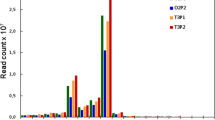
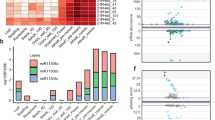
Abstract
Key Message
Differential expression of mi-RNAs targeting developmental processes and progressive downregulation of repeat-associated siRNAs following genome merger and genome duplication in the context of allopolyploid speciation in Spartina.
Abstract
The role of small RNAs on gene expression regulation and genome stability is arousing increased interest and is being explored in various plant systems. In spite of prominence of reticulate evolution and polyploidy that affects the evolutionary history of all plant lineages, very few studies analysed RNAi mechanisms with this respect. Here, we explored small RNAs diversity and expression in the context of recent allopolyploid speciation, using the Spartina system, which offers a unique opportunity to explore the immediate changes following hybridization and genome duplication. Small RNA-Seq analyses were conducted on hexaploid parental species (S. alterniflora and S. maritima), their F1 hybrid S. x townsendii, and the neoallododecaploid S. anglica. We identified 594 miRNAs, 2197 miRNA-target genes, and 3730 repeat-associated siRNAs (mostly targeting Class I/Copia-Ivana- Copia-SIRE and LINEs elements). For both mi- and ra-siRNAs, we detected differential expression patterns following genome merger and genome duplication. These misregulations include non-additive expression of miRNAs in the F1 hybrid and additional changes in the allopolyploid targeting developmental processes. Expression of repeat-associated siRNAs indicates a strengthen of transposable element repression during the allopolyploidization process. Altogether, these results confirm the central role small RNAs play in shaping regulatory changes in naturally formed recent allopolyploids.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott RJ, Lowe AJ (2004) Origins, establishment and evolution of new polyploid species: Senecio cambrensis and S. eboracensis in the British Isles. Biol J Linn Soc 82:467–474. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8312.2004.00333.x
Ainouche ML, Wendel JF (2014) Polyploid speciation and genome evolution: lessons from recent allopolyploids. In: Pontarotti P (ed) Evolutionary biology: genome evolution, speciation, coevolution and origin of life. Springer, New York, pp 87–113
Ainouche ML, Baumel A, Salmon A (2004) Spartina anglica C. E. Hubbard: a natural model system for analysing early evolutionary changes that affect allopolyploid genomes. Biol J Linn Soc 82:475–484. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8312.2004.00334.x
Ainouche ML, Fortune PM, Salmon A, Parisod C, Grandbastien M-A, Fukunaga K, Ricou M, Misset M-T (2009) Hybridization, polyploidy and invasion: lessons from Spartina (Poaceae). Biol Invasions 11:1159–1173
Alix K, Gérard PR, Schwarzacher T, Heslop-Harrison JS (2017) Polyploidy and interspecific hybridization: partners for adaptation, speciation and evolution in plants. Ann Bot 120:183–194. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcx079
Arnon DI, Hoagland DR (1950) The water-culture method for growing plants without soil, Rev. ed./by D.I. Arnon. College of Agriculture, University of California, Berkeley, California (USA)
Axtell MJ (2013) Classification and comparison of small RNAs from plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 64:137–159. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-050312-120043
Axtell MJ, Meyers BC (2018) Revisiting criteria for plant microRNA annotation in the era of big data. Plant Cell 30:272–284. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00851
Barber WT, Zhang W, Win H, Varala KK, Dorweiler JE, Hudson ME, Moose SP (2012) Repeat associated small RNAs vary among parents and following hybridization in maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109:10444–10449. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1202073109
Baumel A, Ainouche ML, Levasseur JE (2001) Molecular investigations in populations of Spartina anglica C.E. Hubbard (Poaceae) invading coastal Brittany (France). Mol Ecol 10:1689–1701. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-294X.2001.01299.x
Baumel A, Ainouche M, Kalendar R, Schulman AH (2002a) Retrotransposons and genomic stability in populations of the young allopolyploid species Spartina anglica C.E. Hubbard (Poaceae). Mol Biol Evol 19:1218–1227. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a004182
Baumel A, Ainouche ML, Bayer RJ, Ainouche AK, Misset MT (2002b) Molecular phylogeny of hybridizing species from the genus Spartina Schreb. (Poaceae). Mol Phylogenet Evol 22:303–314. https://doi.org/10.1006/mpev.2001.1064
Baumel A, Ainouche ML, Misset MT, Gourret J-P, Bayer RJ (2003) Genetic evidence for hybridization between the native Spartina maritima and the introduced Spartina alterniflora (Poaceae) in South-West France: Spartina x neyrautii re-examined. Plant Syst Evol 237:87–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-002-0251-8
Boutte J, Aliaga B, Lima O, Ferreira de Carvalho J, Ainouche A, Macas J, Rousseau-Gueutin M, Coriton O, Ainouche M, Salmon A (2015) Haplotype detection from next generation sequencing in high ploidy-level species: 45S rDNA gene copies in the hexaploid Spartina maritima. G3: Genes Genomes Genetics 6(1):21–40
Boutte J, Ferreira de Carvalho J, Rousseau-Gueutin M, Poulain J, Da Silva C, Wincker P, Ainouche M, Salmon A (2016) Reference transcriptomes and detection of duplicated copies in hexaploid and allododecaploid Spartina species (Poaceae). Genome Biol Evol 8:3030–3044. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evw209
Bullard JH, Purdom E, Hansen KD, Dudoit S (2010) Evaluation of statistical methods for normalization and differential expression in mRNA-Seq experiments. BMC Bioinform 11:94. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-11-94
Camacho C, Coulouris G, Avagyan V, Ma N, Papadopoulos J, Bealer K, Madden TL (2009) BLAST + : architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform 10:421. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-10-421
Cantu D, Vanzetti LS, Sumner A, Dubcovsky M, Matvienko M, Distelfeld A, Michelmore RW, Dubcovsky J (2010) Small RNAs, DNA methylation and transposable elements in wheat. BMC Genomics 11:408. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-11-408
Carthew RW, Sontheimer EJ (2009) Origins and mechanisms of miRNAs and siRNAs. Cell 136:642–655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.035
Castel SE, Martienssen RA (2013) RNA interference in the nucleus: roles for small RNAs in transcription, epigenetics and beyond. Nat Rev Genet 14:100–112. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg3355
Cavé-Radet A, Salmon A, Lima O, Ainouche ML, El Amrani A (2019) Increased tolerance to organic xenobiotics following recent allopolyploidy in Spartina (Poaceae). Plant Sci 280:143–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2018.11.005
Chelaifa H, Mahé F, Ainouche M (2010a) Transcriptome divergence between the hexaploid salt-marsh sister species Spartina maritima and Spartina alterniflora (Poaceae). Mol Ecol 19:2050–2063. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2010.04637.x
Chelaifa H, Monnier A, Ainouche M (2010b) Transcriptomic changes following recent natural hybridization and allopolyploidy in the salt marsh species Spartina x townsendii and Spartina anglica (Poaceae). New Phytol 186:161–174. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03179.x
Chen ZJ, Birchler JA (2013) Polyploid and hybrid genomics. John Wiley & Sons
Cui J, You C, Chen X (2017) The evolution of microRNAs in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 35:61–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2016.11.006
D’Ario M, Griffiths-Jones S, Kim M (2017) Small RNAs: big impact on plant development. Trends Plant Sci 22:1056–1068. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2017.09.009
Dai X, Zhao PX (2011) psRNATarget: a plant small RNA target analysis server. Nucleic Acids Res 39:W155–W159. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkr319
Diez CM, Meca E, Tenaillon MI, Gaut BS (2014) Three groups of transposable elements with contrasting copy number dynamics and host responses in the Maize (Zea mays ssp mays) genome. PLoS Genet. 10:e1004298. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1004298
Ding D, Wang Y, Han M, Fu Z, Li W, Liu Z, Hu Y, Tang J (2012) MicroRNA transcriptomic analysis of heterosis during maize seed germination. PLoS ONE 7:e39578. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0039578
Dong B, Wang H, Song A, Liu T, Chen Y, Fang W, Chen S, Chen F, Guan Z, Jiang J (2016) miRNAs Are involved in determining the improved vigor of autotetrapoid Chrysanthemum nankingense. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01412
Doyle JJ, Flagel LE, Paterson AH, Rapp RA, Soltis DE, Soltis PS, Wendel JF (2008) Evolutionary genetics of genome merger and doubling in plants. Annu Rev Genet 42:443–461. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.genet.42.110807.091524
Fang R, Li L, Li J (2013) Spatial and temporal expression modes of MicroRNAs in an elite rice hybrid and its parental lines. Planta 238:259–269. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-013-1881-5
Ferreira de Carvalho J, Chelaifa H, Boutte J, Poulain J, Couloux A, Wincker P, Bellec A, Fourment J, Bergès H, Salmon A, Ainouche M (2013a) Exploring the genome of the salt-marsh Spartina maritima (Poaceae, Chloridoideae) through BAC end sequence analysis. Plant Mol Biol 83:591–606. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-013-0111-7
Ferreira de Carvalho J, Poulain J, Da Silva C, Wincker P, Michon-Coudouel S, Dheilly A, Naquin D, Boutte J, Salmon A, Ainouche M (2013b) Transcriptome de novo assembly from next-generation sequencing and comparative analyses in the hexaploid salt marsh species Spartina maritima and Spartina alterniflora (Poaceae). Heredity 110:181–193
Ferreira de Carvalho J, Boutte J, Bourdaud P, Chelaifa H, Ainouche K, Salmon A, Ainouche M (2017) Gene expression variation in natural populations of hexaploid and allododecaploid Spartina species (Poaceae). Plant Syst Evol
Ferris C, King RA, Gray AJ (1997) Molecular evidence for the maternal parentage in the hybrid origin of Spartina anglica C.E. Hubbard. Mol Ecol 6:185–187. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-294X.1997.00165.x
Fu D, Mason AS, Xiao M, Yan H (2016a) Effects of genome structure variation, homeologous genes and repetitive DNA on polyploid crop research in the age of genomics. Plant Sci 242:37–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2015.09.017
Fu Y, Xiao M, Yu H, Mason AS, Yin J, Li J, Zhang D, Fu D (2016b) Small RNA changes in synthetic Brassica napus. Planta 244:607–622. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-016-2529-z
Fultz D, Choudury SG, Slotkin RK (2015) Silencing of active transposable elements in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 27:67–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2015.05.027
Ghani MA, Li J, Rao L, Raza MA, Cao L, Yu N, Zou X, Chen L (2014) The role of small RNAs in wide hybridisation and allopolyploidisation between Brassica rapa and Brassica nigra. BMC Plant Biol. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-014-0272-9
Gong L, Kakrana A, Arikit S, Meyers BC, Wendel JF (2013) Composition and expression of conserved microRNA genes in diploid cotton (Gossypium) species. Genome Biol Evol 5:2449–2459. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evt196
Gong L, Masonbrink RE, Grover CE, Renny-Byfield S, Wendel JF (2015) A cluster of recently inserted transposable elements associated with siRNAs in Gossypium raimondii. Plant Genome. https://doi.org/10.3835/plantgenome2014.11.0088
Gray AJ, Marshall DF, Raybould AF (1991) A Century of Evolution in Spartina anglica. Advances in ecological research. Elsevier, New York, pp 1–62
Greaves IK, Gonzalez-Bayon R, Wang L, Zhu A, Liu P-C, Groszmann M, Peacock WJ, Dennis ES (2015) Epigenetic changes in hybrids. Plant Physiol 168:1197–1205. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.15.00231
Groszmann M, Greaves IK, Albertyn ZI, Scofield GN, Peacock WJ, Dennis ES (2011) Changes in 24-nt siRNA levels in Arabidopsis hybrids suggest an epigenetic contribution to hybrid vigor. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108:2617–2622
Grover CE, Gallagher JP, Szadkowski EP, Yoo MJ, Flagel LE, Wendel JF (2012) Homoeolog expression bias and expression level dominance in allopolyploids. New Phytol 196:966–971
Groves H, Groves J (1880) Spartina townsendii. Report of the Botanical Exchange Club of the British Isles for 1880:37
Guan X, Song Q, Chen ZJ (2014) Polyploidy and small RNA regulation of cotton fiber development. Trends Plant Sci 19:516–528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2014.04.007
Ha M, Lu J, Tian L, Ramachandran V, Kasschau KD, Chapman EJ, Carrington JC, Chen X, Wang X-J, Chen ZJ (2009) Small RNAs serve as a genetic buffer against genomic shock in Arabidopsis interspecific hybrids and allopolyploids. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106:17835–17840. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0907003106
He G, Zhu X, Elling AA, Chen L, Wang X, Guo L, Liang M, He H, Zhang H, Chen F, Qi Y, Chen R, Deng X-W (2010) Global epigenetic and transcriptional trends among two rice subspecies and their reciprocal hybrids. Plant Cell 22:17–33. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.109.072041
He G, He H, Deng XW (2013) Epigenetic variations in plant hybrids and their potential roles in heterosis. J Genet Genomics 40:205–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgg.2013.03.011
Hollister JD, Smith LM, Guo Y-L, Ott F, Weigel D, Gaut BS (2011) Transposable elements and small RNAs contribute to gene expression divergence between Arabidopsis thaliana and Arabidopsis lyrata. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108:2322–2327. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1018222108
Jiao Y, Wickett NJ, Ayyampalayam S, Chanderbali AS, Landherr L, Ralph PE, Tomsho LP, Hu Y, Liang H, Soltis PS, Soltis DE, Clifton SW, Schlarbaum SE, Schuster SC, Ma H, Leebens-Mack J, dePamphilis CW (2011) Ancestral polyploidy in seed plants and angiosperms. Nature 473:97–100. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09916
Jiao W, Yuan J, Jiang S, Liu Y, Wang L, Liu M, Zheng D, Ye W, Wang X, Chen ZJ (2018) Asymmetrical changes of gene expression, small RNAs and chromatin in two resynthesized wheat allotetraploids. Plant J 93:828–842. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.13805
Kantar M, Akpınar BA, Valárik M, Lucas SJ, Doležel J, Hernández P, Budak H (2012) Subgenomic analysis of microRNAs in polyploid wheat. Funct Integr Genomics 12:465–479. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-012-0285-0
Kashkush K, Feldman M, Levy AA (2002) Gene loss, silencing and activation in a newly synthesized wheat allotetraploid. Genetics 160:1651–1659
Kawanabe T, Ishikura S, Miyaji N, Sasaki T, Wu LM, Itabashi E, Takada S, Shimizu M, Takasaki-Yasuda T, Osabe K, Peacock WJ, Dennis ES, Fujimoto R (2016) Role of DNA methylation in hybrid vigor in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci 113:E6704–E6711. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1613372113
Kenan-Eichler M, Leshkowitz D, Tal L, Noor E, Melamed-Bessudo C, Feldman M, Levy AA (2011) Wheat hybridization and polyploidization results in deregulation of small RNAs. Genetics 188:263–272. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.111.128348
Khraiwesh B, Zhu J-K, Zhu J (2012) Role of miRNAs and siRNAs in biotic and abiotic stress responses of plants. Biochim Biophys Acta BBA 1819:137–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2011.05.001
Kim VN (2005) MicroRNA biogenesis: coordinated cropping and dicing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6:376–385. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm1644
Kozomara A, Griffiths-Jones S (2014) miRBase: annotating high confidence microRNAs using deep sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D68–D73. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt1181
Langmead B, Salzberg SL (2012) Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat Methods 9:357–359. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1923
Langmead B, Trapnell C, Pop M, Salzberg SL (2009) Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biol 10:R25. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2009-10-3-r25
Lei J, Sun Y (2014) miR-PREFeR: an accurate, fast and easy-to-use plant miRNA prediction tool using small RNA-Seq data. Bioinformatics 30:2837–2839. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu380
Lewis WH (1980) Polyploidy in angiosperms: dicotyledons. In: Lewis WH (ed) Polyploidy. Springer, Boston, pp 241–268
Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, Fennell T, Ruan J, Homer N, Marth G, Abecasis G, Durbin R, 1000 genome project data processing subgroup (2009) The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinform 25:2078–2079. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp352
Li A, Liu D, Wu J, Zhao X, Hao M, Geng S, Yan J, Jiang X, Zhang L, Wu J, Yin L, Zhang R, Wu L, Zheng Y, Mao L (2014a) mRNA and small RNA transcriptomes reveal insights into dynamic homoeolog regulation of allopolyploid heterosis in nascent hexaploid wheat. Plant Cell 26:1878–1900. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.114.124388
Li J, Sun Q, Yu N, Zhu J, Zou X, Qi Z, Ghani MA, Chen L (2014b) The role of small RNAs on phenotypes in reciprocal hybrids between Solanum lycopersicum and S. pimpinellifolium. BMC Plant Biol 14:296. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-014-0296-1
Lorenz R, Bernhart SH, Höner zu Siederdissen C, Tafer H, Flamm C, Stadler PF, Hofacker IL (2011) ViennaRNA Package 2.0. Algorithms Mol Biol 6:26. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-7188-6-26
Love MI, Huber W, Anders S (2014) Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol 15:550. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8
Mackowiak SD (2011) Identification of novel and known miRNAs in deep-sequencing data with miRDeep2. In: Petsko GA, Stein LD, Stormo GD, Baxevanis AD (eds) Current protocols in bioinformatics. Wiley, Hoboken
Marchant CJ (1967) Evolution in Spartina (Gramineae): I. The history and morphology of the genus in Britain. J Linn Soc Lond Bot 60:1–24
Margulies M, Egholm M, Altman WE, Attiya S, Bader JS, Bemben LA, Berka J, Braverman MS, Chen Y-J, Chen Z, Dewell SB, Du L, Fierro JM, Gomes XV, Godwin BC, He W, Helgesen S, Ho CH, Irzyk GP, Jando SC, Alenquer MLI, Jarvie TP, Jirage KB, Kim J-B, Knight JR, Lanza JR, Leamon JH, Lefkowitz SM, Lei M, Li J, Lohman KL, Lu H, Makhijani VB, McDade KE, McKenna MP, Myers EW, Nickerson E, Nobile JR, Plant R, Puc BP, Ronan MT, Roth GT, Sarkis GJ, Simons JF, Simpson JW, Srinivasan M, Tartaro KR, Tomasz A, Vogt KA, Volkmer GA, Wang SH, Wang Y, Weiner MP, Yu P, Begley RF, Rothberg JM (2005) Genome sequencing in microfabricated high-density picolitre reactors. Nature 437:376–380. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03959
Martin M (2011) Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet.journal 17:10. https://doi.org/10.14806/ej.17.1.200
Martinez Palacios P, Jacquemot M-P, Tapie M, Rousselet A, Diop M, Remoué C, Falque M, Lloyd A, Jenczewski E, Lassalle G, Chévre A-M, Lelandais C, Crespi M, Brabant P, Joets J, Alix K (2019) Assessing the response of small RNA populations to allopolyploidy using resynthesized Brassica napus allotetraploids. Mol Biol Evol 36:709–726. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msz007
McClintock B (1984) The significance of responses of the genome to challenge. Science 226:792–801
Meyers BC, Axtell MJ, Bartel B, Bartel DP, Baulcombe D, Bowman JL, Cao X, Carrington JC, Chen X, Green PJ, Griffiths-Jones S, Jacobsen SE, Mallory AC, Martienssen RA, Poethig RS, Qi Y, Vaucheret H, Voinnet O, Watanabe Y, Weigel D, Zhu J-K (2008) Criteria for annotation of plant MicroRNAs. Plant Cell Online 20:3186–3190. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.108.064311
Mobberley DG (1956) Taxonomy and distribution of the genus Spartina. Iowa State University
Moran Y, Agron M, Praher D, Technau U (2017) The evolutionary origin of plant and animal microRNAs. Nat Ecol Evol 1:0027. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41559-016-0027
Nawrocki EP, Burge SW, Bateman A, Daub J, Eberhardt RY, Eddy SR, Floden EW, Gardner PP, Jones TA, Tate J, Finn RD (2015) Rfam 12.0: updates to the RNA families database. Nucleic Acids Res 43:D130–D137. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku1063
Ng DW-K, Lu J, Chen ZJ (2012) Big roles for small RNAs in polyploidy, hybrid vigor, and hybrid incompatibility. Curr Opin Plant Biol 15:154–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2012.01.007
Novák P, Neumann P, Pech J, Steinhaisl J, Macas J (2013) RepeatExplorer: a Galaxy-based web server for genome-wide characterization of eukaryotic repetitive elements from next-generation sequence reads. Bioinformatics 29:792–793. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btt054
Novák P, Neumann P, Macas J (2010) Graph-based clustering and characterization of repetitive sequences in next-generation sequencing data. BMC Bioinform 11:378. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-11-378
Parisod C, Salmon A, Zerjal T, Tenaillon M, Grandbastien M-A, Ainouche M (2009) Rapid structural and epigenetic reorganization near transposable elements in hybrid and allopolyploid genomes in Spartina. New Phytol 184:1003–1015
Parisod C, Alix K, Just J, Petit M, Sarilar V, Mhiri C, Ainouche M, Chalhoub B, Grandbastien M-A (2010) Impact of transposable elements on the organization and function of allopolyploid genomes. New Phytol 186:37–45. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.03096.x
Pereira V (2004) Insertion bias and purifying selection of retrotransposons in the Arabidopsis thaliana genome. Genome Biol 5:79
Peterson PM, Romaschenko K, Arrieta YH, Saarela JM (2014) A molecular phylogeny and new subgeneric classification of Sporobolus; (Poaceae: Chloridoideae: Sporobolinae). Taxon 63:1212–1243
Piriyapongsa J, Jordan IK (2008) Dual coding of siRNAs and miRNAs by plant transposable elements. RNA 14:814–821. https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.916708
Qin Z, Chen J, Jin L, Duns GJ, Ouyang P (2015) Differential expression of miRNAs under salt stress in Spartina alterniflora leaf tissues. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 15:1554–1561. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2015.9004
Ren R, Wang H, Guo C, Zhang N, Zeng L, Chen Y, Ma H, Qi J (2018) Widespread whole genome duplications contribute to genome complexity and species diversity in Angiosperms. Mol Plant 11:414–428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2018.01.002
Renny-Byfield S, Wendel JF (2014) Doubling down on genomes: polyploidy and crop plants. Am J Bot 101:1711–1725. https://doi.org/10.3732/ajb.1400119
Risso D, Schwartz K, Sherlock G, Dudoit S (2011) GC-content normalization for RNA-Seq data. BMC Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-12-480
Rousseau-Gueutin M, Bellot S, Martin GE, Boutte J, Chelaifa H, Lima O, Michon-Coudouel S, Naquin D, Salmon A, Ainouche K, Ainouche M (2015) The chloroplast genome of the hexaploid Spartina maritima (Poaceae, Chloridoideae): comparative analyses and molecular dating. Mol Phylogenet Evol 93:5–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2015.06.013
Salmon A, Ainouche ML, Wendel JF (2005) Genetic and epigenetic consequences of recent hybridization and polyploidy in Spartina (Poaceae). Mol Ecol 14:1163–1175
Sarilar V, Palacios PM, Rousselet A, Ridel C, Falque M, Eber F, Chèvre A-M, Joets J, Brabant P, Alix K (2013) Allopolyploidy has a moderate impact on restructuring at three contrasting transposable element insertion sites in resynthesized Brassica napus allotetraploids. New Phytol 198:593–604. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12156
Shen Y, Sun S, Hua S, Shen E, Ye C-Y, Cai D, Timko MP, Zhu Q-H, Fan L (2017) Analysis of transcriptional and epigenetic changes in hybrid vigor of allopolyploid Brassica napus uncovers key roles for small RNAs. Plant J 91:874–893. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.13605
Shimizu-Inatsugi R, Lihová J, Iwanaga H, Kudoh H, Marhold K, Savolainen O, Watanabe K, Yakubov VV, Shimizu KK (2009) The allopolyploid Arabidopsis kamchatica originated from multiple individuals of Arabidopsis lyrata and Arabidopsis halleri. Mol Ecol 18:4024–4048. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2009.04329.x
Shivaprasad PV, Dunn RM, Santos BA, Bassett A, Baulcombe DC (2012) Extraordinary transgressive phenotypes of hybrid tomato are influenced by epigenetics and small silencing RNAs: RNA silencing influences transgressive hybrid phenotypes. EMBO J 31:257–266. https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2011.458
Simon SA, Meyers BC (2011) Small RNA-mediated epigenetic modifications in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 14:148–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2010.11.007
Slotkin RK, Martienssen R (2007) Transposable elements and the epigenetic regulation of the genome. Nat Rev Genet 8:272–285. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2072
Slotkin RK, Vaughn M, Borges F, Tanurdžić M, Becker JD, Feijó JA, Martienssen RA (2009) Epigenetic reprogramming and small RNA silencing of transposable elements in pollen. Cell 136:461–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2008.12.038
Soltis DE, Soltis PS, Pires JC, Kovarik A, Tate JA, Mavrodiev E (2004) Recent and recurrent polyploidy in Tragopogon (Asteraceae): cytogenetic, genomic and genetic comparisons. Biol J Linn Soc 82:485–501. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8312.2004.00335.x
Soltis PS, Marchant DB, Van de Peer Y, Soltis DE (2015) Polyploidy and genome evolution in plants. Curr Opin Genet Dev 35:119–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gde.2015.11.003
Srivastava PK, Moturu T, Pandey P, Baldwin IT, Pandey SP (2014) A comparison of performance of plant miRNA target prediction tools and the characterization of features for genome-wide target prediction. BMC Genomics 15:348. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-15-348
Stapley J, Santure AW, Dennis SR (2015) Transposable elements as agents of rapid adaptation may explain the genetic paradox of invasive species. Mol Ecol 24:2241–2252. https://doi.org/10.1111/mec.13089
Strong D, Ayres D (2013) Ecological and evolutionary misadventures of Spartina. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 44:389–410
Sunkar R (2005) Identification and characterization of endogenous small interfering RNAs from rice. Nucleic Acids Res 33:4443–4454. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gki758
Taylor RS, Tarver JE, Hiscock SJ, Donoghue PCJ (2014) Evolutionary history of plant microRNAs. Trends Plant Sci 19:175–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2013.11.008
Taylor RS, Tarver JE, Foroozani A, Donoghue PCJ (2017) MicroRNA annotation of plant genomes—do it right or not at all. BioEssays 39:1600113. https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.201600113
Van de Peer Y, Mizrachi E, Marchal K (2017) The evolutionary significance of polyploidy. Nat Rev Genet 18:411–424. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg.2017.26
Vicient CM (2010) Transcriptional activity of transposable elements in maize. BMC Genomics 11:601. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-11-601
Vicient CM, Casacuberta JM (2017) Impact of transposable elements on polyploid plant genomes. Ann Bot 120:195–207. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcx078
Voinnet O (2009) Origin, biogenesis, and activity of plant microRNAs. Cell 136:669–687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.046
Wang L, Wang M-B, Tu J-X, Helliwell CA, Waterhouse PM, Dennis ES, Fu T-D, Fan Y-L (2007) Cloning and characterization of microRNAs from Brassica napus. FEBS Lett 581:3848–3856. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2007.07.010
Wendel JF (2000) Genome evolution in polyploids. Plant Mol Biol 42:225–249. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006392424384
Wu L, Zhou H, Zhang Q, Zhang J, Ni F, Liu C, Qi Y (2010) DNA methylation mediated by a microRNA pathway. Mol Cell 38:465–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2010.03.008
Xie M, Yu B (2015) siRNA-directed DNA methylation in plants. Curr Genomics 16:23–31. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389202915666141128002211
Yang Q, Ye QA, Liu Y (2015) Mechanism of siRNA production from repetitive DNA. Genes Dev 29:526–537. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.255828.114
Yi X, Zhang Z, Ling Y, Xu W, Su Z (2015) PNRD: a plant non-coding RNA database. Nucleic Acids Res 43:D982–D989. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku1162
Yoo M-J, Liu X, Pires JC, Soltis PS, Soltis DE (2014) Nonadditive gene expression in polyploids. Annu Rev Genet 48:485–517. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-genet-120213-092159
Zandkarimi H, Bedre R, Solis J, Mangu V, Baisakh N (2015) Sequencing and expression analysis of salt-responsive miRNAs and target genes in the halophyte smooth cordgrass (Spartina alternifolia Loisel). Mol Biol Rep 42:1341–1350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-015-3880-z
Zhang B (2015) MicroRNA: a new target for improving plant tolerance to abiotic stress. J Exp Bot 66:1749–1761. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv013
Zhang L, Peng Y, Wei X, Dai Y, Yuan D, Lu Y, Pan Y, Zhu Z (2014) Small RNAs as important regulators for the hybrid vigour of super-hybrid rice. J Exp Bot 65:5989–6002. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eru337
Zhou M, Zhu Y, Bai Y, Hänninen H, Meng X (2017) Transcriptionally active LTR retroelement-related sequences and their relationship with small RNA in moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). Mol Breed. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-017-0733-6
Acknowledgements
This work was financed under the International Associated Laboratory “Ecological Genomics of Polyploidy” supported by CNRS (INEE, UMR CNRS 6553 Ecobio), University of Rennes 1 and the Iowa State University (USA). The analyses benefited from the Molecular Ecology (UMR CNRS 6553 Ecobio) and Genouest (Biogenouest) facilities. A. C. R. and D. G. benefited from a PhD scholarship from the University of Rennes 1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ACR and DG contributed equally to this work. AS, AEA and MA designed the experiments. OL and ACR performed the experiments. ACR, DG, AS, AEA, and MA analysed data. ACR, DG, MA, AEA, and AS wrote the article.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cavé-Radet, A., Giraud, D., Lima, O. et al. Evolution of small RNA expression following hybridization and allopolyploidization: insights from Spartina species (Poaceae, Chloridoideae). Plant Mol Biol 102, 55–72 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-019-00931-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-019-00931-w