Vaziri ND, Liu XH, Bai X, Zhang L, Zhao YY (2017) Gene and protein expressions and metabolomics exhibit activated redox signaling and Wnt/β-catenin pathway are associated with metabolite dysfunction in patients with chronic kidney disease. Redox Biol 12:505–521
Zhang ZH, Chen H, Vaziri ND, Mao JR, Zhang L, Bai X, Zhao YY (2016) Metabolomic signatures of chronic kidney disease of diverse etiologies in the rats and humans. J Proteome Res 15:3802–3812
Zhao YY, Cheng XL, Wei F, Xiao XY, Sun WJ, Zhang Y, Lin RC (2012) Serum metabonomics study of adenine-induced chronic renal failure in rats by ultra performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Biomarkers 17:48–55
Kikuchi M, Ueno M, Itoh Y, Suda W, Hattori M (2017) Uremic toxin-producing gut microbiota in rats with chronic kidney disease. Nephron 135:51–60
Meyer TW, Hostetter TH (2012) Uremic solutes from colon microbes. Kidney Int 81:949–954
Zeisel SH, Warrier M (2017) Trimethylamine N-oxide, the microbiome, and heart and kidney disease. Annu Rev Nutr 37:157–181
Zhao YY, Liu J, Cheng XL, Bai X, Lin RC (2012) Urinary metabonomics study on biochemical changes in an experimental model of chronic renal failure by adenine based on UPLC Q-TOF/MS. Clin Chim Acta 413:642–649
Zhao YY, Cheng XL, Wei F, Bai X, Tan XJ, Lin RC, Mei Q (2013) Intrarenal metabolomic investigation of chronic kidney disease and its TGF-β1 mechanism in induced-adenine rats using UPLC Q-TOF/HSMS/MSE. J Proteome Res 12:2692–2703
Zhao YY, Cheng XL, Wei F, Bai X, Lin RC (2012) Application of faecal metabonomics on an experimental model of tubulointerstitial fibrosis by ultra performance liquid chromatography/high-sensitivity mass spectrometry with MSE data collection technique. Biomarkers 17:721–729
Li Y, Sekula P, Wuttke M, Wahrheit J, Hausknecht B, Schultheiss UT, Gronwald W, Schlosser P, Tucci S, Ekici AB, Spiekerkoetter U, Kronenberg F, Eckardt KU, Oefner PJ, Kottgen A (2018) Genome-wide association studies of metabolites in patients with CKD identify multiple loci and illuminate tubular transport mechanisms. J Am Soc Nephrol 29:1513–1524
Zhao YY, Feng YL, Du X, Xi ZH, Cheng XL, Wei F (2012) Diuretic activity of the ethanol and aqueous extracts of the surface layer of Poria cocos in rat. J Ethnopharmacol 144:775–778
Feng YL, Lei P, Tian T, Yin L, Chen DQ, Chen H, Mei Q, Zhao YY, Lin RC (2013) Diuretic activity of some fractions of the epidermis of Poria cocos. J Ethnopharmacol 150:1114–1118
Chen L, Cao G, Wang M, Feng YL, Chen DQ, Vaziri ND, Zhuang S, Zhao YY (2019) The matrix metalloproteinase-13 Inhibitor poricoic acid ZI ameliorates renal fibrosis by mitigating epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Mol Nutr Food Res 63:1900132
Zhao YY, Feng YL, Bai X, Tan XJ, Lin RC, Mei Q (2013) Ultra performance liquid chromatography-based metabonomic study of therapeutic effect of the surface layer of Poria cocos on adenine-induced chronic kidney disease provides new insight into anti-fibrosis mechanism. PLoS One 8:e59617
Zhao YY, Li HT, Feng YI, Bai X, Lin RC (2013) Urinary metabonomic study of the surface layer of Poria cocos as an effective treatment for chronic renal injury in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 148:403–410
Zhao YY, Lei P, Chen DQ, Feng YL, Bai X (2013) Renal metabolic profiling of early renal injury and renoprotective effects of Poria cocos epidermis using UPLC Q-TOF/HSMS/MSE. J Pharm Biomed Anal 81–82:202–209
Miao H, Zhao YH, Vaziri ND, Tang DD, Chen H, Chen H, Khazaeli M, Tarbiat-Boldaji M, Hatami L, Zhao YY (2016) Lipidomics biomarkers of diet-induced hyperlipidemia and Its treatment with Poria cocos. J Agric Food Chem 64:969–979
Chen DQ, Feng YL, Chen L, Liu JR, Wang M, Vaziri ND, Zhao YY (2019) Poricoic acid A enhances melatonin inhibition of AKI-to-CKD transition by regulating Gas6/Axl-NF-κB/Nrf2 axis. Free Radic Biol Med 134:484–497
Wang M, Chen DQ, Wang MC, Chen H, Chen L, Liu D, Zhao H, Zhao YY (2017) Poricoic acid ZA, a novel RAS inhibitor, attenuates tubulo-interstitial fibrosis and podocyte injury by inhibiting TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway. Phytomedicine 36:243–253
Wang M, Chen DQ, Chen L, Zhao H, Liu D, Zhang ZH, Vaziri ND, Guo Y, Zhao YY, Cao G (2018) Novel RAS inhibitors poricoic acid ZG and poricoic acid ZH attenuate renal fibrosis via Wnt/β-catenin pathway and targeted phosphorylation of smad3 signaling. J Agric Food Chem 66:1828–1842
Yang T, Richards EM, Pepine CJ, Raizada MK (2018) The gut microbiota and the brain-gut-kidney axis in hypertension and chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol 14:442–456
Chen H, Cao G, Chen DQ, Wang M, Vaziri ND, Zhang ZH, Mao JR, Bai X, Zhao YY (2016) Metabolomics insights into activated redox signaling and lipid metabolism dysfunction in chronic kidney disease progression. Redox Biol 10:168–178
Chen DQ, Chen H, Chen L, Vaziri ND, Wang M, Li XR, Zhao YY (2017) The link between phenotype and fatty acid metabolism in advanced chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant 32:1154–1166
Kieffer DA, Piccolo BD, Vaziri ND, Liu S, Lau WL, Khazaeli M, Nazertehrani S, Moore ME, Marco ML, Martin RJ, Adams SH (2016) Resistant starch alters gut microbiome and metabolomic profiles concurrent with amelioration of chronic kidney disease in rats. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 310:F857–F871
Vaziri ND, Liu SM, Lau WL, Khazaeli M, Nazertehrani S, Farzaneh SH, Kieffer DA, Adams SH, Martin RJ (2014) High amylose resistant starch diet ameliorates oxidative stress, inflammation, and progression of chronic kidney disease. PLoS One 9:e114881
Wang F, Jiang H, Shi K, Ren Y, Zhang P, Cheng S (2012) Gut bacterial translocation is associated with microinflammation in end-stage renal disease patients. Nephrology 17:733–738
Gaastra W, Kusters JG, van Duijkeren E, Lipman LJ (2014) Escherichia fergusonii. Vet Microbiol 172:7–12
Oh JY, Kang MS, An BK, Shin EG, Kim MJ, Kwon JH, Kwon YK (2012) Isolation and epidemiological characterization of heat-labile enterotoxin-producing Escherichia fergusonii from healthy chickens. Vet Microbiol 160:170–175
Hida M, Aiba Y, Sawamura S, Suzuki N, Satoh T, Koga Y (1996) Inhibition of the accumulation of uremic toxins in the blood and their precursors in the feces after oral administration of Lebenin, a lactic acid bacteria preparation, to uremic patients undergoing hemodialysis. Nephron 74:349–355
Zeng YQ, Dai Z, Lu F, Lu Z, Liu X, Chen C, Qu P, Li D, Hua Z, Qu Y, Zou C (2016) Emodin via colonic irrigation modulates gut microbiota and reduces uremic toxins in rats with chronic kidney disease. Oncotarget 7:17468–17478
Barrios C, Beaumont M, Pallister T, Villar J, Goodrich JK, Clark A, Pascual J, Ley RE, Spector TD, Bell JT, Menni C (2015) Gut-microbiota-metabolite axis in early renal function decline. PLoS One 10:e0134311
Nazzal L, Roberts J, Singh P, Jhawar S, Matalon A, Gao Z, Holzman R, Liebes L, Blaser MJ, Lowenstein J (2017) Microbiome perturbation by oral vancomycin reduces plasma concentration of two gut-derived uremic solutes, indoxyl sulfate and p-cresyl sulfate, in end-stage renal disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant 32:1809–1817
Mishima E, Fukuda S, Shima H, Hirayama A, Akiyama Y, Takeuchi Y, Fukuda NN, Suzuki T, Suzuki C, Yuri A, Kikuchi K, Tomioka Y, Ito S, Soga T, Abe T (2015) Alteration of the intestinal environment by lubiprostone is associated with amelioration of adenine-induced CKD. J Am Soc Nephrol 26:1787–1794
Xu KY, Xia GH, Lu JQ, Chen MX, Zhen X, Wang S, You C, Nie J, Zhou HW, Yin J (2017) Impaired renal function and dysbiosis of gut microbiota contribute to increased trimethylamine-N-oxide in chronic kidney disease patients. Sci Rep 7:1445
Jiang S, Xie S, Lv D, Wang P, He H, Zhang T, Zhou Y, Lin Q, Zhou H, Jiang J, Nie J, Hou F, Chen Y (2017) Alteration of the gut microbiota in Chinese population with chronic kidney disease. Sci Rep 7:2870
Stern JM, Moazami S, Qiu Y, Kurland I, Chen Z, Agalliu I, Burk R, Davies KP (2016) Evidence for a distinct gut microbiome in kidney stone formers compared to non-stone formers. Urolithiasis 44:399–407
Santisteban MM, Qi Y, Zubcevic J, Kim S, Yang T, Shenoy V, Cole-Jeffrey CT, Lobaton GO, Stewart DC, Rubiano A, Simmons CS, Garcia-Pereira F, Johnson RD, Pepine CJ, Raizada MK (2017) Hypertension-linked pathophysiological alterations in the gut. Circ Res 120:312–323
Pryde SE, Duncan SH, Hold GL, Stewart CS, Flint HJ (2002) The microbiology of butyrate formation in the human colon. FEMS Microbiol Lett 217:133–139
Li YN, Huang F, Cheng HJ, Li SY, Liu L, Wang LY (2014) Intestine-derived Clostridium leptum induces murine tolerogenic dendritic cells and regulatory T cells in vitro. Hum Immunol 75:1232–1238
Besouw M, Cornelissen E, Cassiman D, Kluijtmans L, van den Heuvel L, Levtchenko E (2014) Carnitine profile and effect of suppletion in children with renal fanconi syndrome due to cystinosis. JIMD Rep 16:25–30
Araujo MV, Hong BY, Fava PL, Khan S, Burleson JA, Fares G, Samson W, Strausbaugh LD, Diaz PI, Ioannidou E (2015) End stage renal disease as a modifier of the periodontal microbiome. BMC Nephrol 16:80
Tain YL, Lee WC, Wu KLH, Leu S, Chan JYH (2018) Resveratrol prevents the development of hypertension programmed by maternal Plus post-weaning high-fructose consumption through modulation of oxidative stress, nutrient-sensing signals, and gut microbiota. Mol Nutr Food Res 62:e1800066
Sindhu KK (2016) Uremic toxins: some thoughts on acrolein and spermine. Ren Fail 38:1755–1758
Goek ON, Prehn C, Sekula P, Romisch-Margl W, Doring A, Gieger C, Heier M, Koenig W, Wang-Sattler R, Illig T, Suhre K, Adamski J, Kottgen A, Meisinger C (2013) Metabolites associate with kidney function decline and incident chronic kidney disease in the general population. Nephrol Dial Transplant 28:32131–32138
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 81872985, 81673578, 81603271).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, YL., Cao, G., Chen, DQ. et al. Microbiome–metabolomics reveals gut microbiota associated with glycine-conjugated metabolites and polyamine metabolism in chronic kidney disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 76, 4961–4978 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-019-03155-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-019-03155-9