Abstract
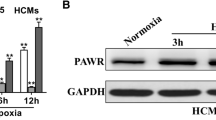
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are effector molecules that exert functions in cardiovascular diseases. Nevertheless, the effects of circRNAs on myocardial ischemia remain uninvestigated. This paper aimed to explore the functions of circ_0010729 in oxygen–glucose–deprivation (OGD)-caused injury of human cardiomyocytes (HCM). HCM were exposed to OGD environment for 4 h. Then the expression of circ_0010729 was evaluated by RT-qPCR. After transfection, cell viability, apoptosis, and migration were examined to evaluate the impact of overexpression and knockdown of circ_0010729 on OGD-induced cell injury. The regulation between circ_0010729 and microRNA-145-5p (miR-145-5p) was verified. After miR-145-5p inhibitor transfection, whether aberrant miR-145-5p expression affected the modulation of circ_0010729 in OGD-induced cell injury was measured. Western blot was utilized to analyze mTOR and MEK/ERK pathway-related proteins. OGD treatment enhanced circ_0010729 expression and evoked cell injury in HCM. Moreover, OGD-induced injury was aggrandized by circ_0010729 overexpression via suppressing cell growth and migration in HCM. Knockdown of circ_0010729 attenuated OGD-induced injury. In addition, circ_0010729 negatively regulated miR-145-5p expression. MiR-145-5p inhibition reversed the effects of silencing circ_0010729 on OGD-induced injury and mTOR and MEK/ERK pathways. We demonstrated that silencing circ_0010729 activated mTOR and MEK/ERK pathways by up-regulating miR-145-5p, thereby protecting HCM from OGD-induced injury.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Change history
12 January 2022
This article has been retracted. Please see the Retraction Notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-022-04355-x
References
Moran AE, Forouzanfar MH, Roth GA, Mensah GA, Ezzati M, Flaxman A, Murray CJ, Naghavi M (2014) The global burden of ischemic heart disease in 1990 and 2010: the Global Burden of Disease 2010 study. Circulation 129:1493–1501
Baccarelli A, Wright R, Bollati V, Litonjua A, Zanobetti A, Tarantini L, Sparrow D, Vokonas P, Schwartz J (2010) Ischemic heart disease and stroke in relation to blood DNA methylation. Epidemiology (Cambridge, Mass.) 21:819
Varbo A, Benn M, Tybjærg-Hansen A, Jørgensen AB, Frikke-Schmidt R, Nordestgaard BG (2013) Remnant cholesterol as a causal risk factor for ischemic heart disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 61:427–436
Roerecke M, Rehm J (2010) Irregular heavy drinking occasions and risk of ischemic heart disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Epidemiol 171:633–644. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwp451
Thomsen M, Nordestgaard BG (2014) Myocardial infarction and ischemic heart disease in overweight and obesity with and without metabolic syndrome. JAMA Intern Med 174:15–22
Steg PG, Greenlaw N, Tendera M, Tardif J-C, Ferrari R, Al-Zaibag M, Dorian P, Hu D, Shalnova S, Sokn FJ (2014) Prevalence of anginal symptoms and myocardial ischemia and their effect on clinical outcomes in outpatients with stable coronary artery disease: data from the International Observational CLARIFY Registry. JAMA Intern Med 174:1651–1659
Marzilli M, Merz CNB, Boden WE, Bonow RO, Capozza PG, Chilian WM, DeMaria AN, Guarini G, Huqi A, Morrone D, Patel MR, Weintraub WS (2012) Obstructive coronary atherosclerosis and ischemic heart disease: an elusive link! J Am Coll Cardiol 60:951–956. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2012.02.082
Chen LL (2016) The biogenesis and emerging roles of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 17:205–211. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm.2015.32
Wang Y, Mo Y, Gong Z, Yang X, Yang M, Zhang S, Xiong F, Xiang B, Zhou M, Liao Q, Zhang W, Li X, Li X, Li Y, Li G, Zeng Z, Xiong W (2017) Circular RNAs in human cancer. Mol Cancer 16:25. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-017-0598-7
Fan X, Weng X, Zhao Y, Chen W, Gan T, Xu D (2017) Circular RNAs in cardiovascular disease: an overview. Biomed Res Int 2017:5135781
Geng H-H, Li R, Su Y-M, Xiao J, Pan M, Cai X-X, Ji X-P (2016) The circular RNA Cdr1as promotes myocardial infarction by mediating the regulation of miR-7a on its target genes expression. PLoS ONE 11:e0151753
Zhou B, Yu J-W (2017) A novel identified circular RNA, circRNA_010567, promotes myocardial fibrosis via suppressing miR-141 by targeting TGF-β1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 487:769–775
Zhou L-Y, Zhai M, Huang Y, Xu S, An T, Wang Y-H, Zhang R-C, Liu C-Y, Dong Y-H, Wang M (2018) The circular RNA ACR attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by suppressing autophagy via modulation of the Pink1/FAM65B pathway. Cell Death Differ 26(7):1299
Dang RY, Liu FL, Li Y (2017) Circular RNA hsa_circ_0010729 regulates vascular endothelial cell proliferation and apoptosis by targeting the miR-186/HIF-1alpha axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 490:104–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.05.164
Adnan M, Morton G, Hadi S (2011) Analysis of rpoS and bolA gene expression under various stress-induced environments in planktonic and biofilm phase using 2 − ΔΔCT method. Mol Cell Biochem 357:275–282
Kong QR, Ji DM, Li FR, Sun HY, Wang QX (2019) MicroRNA-221 promotes myocardial apoptosis caused by myocardial ischemia-reperfusion by down-regulating PTEN. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23:3967–3975. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201905_17826
Yuan M, Zhang L, You F, Zhou J, Ma Y, Yang F, Tao L (2017) MiR-145-5p regulates hypoxia-induced inflammatory response and apoptosis in cardiomyocytes by targeting CD40. Mol Cell Biochem 431:123–131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-2982-4
Nabel EG, Braunwald E (2012) A tale of coronary artery disease and myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med 366:54–63
Xu F, Yu H, Liu J, Cheng L (2014) Pyrroloquinoline quinone inhibits oxygen/glucose deprivation-induced apoptosis by activating the PI3 K/AKT pathway in cardiomyocytes. Mol Cell Biochem 386:107–115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1849-6
Zhang Z, Li H, Chen S, Li Y, Cui Z, Ma J (2017) Knockdown of microRNA-122 protects H9c2 cardiomyocytes from hypoxia-induced apoptosis and promotes autophagy. Med Sci Monit 23:4284
Li M, Ding W, Tariq MA, Chang W, Zhang X, Xu W, Hou L, Wang Y, Wang J (2018) A circular transcript of ncx1 gene mediates ischemic myocardial injury by targeting miR-133a-3p. Theranostics 8:5855–5869. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.27285
Zhou LY, Zhai M, Huang Y, Xu S, An T, Wang YH, Zhang RC, Liu CY, Dong YH, Wang M, Qian LL, Ponnusamy M, Zhang YH, Zhang J, Wang K (2019) The circular RNA ACR attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by suppressing autophagy via modulation of the Pink1/FAM65B pathway. Cell Death Differ 26:1299–1315. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-018-0206-4
Kulcheski FR, Christoff AP, Margis R (2016) Circular RNAs are miRNA sponges and can be used as a new class of biomarker. J Biotechnol 238:42–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2016.09.011
Li JH, Liu S, Zhou H, Qu LH, Yang JH (2014) starBase v2.0: decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D92–D97. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt1248
Wu Z, Zhao S, Li C, Liu C (2018) LncRNA TUG1 serves an important role in hypoxia-induced myocardial cell injury by regulating the miR-145-5p-Binp3 axis. Mol Med Rep 17:2422–2430
Saxton RA, Sabatini DM (2017) mTOR signaling in growth, metabolism, and disease. Cell 168:960–976. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.02.004
Laplante M, Sabatini DM (2012) mTOR signaling in growth control and disease. Cell 149:274–293
Wang Z-G, Wang Y, Huang Y, Lu Q, Zheng L, Hu D, Feng W-K, Liu Y-L, Ji K-T, Zhang H-Y, Fu X-B, Li X-K, Chu M-P, Xiao J (2015) bFGF regulates autophagy and ubiquitinated protein accumulation induced by myocardial ischemia/reperfusion via the activation of the PI3 K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Sci Rep 5:9287. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep09287
Zhang J, Wang C, Yu S, Luo Z, Chen Y, Liu Q, Hua F, Xu G, Yu P (2014) Sevoflurane postconditioning protects rat hearts against ischemia-reperfusion injury via the activation of PI3 K/AKT/mTOR signaling. Sci Rep 4:7317. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep07317
Cui H, Li X, Li N, Qi K, Li Q, Jin C, Zhang Q, Jiang L, Yang Y (2014) Induction of autophagy by tongxinluo through the MEK/ERK pathway protects human cardiac microvascular endothelial cells from hypoxia/reoxygenation injury. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 64:180–190. https://doi.org/10.1097/fjc.0000000000000104
Zhang Z, Li S, Cui M, Gao X, Sun D, Qin X, Narsinh K, Li C, Jia H, Li C, Han Y, Wang H, Cao F (2013) Rosuvastatin enhances the therapeutic efficacy of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells for myocardial infarction via PI3 K/Akt and MEK/ERK pathways. Basic Res Cardiol 108:333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-013-0333-5
Funding
This research did not receive any specific Grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: Qifeng Jin, Yuanyuan Chen. Performed the experiments and analyzed the data: Qifeng Jin. Wrote the manuscript: Qifeng Jin, Yuanyuan Chen.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Informed consent
All authors are informed and agree to publish.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article has been retracted. Please see the retraction notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-022-04355-x"
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, Q., Chen, Y. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Silencing circular RNA circ_0010729 protects human cardiomyocytes from oxygen–glucose deprivation-induced injury by up-regulating microRNA-145-5p. Mol Cell Biochem 462, 185–194 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-019-03621-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-019-03621-9