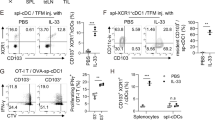
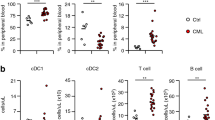
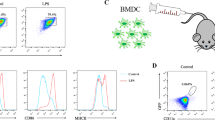
Abstract
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a malignancy of mature B lymphocytes. The microenvironment of the CLL cells is a vital element in the regulation of the survival of these malignant cells. CLL cell longevity is dependent on external signals, originating from cells in their microenvironment including secreted and surface-bound factors. Dendritic cells (DCs) play an important part in tumor microenvironment, but their role in the CLL bone marrow (BM) niche has not been studied. We show here that CLL cells induce accumulation of bone marrow dendritic cells (BMDCs). Depletion of this population attenuates disease expansion. Our results show that the support of the microenvironment is partly dependent on CD84, a cell surface molecule belonging to the Signaling Lymphocyte Activating Molecule (SLAM) family of immunoreceptors. Our results suggest a novel therapeutic strategy whereby eliminating BMDCs or blocking the CD84 expressed on these cells may reduce the tumor load.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The RNAseq results were submitted to GEO (GSE119115).
References
Klein U, Dalla-Favera R. New insights into the pathogenesis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Semin Cancer Biol. 2010;20:377–83.
Montserrat E, Moreno C. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: a short overview. Ann Oncol. 2008;19(Suppl 7):vii320–25.
Caligaris-Cappio F, Hamblin TJ. B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a bird of a different feather. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:399–408.
Kipps TJ. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Curr Opin Hematol. 1998;5:244–53.
Gale RP, Caligaris-Cappio F, Dighiero G, Keating M, Montserrat E, Rai K. Recent progress in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. International Workshop on chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Leukemia. 1994;8:1610–4.
Binet JL, Leporrier M, Dighiero G, Charron D, Dathis P, Vaugier G, et al. Clinical staging system for chronic lymphocytic-leukemia—prognostic significance. Cancer. 1977;40:855–64.
Rai KR, Sawitsky A, Cronkite EP, Chanana AD, Levy RN, Pasternack BS. Clinical staging of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 1975;46:219–34.
Nicholas NS, Apollonio B, Ramsay AG. Tumor microenvironment (TME)-driven immune suppression in B cell malignancy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1863:471–82.
Bichi R, Shinton SA, Martin ES, Koval A, Calin GA, Cesari R, et al. Human chronic lymphocytic leukemia modeled in mouse by targeted TCL1 expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:6955–60.
Burger JA. No cell is an island unto itself: the stromal microenvironment in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk Res. 2007;31:887–8.
Ramsay AD, Rodriguez-Justo M. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia-the role of the microenvironment pathogenesis and therapy. Br J Haematol. 2013;162:15–24.
Lagneaux L, Delforge A, Bron D, De Bruyn C, Stryckmans P. Chronic lymphocytic leukemic B cells but not normal B cells are rescued from apoptosis by contact with normal bone marrow stromal cells. Blood. 1998;91:2387–96.
de Visser KE, Eichten A, Coussens LM. Paradoxical roles of the immune system during cancer development. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:24–37.
Sapoznikov A, Pewzner-Jung Y, Kalchenko V, Krauthgamer R, Shachar I, Jung S. Perivascular clusters of dendritic cells provide critical survival signals to B cells in bone marrow niches. Nat Immunol. 2008;9:388–95.
Karthaus N, Torensma R, Tel J. Deciphering the message broadcast by tumor-infiltrating dendritic cells. Am J Pathol. 2012;181:733–42.
Calpe S, Wang NH, Romero X, Berger SB, Lanyi A, Engel P, et al. The SLAM and SAP gene families control innate and adaptive immune responses. Adv Immunol. 2008;97:177–250.
Martin M, Romero X, de la Fuente MA, Tovar V, Zapater N, Esplugues E, et al. CD84 functions as a homophilic adhesion molecule and enhances IFN-gamma secretion: adhesion is mediated by Ig-like domain 1. J Immunol. 2001;167:3668–76.
Romero X, Zapater N, Calvo M, Kalko SG, de la Fuente MA, Tovar V, et al. CD229 (Ly9) lymphocyte cell surface receptor interacts homophilically through its N-terminal domain and relocalizes to the immunological synapse. J Immunol. 2005;174:7033–42.
Yan QR, Malashkevich VN, Fedorov A, Fedorov E, Cao E, Lary JW, et al. Structure of CD84 provides insight into SLAM family function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:10583–8.
Binsky-Ehrenreich I, Marom A, Sobotta MC, Shvidel L, Berrebi A, Hazan-Halevy I, et al. CD84 is a survival receptor for CLL cells. Oncogene. 2014;33:1006–16.
Marom A, Barak AF, Kramer MP, Lewinsky H, Binsky-Ehrenreich I, Cohen S, et al. CD84 mediates CLL-microenvironment interactions. Oncogene. 2017;36:628–38.
Lewinsky H, Barak AF, Huber V, Kramer MP, Radomir L, Sever L, et al. CD84 regulates PD-1/PD-L1 expression and function in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Investig. 2018;128:5465–78.
Hofbauer JP, Heyder C, Denk U, Kocher T, Holler C, Trapin D, et al. Development of CLL in the TCL1 transgenic mouse model is associated with severe skewing of the T-cell compartment homologous to human CLL. Leukemia. 2011;25:1452–8.
Saulep-Easton D, Vincent FB, Le Page M, Wei A, Ting SB, Croce CM, et al. Cytokine-driven loss of plasmacytoid dendritic cell function in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia. 2014;28:2005–15.
Mildner A, Jung S. Development and function of dendritic cell subsets. Immunity. 2014;40:642–56.
Ginhoux F, Jung S. Monocytes and macrophages: developmental pathways and tissue homeostasis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014;14:392–404.
Serbina NV, Pamer EG. Monocyte emigration from bone marrow during bacterial infection requires signals mediated by chemokine receptor CCR2. Nat Immunol. 2006;7:311–7.
Jung S, Aliberti J, Graemmel P, Sunshine MJ, Kreutzberg GW, Sher A, et al. Analysis of fractalkine receptor CX(3)CR1 function by targeted deletion and green fluorescent protein reporter gene insertion. Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20:4106–14.
Cabanas C, Sanchez-Madrid F. CD11c (leukocyte integrin CR4 alpha subunit). J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 1999;13:134–6.
Yang J, Zhang L, Yu C, Yang XF, Wang H. Monocyte and macrophage differentiation: circulation inflammatory monocyte as biomarker for inflammatory diseases. Biomark Res. 2014;2:1.
Galletti G, Scielzo C, Barbaglio F, Rodriguez TV, Riba M, Lazarevic D, et al. Targeting macrophages sensitizes chronic lymphocytic leukemia to apoptosis and inhibits disease progression. Cell Rep. 2016;14:1748–60.
Birnberg T, Bar-On L, Sapoznikov A, Caton ML, Cervantes-Barragan L, Makia D, et al. Lack of conventional dendritic cells is compatible with normal development and T cell homeostasis, but causes myeloid proliferative syndrome. Immunity. 2008;29:986–97.
Zlotnikov-Klionsky Y, Nathansohn-Levi B, Shezen E, Rosen C, Kagan S, Bar-On L, et al. Perforin-positive dendritic cells exhibit an immuno-regulatory role in metabolic syndrome and autoimmunity. Immunity. 2015;43:776–87.
Jung S, Unutmaz D, Wong P, Sano G, De los Santos K, Sparwasser T, et al. In vivo depletion of CD11c(+) dendritic cells abrogates priming of CD8(+) T cells by exogenous cell-associated antigens. Immunity. 2002;17:211–20.
Sapoznikov A, Jung S. Probing in vivo dendritic cell functions by conditional cell ablation. Immunol Cell Biol. 2008;86:409–15.
Hanna BS, McClanahan F, Yazdanparast H, Zaborsky N, Kalter V, Rossner PM, et al. Depletion of CLL-associated patrolling monocytes and macrophages controls disease development and repairs immune dysfunction in vivo. Leukemia. 2016;30:570–9.
Ghiringhelli F, Puig PE, Roux S, Parcellier A, Schmitt E, Solary E, et al. Tumor cells convert immature myeloid dendritic cells into TGF-beta-secreting cells inducing CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cell proliferation. J Exp Med. 2005;202:919–29.
Engelhardt JJ, Boldajipour B, Beemiller P, Pandurangi P, Sorensen C, Werb Z, et al. Marginating dendritic cells of the tumor microenvironment cross-present tumor antigens and stably engage tumor-specific T cells. Cancer Cell. 2012;21:402–17.
Krempski J, Karyampudi L, Behrens MD, Erskine CL, Hartmann L, Dong H, et al. Tumor-infiltrating programmed death receptor-1+ dendritic cells mediate immune suppression in ovarian cancer. J Immunol. 2011;186:6905–13.
Freeman GJ, Long AJ, Iwai Y, Bourque K, Chernova T, Nishimura H, et al. Engagement of the PD-1 immunoinhibitory receptor by a novel B7 family member leads to negative regulation of lymphocyte activation. J Exp Med. 2000;192:1027–34.
Greaves P, Gribben JG. The role of B7 family molecules in hematologic malignancy. Blood. 2013;121:734–44.
Cannons JL, Qi H, Lu KT, Dutta M, Gomez-Rodriguez J, Cheng J, et al. Optimal germinal center responses require a multistage T cell:B cell adhesion process involving integrins, SLAM-associated protein, and CD84. Immunity. 2010;32:253–65.
Kuziel WA, Morgan SJ, Dawson TC, Griffin S, Smithies O, Ley K, et al. Severe reduction in leukocyte adhesion and monocyte extravasation in mice deficient in CC chemokine receptor 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:12053–8.
Brockschnieder D, Pechmann Y, Sonnenberg-Riethmacher E, Riethmacher D. An improved mouse line for Cre-induced cell ablation due to diphtheria toxin A, expressed from the Rosa26 locus. Genesis. 2006;44:322–7.
Anders S, Pyl PT, Huber W. HTSeq-a Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics. 2015;31:166–9.
Dobin A, Davis CA, Schlesinger F, Drenkow J, Zaleski C, Jha S, et al. STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics. 2013;29:15–21.
Love MI, Huber W, Anders S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014;15:550.
Varol C, Landsman L, Fogg DK, Greenshtein L, Gildor B, Margalit R, et al. Monocytes give rise to mucosal, but not splenic, conventional dendritic cells. J Exp Med. 2007;204:171–80.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank members of the Shachar lab for fruitful discussion and support. IS is the incumbent of the Dr Morton and Ann Kleiman Professorial Chair. This research was supported by the DKFZ-MOST cooperation in cancer research, ERA-NET TRANSCAN-2 program JTC 2014–project FIRE-CLL and the Binational Science Foundation (BSF) grant no 711979. This research was performed without the support of the Israel Science Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Author contributions
AFB—designed research, performed research, analyzed data and wrote the paper. HL—designed research, performed research and analyzed data. MP—designed research, performed research and analyzed data. VH—designed research, performed research and analyzed data. LR—designed research, performed research and analyzed data. MPK—designed research, performed research and analyzed data. LS—performed research, analyzed data. YW—designed research and contributed vital reagent. MS—designed research and contributed vital reagent. YH—designed research and contributed vital reagent. SJ—designed research, contributed vital reagent and wrote the paper. SB-H—designed research, performed research, analyzed data. IS—designed research, analyzed data, and wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barak, A.F., Lewinsky, H., Perpinial, M. et al. Bone marrow dendritic cells support the survival of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells in a CD84 dependent manner. Oncogene 39, 1997–2008 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-019-1121-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-019-1121-y