Abstract
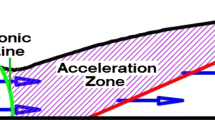
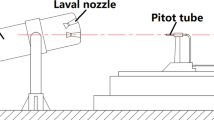
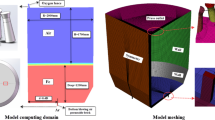
Supersonic jet characteristics of oxygen lance nozzles have a significant influence on smelting; however, presently, little research has been carried out to investigate the influence of wear on the jet characteristics at the nozzle exit. A numerical model and aerodynamic testing platform were developed to analyze supersonic jet characteristics under different inlet pressures and wear levels at the nozzle exit. The numerical model was first validated by comparing the numerical results with the measured data of the aerodynamic testing experiment. Then, the effects of the inlet pressure and nozzle exit wear on the jet velocity and degree of aggregation were studied. An increase in the nozzle inlet pressure is conducive to an increase in jet velocity but also causes earlier jet convergence. An increase in the nozzle exit wear results in the faster attenuation of jet velocity, not only reducing the jet velocity but also leading to an earlier convergence point for each jet. The results of this study can provide theoretical support for the design of an oxygen lance nozzle and process optimization of smelting in industrial application.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.L. Wang, Y.H. Lv, W.Y. Yang, S.G. Li, and X.W. Xu: Journal of Iron and Steel Research, International, 2011, vol. 18, pp. 12-16.
J.G. Li, Y.N. Zeng, J.Q. Wang, and Z.J. Han: J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 2011, vol. 18, pp. 1-18.
C.L. He, N.C. Yang, Q.M. Huang, C.T. Liu, L. Wu, Y. Hu, Z.H. Fu, and Z. Gao: Procedia Earth Planet. Sci., 2011, vol. 2, pp. 64-69.
Z.F. Yuan, X. Yang, Z.X. Lv, J.N. Huang, Y.F. Pan, and E.X. Ma: J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 2007, vol. 14, pp. 1-6.
Q. Li, M.M. Li, S.B. Kuang, and Z.S. Zou: Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2015, vol. 46, pp. 1494-1509.
M. Alam, J. Naser, and G.Brooks: Metallurgical & Materials Transactions B, 2010, vol. 41, pp. 636-645.
M. Lv, R. Zhu, Y.G. Guo, and Y.W. Wang: Metallurgical & Materials Transactions B, 2013, vol. 44, pp. 1560-1571.
R. Sambasivam, S.N. Lenka, F. Durst, M. Bock, S. Chandra, and S.K. Ajmania: Metallurgical & Materials Transactions B, 2007, vol. 38, pp. 45-53.
Z.L. Li, and D.Q. Cang: Steel research international, 2017, vol. 88, pp. 1600209.
G.S. Wei, R. Zhu, T. Cheng, and F. Zhao: Journal of Iron and Steel Research, International, 2016, vol. 23, pp. 997-1006.
N. Asahara, K.I. Naito, I. Kitagawa, M. Matsuo, M. Kumakura, and M. Iwasaki: Steel Research International, 2011, vol. 82, pp. 587-594.
A. Beketaeva, A.H. Abdalla, and Y. Moisseyeva: Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2015, vol. 798, pp. 5.
X.T. Liang: Steelmaking, 2014, vol. 30, pp. 30–33 + 74.
H.L. Chi, J.G. Li, and S. Feng: Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2014, vol. 35, pp. 91–96.
C.Y. Wang, L.B. Yang, X.C. Li, and H.Z. Cui: China Metallurgy, 2016, vol. 26, pp. 53-58.
X.Y. Wei, R. Zhu, L.D. Liu, D.S. Zhang, and C.T. Yang: Steelmaking, 2011, vol. 27, pp. 28–30 + 43.
M.M. Li, Q. Li, S.B. Kuang, and Z.S. Zou: Steel research international, 2015, vol. 86, pp. 1517-1529.
W.J. Wang, Z.F. Yuan, H. Matsuura, H.X. Zhao, C. Dai, and F. Tsukihashi: ISIJ International, 2010, vol. 50, pp. 491–500.
W.Y. Yang, C. Feng, M.L. Wang, Y.H. Lv, Y.B. Hu, X.Y. Peng: J. Iron Steel Res., 2017, vol. 29, pp. 807–15.
F. Liu, D. Sun, R. Zhu, and J. Ke: Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 2016, vol. 44, pp. 640-648.
F.S. Garajau, M.S. Guerra, B.T. Maiaa, and P.R. Cetlinb: Engineering Failure Analysis, 2019, vol. 96, pp. 175-185.
C.Feng, W.B. Tang, B.H. Liang, Y.M. Ma, W.M. Tang, H.Y. Qin, and Y.Liao: Energy for Metallurgical Industry, 2016, vol. 35, pp. 9-11.
I.M. Ghauri, M.Z. Butt, and S.M. Raza: J. Mater. Sci., 1990, vol. 25, pp. 4782–84.
C.B. Liu and W.Y. Yang:Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 1993, vol.5, pp. 94-100.
E.X. Ma, Z.P. Cai, Z.M. Qian, W.S. Wei, H. Tu, C.C. Wen, D.C. Chen, and K.Q.Tang: Engineering Chemistry & Metallurgy, 1991, vol. 12, pp. 370-376.
Z.P. Cai, and C.X. Zhang: Journal of University of Science and technology Beijing, 1995, vol. 17, pp. 75-79.
C.X. Zhang, Z.P. Cai, Z.H. Xu, and Y. Liang: Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 1995, vol. 17, pp. 94-99.
K. Liu: Doctoral Thesis, Northeastern University, 2008, pp. 68–69.
B.B. Ji and J.P. Chen: ANSYS ICEM CFD Detailed Illustration of Grid Generation Technology, 1st ed., China Water & Power Press, Beijing, 2012, pp. 153–70.
J.Z.Zhou, X.P.Xu, W.J.Chu, Z.C.Zhu, Y.H.Chen, and S.W.Lai: Applied Mechanics & Materials, 2013, vol. 423-426, pp. 1677-1684.
J.Z.Zhou, X.P.Xu, Z.C.Zhu, Y.C.Liu, W.J.Chu, and S.W.Lai: Machine Tool & Hydraulics, 2014, vol. 17, pp. 157-160.
C.X. Zhang, H. Tu, and Z.P. Cai: Journal of Iron and Steel Research,1996, vol. 8, pp. 47-50.
E.Brandaleze, E.Benavidez, V.Peirani, L.Santini, and C.Gorosurreta: Advances in Science and Technology, 2010, vol. 70, pp. 205-210.
C.B. Liu, W.Y. Yang, D.C.Chen, K.Q.Tang, D.R.Zhang, and G.C.Li: Iron and Steel, 1996, vol. 3, pp. 21-26.
F.S. Garajau, M.S. Guerra, B.T. Maiaa, P.R. Cetlinb, and D.A. Moreira: AISTech 2017 Proceedings, Pennsylvania, pp. 1365–75.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their thanks for the support by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (No. 51574021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Manuscript submitted May 13, 2019.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, C., Zhu, R., Han, B. et al. Effect of Nozzle Exit Wear on the Fluid Flow Characteristics of Supersonic Oxygen Lance. Metall Mater Trans B 51, 187–199 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-019-01722-w
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-019-01722-w