Abstract
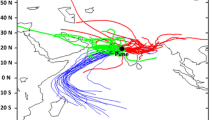
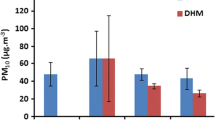
This study reports for the first-time the ambient concentrations of HULIS mass (HULIS-OM, Humic-like substances) and HULIS-C (carbon) in PM10 (particulate matter with aerodynamic diameter ≤ 10 μm) from the Indo-Gangetic Plain (IGP at Kanpur, wintertime). HULIS extraction followed by purification and isolation protocol with methanol: acetonitrile (1:1 v/v) on HLB (Hydrophilic-Lipophilic Balanced) cartridge has been established. Quantification of HULIS-C was achieved on a total organic carbon (TOC) analyser whereas HULIS-OM was determined gravimetrically. Consistently high recovery (> 90%) of HULIS-C based on analysis of Humic standard (sodium salt of Humic acid) suggested suitability of our established analytical protocol involving solvent extraction, purification and accurate quantification of HULIS. HULIS-OM varied from 17.3–38 μg m−3 during daytime and from 19.8–40.6 μg m−3 during night in this study. During daytime the HULIS-OM constituted 20–30% mass fraction of OMTotal and 10–15% of PM10 mass. However, a relatively low contribution of HULIS-OM has been observed during the night. This observation has been attributed to higher concentrations of OM and PM10 in night owing to nighttime chemical reactivity and condensation of organics in conjunction with shallower planetary boundary layer height. Strong correlation of HULIS-C with K+BB (R2 > 0.80) and significant day-night variability of HULIS-C/WSOC ratio in conjunction with air-mass back trajectories (showing transport of pollutants from upwind IGP) suggest biomass burning emission and secondary transformations as important sources of HULIS over IGP. High-loading of atmospheric PM10 (as high as 440 μg m−3) with significant contribution of water-soluble organic aerosols (WSOC/OC: ~ 0.40–0.80) during wintertime highlights their plausible potential role in fog and haze formation and their impact on regional-scale atmospheric radiative forcing over the IGP.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albinet, A., Minero, C., Vione, D.: Photochemical generation of reactive species upon irradiation of rainwater: negligible photoactivity of dissolved organic matter. Sci. Total Environ. 408(16), 3367–3373 (2010)
Andreae, M.O.: Soot carbon and excess fine potassium: long-range transport of combustion-derived aerosols. Science. 220(4602), 1148–1151 (1983)
Baduel, C., Voisin, D., Jaffrezo, J.L.: Seasonal variations of concentrations and optical properties of water soluble HULIS collected in urban environments. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 10(9), 4085–4095 (2010)
Birch, M.E., Cary, R.A.: Elemental carbon-based method for monitoring occupational exposures to particulate diesel exhaust. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 25(3), 221–241 (1996)
Castro, L.M., Pio, C.A., Harrison, R.M., Smith, D.J.T.: Carbonaceous aerosol in urban and rural European atmospheres: estimation of secondary organic carbon concentrations. Atmos. Environ. 33(17), 2771–2781 (1999)
Chakraborty, A., et al.: Water soluble organic aerosols in Indo-Gangetic Plain (IGP): Insights from aerosol mass spectrometry. Sci. Total Environ. 599–600, 1573–1582 (2017)
Choudhary, V., Rajput, P., Singh, D.K., Singh, A.K., Gupta, T.: Light absorption characteristics of brown carbon during foggy and non-foggy episodes over the Indo-Gangetic plain. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 9, 494–501 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2017.11.012
Claeys, M., Vermeylen, R., Yasmeen, F., Gómez-González, Y., Chi, X., Maenhaut, W., Mészáros, T., Salma, I.: Chemical characterisation of humic-like substances from urban, rural and tropical biomass burning environments using liquid chromatography with UV/Vis photodiode array detection and electrospray ionisation mass spectrometry. Environ. Chem. 9(3), 273–284 (2012)
Decesari, S., Facchini, M.C., Matta, E., Mircea, M., Fuzzi, S., Chughtai, A.R., Smith, D.M.: Water soluble organic compounds formed by oxidation of soot. Atmos. Environ. 36(11), 1827–1832 (2002)
Dinar, E., Taraniuk, I., Graber, E.R., Katsman, S., Moise, T., Anttila, T., Mentel, T.F., Rudich, Y.: Cloud condensation nuclei properties of model and atmospheric HULIS. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 6(9), 2465–2482 (2006)
Draxler, R.R., Rolph, G.D.: HYSPLIT (Hybrid Single-Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory) Model access via NOAA ARL READY Website. NOAA Air Resources Laboratory, Silver Spring (2003). http://www.arl.noaa.gov/ready/hysplit4.html
Duarte, R.M.B.O., Santos, E.B.H., Pio, C.A., Duarte, A.C.: Comparison of structural features of water-soluble organic matter from atmospheric aerosols with those of aquatic humic substances. Atmos. Environ. 41(37), 8100–8113 (2007)
Falkovich, A.H., Graber, E.R., Schkolnik, G., Rudich, Y., Maenhaut, W., Artaxo, P.: Low molecular weight organic acids in aerosol particles from Rondônia, Brazil, during the biomass-burning, transition and wet periods. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 5(3), 781–797 (2005)
Fan, X., Song, J., Peng, P.A.: Temporal variations of the abundance and optical properties of water soluble Humic-Like Substances (HULIS) in PM2.5 at Guangzhou, China. Atmos. Res. 172–173, 8–15 (2016a)
Fan, X., et al.: Comprehensive characterization of humic-like substances in smoke PM2.5 emitted from the combustion of biomass materials and fossil fuels. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2016, 1–39 (2016b)
Feczko, T., Puxbaum, H., Kasper-Giebl, A., Handler, M., Limbeck, A., Gelencsér, A., Pio, C., Preunkert, S., Legrand, M.: Determination of water and alkaline extractable atmospheric humic-like substances with the TU Vienna HULIS analyzer in samples from six background sites in Europe. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 112(D23), (2007). https://doi.org/10.1029/2006JD008331
Fu, P.Q., Kawamura, K., Pavuluri, C.M., Swaminathan, T., Chen, J.: Molecular characterization of urban organic aerosol in tropical India: contributions of primary emissions and secondary photooxidation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 10(6), 2663–2689 (2010)
Graber, E.R., Rudich, Y.: Atmospheric HULIS: how humic-like are they? A comprehensive and critical review. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 6(3), 729–753 (2006)
Hoffer, A., Gelencsér, A., Guyon, P., Kiss, G., Schmid, O., Frank, G.P., Artaxo, P., Andreae, M.O.: Optical properties of humic-like substances (HULIS) in biomass-burning aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 6(11), 3563–3570 (2006)
Kanakidou, M., Seinfeld, J.H., Pandis, S.N., Barnes, I., Dentener, F.J., Facchini, M.C., van Dingenen, R., Ervens, B., Nenes, A., Nielsen, C.J., Swietlicki, E., Putaud, J.P., Balkanski, Y., Fuzzi, S., Horth, J., Moortgat, G.K., Winterhalter, R., Myhre, C.E.L., Tsigaridis, K., Vignati, E., Stephanou, E.G., Wilson, J.: Organic aerosol and global climate modelling: a review. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 5(4), 1053–1123 (2005)
Kaul, D.S., Gupta, T., Tripathi, S.N., Tare, V., Collett Jr., J.L.: Secondary organic aerosol: a comparison between foggy and nonfoggy days. Environ. Sci. Technol. 45(17), 7307–7313 (2011)
Kawamura, K., Imai, Y., Barrie, L.A.: Photochemical production and loss of organic acids in high Arctic aerosols during long-range transport and polar sunrise ozone depletion events. Atmos. Environ. 39(4), 599–614 (2005)
Keene, W.C., Pszenny, A.A.P., Galloway, J.N., Hawley, M.E.: Sea-salt corrections and interpretation of constituent ratios in marine precipitation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 91(D6), 6647–6658 (1986)
Kiss, G., et al.: Characterization of water-soluble organic matter isolated from atmospheric fine aerosol. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 107(D21), 8339 (2002)
Krivácsy, Z., Gelencsér, A., Kiss, G., Mészáros, E., Molnár, Á., Hoffer, A., Mészáros, T., Sárvári, Z., Temesi, D., Varga, B., Baltensperger, U., Nyeki, S., Weingartner, E.: Study on the chemical character of water soluble organic compounds in fine atmospheric aerosol at the Jungfraujoch. J. Atmos. Chem. 39(3), 235–259 (2001)
Krivácsy, Z., Kiss, G., Ceburnis, D., Jennings, G., Maenhaut, W., Salma, I., Shooter, D.: Study of water-soluble atmospheric humic matter in urban and marine environments. Atmos. Res. 87(1), 1–12 (2008)
Kumar, V., Goel, A., Rajput, P.: Compositional and surface characterization of HULIS by UV-Vis, FTIR, NMR and XPS: Wintertime study in Northern India. Atmos. Environ. 164, 468–475 (2017)
Lin, P., Huang, X.F., He, L.Y., Zhen Yu, J.: Abundance and size distribution of HULIS in ambient aerosols at a rural site in South China. J. Aerosol Sci. 41(1), 74–87 (2010)
Ming, Y., Ramaswamy, V., Ginoux, P.A., Horowitz, L.H.: Direct radiative forcing of anthropogenic organic aerosol. J. Geophys. Res. 110(D20), D20208 (2005)
Pavlovic, J., Hopke, P.K.: Chemical nature and molecular weight distribution of the water-soluble fine and ultrafine PM fractions collected in a rural environment. Atmos. Environ. 59, 264–271 (2012)
Qiao, T., et al.: Simultaneous monitoring and compositions analysis of PM1 and PM2.5 in Shanghai: Implications for characterization of haze pollution and source apportionment. Sci. Total Environ. 557–558, 386–394 (2016)
Rajeev, P., Rajput, P., Gupta, T.: Chemical characteristics of aerosol and rain water during an El Niño and PDO influenced Indian summer monsoon. Atmos. Environ. 145, 192–200 (2016)
Rajput, P.: OM/OC ratio of polar and non-polar organic matter during wintertime from Indo-Gangetic plain: implications to regional-scale radiative forcing. Aerosol Science and Engineering. 2, 153–164 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41810-018-0032-6
Rajput, P., Sarin, M.M.: Polar and non-polar organic aerosols from large-scale agricultural-waste burning emissions in northern India: implications to organic mass-to-organic carbon ratio. Chemosphere. 103(0), 74–79 (2014)
Rajput, P., Sarin, M.M., Rengarajan, R., Singh, D.: Atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) from post-harvest biomass burning emissions in the Indo-Gangetic plain: isomer ratios and temporal trends. Atmos. Environ. 45(37), 6732–6740 (2011)
Rajput, P., Sarin, M.M., Kundu, S.S.: Atmospheric particulate matter (PM2.5), EC, OC, WSOC and PAHs from NE-Himalaya: abundances and chemical characteristics. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 4(2), 214–221 (2013)
Rajput, P., Sarin, M., Sharma, D., Singh, D.: Characteristics and emission budget of carbonaceous species from post-harvest agricultural-waste burning in source region of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. Tellus-B. 66, (2014a). https://doi.org/10.3402/tellusb.v66.21026
Rajput, P., Sarin, M.M., Sharma, D., Singh, D.: Organic aerosols and inorganic species from post-harvest agricultural-waste burning emissions over northern India: impact on mass absorption efficiency of elemental carbon. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts. 16(0), 2371–2379 (2014b)
Rajput, P., et al.: Wintertime source-apportionment of PM1 from Kanpur in the indo-Gangetic plain. Clim. Chang. 1(4), 503–507 (2015)
Rajput, P., Gupta, T., Kumar, A.: The diurnal variability of sulfate and nitrate aerosols during wintertime in the Indo-Gangetic plain: implications for heterogeneous phase chemistry. RSC Adv. 6(92), 89879–89887 (2016)
Rajput, P., Anjum, M.H., Gupta, T.: One year record of bioaerosols and particles concentration in Indo-Gangetic Plain: Implications of biomass burning emissions to high-level of endotoxin exposure. Environ. Pollut. 224, 98–106 (2017)
Rajput, P., Singh, D.K., Singh, A.K., Gupta, T.: Chemical composition and source-apportionment of sub-micron particles during wintertime over Northern India: New insights on influence of fog-processing. Environ. Pollut. 233, 81–91 (2018)
Ramanathan, V., Ramana, M.V., Roberts, G., Kim, D., Corrigan, C., Chung, C., Winker, D.: Warming trends in Asia amplified by brown cloud solar absorption. Nature. 448(7153), 575–578 (2007)
Rengarajan, R., Sarin, M.M., Sudheer, A.K.: Carbonaceous and inorganic species in atmospheric aerosols during wintertime over urban and high-altitude sites in North India. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 112(D21), D21307 (2007)
Salma, I., Ocskay, R., Chi, X., Maenhaut, W.: Sampling artefacts, concentration and chemical composition of fine water-soluble organic carbon and humic-like substances in a continental urban atmospheric environment. Atmos. Environ. 41(19), 4106–4118 (2007)
Salma, I., Mészáros, T., Maenhaut, W., Vass, E., Majer, Z.: Chirality and the origin of atmospheric humic-like substances. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 10(3), 1315–1327 (2010)
Salma, I., Mészáros, T., Maenhaut, W.: Mass size distribution of carbon in atmospheric humic-like substances and water soluble organic carbon for an urban environment. J. Aerosol Sci. 56, 53–60 (2013)
Samburova, V., Szidat, S., Hueglin, C., Fisseha, R., Baltensperger, U., Zenobi, R., Kalberer, M.: Seasonal variation of high-molecular-weight compounds in the water-soluble fraction of organic urban aerosols. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 110(D23), (2005). https://doi.org/10.1029/2005JD005910
Samburova, V., Connolly, J., Gyawali, M., Yatavelli, R.L.N., Watts, A.C., Chakrabarty, R.K., Zielinska, B., Moosmüller, H., Khlystov, A.: Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in biomass-burning emissions and their contribution to light absorption and aerosol toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 568, 391–401 (2016)
Seinfeld, J.H., Pandis, S.N.: Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics - from Air Pollution to Climate Change, 2nd edn. John Wiley & Sons, New York (2006)
Singh, A., et al.: Black Carbon and Elemental Carbon from Postharvest Agricultural-Waste Burning Emissions in the Indo-Gangetic Plain. Adv. Meteorol. 2014, 10 (2014)
Song, J., He, L., Peng, P.’., Zhao, J., Ma, S.: Chemical and isotopic composition of humic-like substances (HULIS) in ambient aerosols in Guangzhou. South China. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 46(5), 533–546 (2012)
Sorathia, F., Rajput, P., Gupta, T.: Dicarboxylic acids and levoglucosan in aerosols from Indo-Gangetic Plain: Inferences from day night variability during wintertime. Sci. Total Environ. 624, 451–460 (2018)
Stein, A.F., Draxler, R.R., Rolph, G.D., Stunder, B.J.B., Cohen, M.D., Ngan, F.: NOAA’s HYSPLIT atmospheric transport and dispersion modeling system. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 96(12), 2059–2077 (2015)
Sullivan, A.P., et al.: A method for on-line measurement of water-soluble organic carbon in ambient aerosol particles: results from an urban site. Geophys. Res. Lett. 31(13), L13105 (2004)
Turpin, B.J., Lim, H.-J.: Species Contributions to PM2.5 Mass Concentrations: Revisiting Common Assumptions for Estimating Organic Mass. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 35(1), 602–610 (2001)
Varga, B., Kiss, G., Ganszky, I., Gelencsér, A., Krivácsy, Z.: Isolation of water-soluble organic matter from atmospheric aerosol. Talanta. 55(3), 561–572 (2001)
Weber, R.J., et al.: A study of secondary organic aerosol formation in the anthropogenic-influenced southeastern United States. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 112(D13), D13302 (2007)
Yamasoe, M.R.A., Artaxo, P., Miguel, A.H., Allen, A.G.: Chemical composition of aerosol particles from direct emissions of vegetation fires in the Amazon Basin: water-soluble species and trace elements. Atmos. Environ. 34(10), 1641–1653 (2000)
Yue, S., Ren, H., Fan, S., Sun, Y., Wang, Z., Fu, P.: Springtime precipitation effects on the abundance of fluorescent biological aerosol particles and HULIS in Beijing. Sci. Rep. 6, 29618 (2016)
Zappoli, S., Andracchio, A., Fuzzi, S., Facchini, M.C., Gelencsér, A., Kiss, G., Krivácsy, Z., Molnár, Á., Mészáros, E., Hansson, H.C., Rosman, K., Zebühr, Y.: Inorganic, organic and macromolecular components of fine aerosol in different areas of Europe in relation to their water solubility. Atmos. Environ. 33(17), 2733–2743 (1999)
Zhang, F., Li, Z., Li, Y., Sun, Y., Wang, Z., Li, P., Sun, L., Wang, P., Cribb, M., Zhao, C., Fan, T., Yang, X., Wang, Q.: Impacts of organic aerosols and its oxidation level on CCN activity from measurement at a suburban site in China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 16(8), 5413–5425 (2016)
Zheng, G., He, K., Duan, F., Cheng, Y., Ma, Y.: Measurement of humic-like substances in aerosols: A review. Environ. Pollut. 181, 301–314 (2013)
Acknowledgements
We thankfully acknowledge internal funding support from IIT Kanpur. PR is thankful to the Council of Scientific & Industrial Research, New Delhi, India for providing CSIR-Senior Research Associate-ship (Pool Scientist # 8934-A/2017). Authors thank both the anonymous reviewers for their fruitful comments and suggestions and Prof. E. L. Atlas for editorial handling of our manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 83 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, V., Rajput, P. & Goel, A. Atmospheric abundance of HULIS during wintertime in Indo-Gangetic Plain: impact of biomass burning emissions. J Atmos Chem 75, 385–398 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10874-018-9381-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10874-018-9381-4