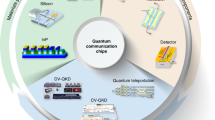
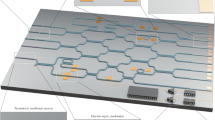
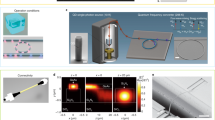
Abstract
Quantum technologies comprise an emerging class of devices capable of controlling superposition and entanglement of quantum states of light or matter, to realize fundamental performance advantages over ordinary classical machines. The technology of integrated quantum photonics has enabled the generation, processing and detection of quantum states of light at a steadily increasing scale and level of complexity, progressing from few-component circuitry occupying centimetre-scale footprints and operating on two photons, to programmable devices approaching 1,000 components occupying millimetre-scale footprints with integrated generation of multiphoton states. This Review summarizes the advances in integrated photonic quantum technologies and its demonstrated applications, including quantum communications, simulations of quantum chemical and physical systems, sampling algorithms, and linear-optic quantum information processing.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Freedman, S. J. & Clauser, J. F. Experimental test of local hidden-variable theories. Phys. Rev. Lett. 28, 938–941 (1972).
Wu, L.-A., Kimble, H. J., Hall, J. L. & Wu, H. Generation of squeezed states by parametric down conversion. Phys. Rev. Lett. 57, 2520–2523 (1986).
Bouwmeester, D. et al. Experimental quantum teleportation. Nature 390, 575–579 (1997).
Shalm, L. K. et al. Strong loophole-free test of local realism. Phys. Rev. Lett. 115, 250402 (2015).
Gisin, N., Ribordy, G., Tittel, W. & Zbinden, H. Quantum cryptography. Rev. Mod. Phys. 74, 145–195 (2002).
Ladd, T. D. et al. Quantum computers. Nature 464, 45–53 (2010).
Aspuru-Guzik, A. & Walther, P. Photonic quantum simulators. Nat. Phys. 8, 285–291 (2012).
Awschalom, D. D., Hanson, R., Wrachtrup, J. & Zhou, B. B. Quantum technologies with optically interfaced solid-state spins. Nat. Photon. 12, 516–527 (2018).
Knill, E., Laflamme, R. & Milburn, G. J. A scheme for efficient quantum computation with linear optics. Nature 409, 46–52 (2000).
Gottesman, D. & Chuang, I. L. Demonstrating the viability of universal quantum computation using teleportation and single-qubit operations. Nature 402, 390–393 (1999).
Raussendorf, R. & Briegel, H. J. A one-way quantum computer. Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 5188–5191 (2001).
Nielsen, M. A. Optical quantum computation using cluster states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 040503 (2004).
Aaronson, S. & Arkhipov, A. The computational complexity of linear optics. In Proc. Forty-third Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing 333–342 (Association for Computing Machinery, 2011).
Politi, A., Cryan, M. J., Rarity, J. G., Yu, S. & O’Brien, J. L. Silica-on-silicon waveguide quantum circuits. Science 320, 646–649 (2008).
Zhong, H.-S. et al. 12-photon entanglement and scalable scattershot Boson sampling with optimal entangled-photon pairs from parametric down-conversion. Phys. Rev. Lett. 121, 250505 (2018).
Matthews, J. C. F., Politi, A., Andre, S. & O’Brien, J. L. Manipulation of multiphoton entanglement in waveguide quantum circuits. Nat. Photon. 3, 346–350 (2009).
Shadbolt, P. J. et al. Generating, manipulating and measuring entanglement and mixture with a reconfigurable photonic circuit. Nat. Photon. 6, 45–49 (2012).
Laing, A. et al. High-fidelity operation of quantum photonic circuits. Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 211109 (2010).
Smith, B. J., Kundys, D., Thomas-Peter, N., Smith, P. G. R. & Walmsley, I. A. Phase-controlled integrated photonic quantum circuits. Opt. Express 17, 13516–13525 (2009).
Corrielli, G. et al. Rotated waveplates in integrated waveguide optics. Nat. Commun. 5, 4249 (2014).
Sansoni, L. et al. Polarization entangled state measurement on a chip. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 200503 (2010).
Crespi, A. et al. Integrated photonic quantum gates for polarization qubits. Nat. Commun. 2, 566 (2011).
Takesue, H. et al. Entanglement generation using silicon wire waveguide. Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 201108 (2007).
Bonneau, D. et al. Quantum interference and manipulation of entanglement in silicon wire waveguide quantum circuits. New J. Phys. 14, 045003 (2012).
Silverstone, J. W. et al. On-chip quantum interference between silicon photon-pair sources. Nat. Photon. 8, 104–108 (2013).
Zhang, M. et al. Generation of multiphoton quantum states on silicon. Light Sci. Appl. 8, 41 (2019).
Pernice, W. H. P. et al. High-speed and high-efficiency travelling wave single-photon detectors embedded in nanophotonic circuits. Nat. Commun. 3, 1325 (2012).
Lu, X. et al. Chip-integrated visible-telecom entangled photon pair source for quantum communication. Nat. Phys. 15, 373–381 (2019).
Zhang, X. et al. Integrated silicon nitride time-bin entanglement circuits. Opt. Lett. 43, 3469–3472 (2018).
Dutt, A. et al. On-chip optical squeezing. Phys. Rev. Appl. 3, 044005 (2015).
Schuck, C. et al. Quantum interference in heterogeneous superconducting-photonic circuits on a silicon chip. Nat. Commun. 7, 10352 (2016).
Tanzilli, S. et al. PPLN waveguide for quantum communication. Eur. Phys. J. D 18, 155–160 (2002).
Jin, H. et al. On-chip generation and manipulation of entangled photons based on reconfigurable lithium-niobate waveguide circuits. Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 103601 (2014).
Höpker, J. P. et al. Towards integrated superconducting detectors on lithium niobate waveguides. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/1708.06232 (2017).
Horn, R. et al. Monolithic source of photon pairs. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 153605 (2012).
Wang, J. et al. Gallium arsenide (GaAs) quantum photonic waveguide circuits. Opt. Commun. 327, 49–55 (2014).
Sprengers, J. P. et al. Waveguide superconducting single photon detectors for integrated quantum photonic circuits. Appl. Phys. Lett. 99, 181110 (2011).
Sibson, P. et al. Chip-based quantum key distribution. Nat. Commun. 8, 13984 (2017).
Abellan, C. et al. Quantum entropy source on an InP photonic integrated circuit for random number generation. Optica 3, 989–994 (2016).
Kues, M. et al. On-chip generation of high-dimensional entangled quantum states and their coherent control. Nature 546, 622–626 (2017).
Santagati, R. et al. Silicon photonic processor of two-qubit entangling quantum logic. J. Opt. 19, 114006 (2017).
Meany, T. et al. Laser written circuits for quantum photonics. Laser Photon. Rev. 9, 363–384 (2015).
Matsuda, N. et al. A monolithically integrated polarization entangled photon pair source on a silicon chip. Sci. Rep. 2, 817 (2012).
Wang, J. et al. Multidimensional quantum entanglement with large-scale integrated optics. Science 360, 285–291 (2018).
Feng, L.-T. et al. On-chip coherent conversion of photonic quantum entanglement between different degrees of freedom. Nat. Commun. 7, 11985 (2016).
Mohanty, A. et al. Quantum interference between transverse spatial waveguide modes. Nat. Commun. 8, 14010 (2017).
Harris, N. C. et al. Quantum transport simulations in a programmable nanophotonic processor. Nat. Photon. 11, 447–452 (2017).
Rudolph, T. Why I am optimistic about the silicon-photonic route to quantum computing. APL Photon. 2, 030901 (2017).
Engin, E. et al. Photon pair generation in a silicon micro-ring resonator with reverse bias enhancement. Opt. Express 21, 27826–27834 (2013).
Spring, J. B. et al. Chip-based array of near-identical, pure, heralded single-photon sources. Optica 4, 90–96 (2017).
Llewellyn, D. et al. Demonstration of chip-to-chip quantum teleportation. In Conference on Lasers Electro-Optics (CLEO) JTh5C.4 (Optical Society of America, 2019).
Kaneda, F. & Kwiat, P. G. High-efficiency single-photon generation via large-scale active time multiplexing. Sci. Adv. 5, eaaw8586 (2019).
Collins, M. J. et al. Integrated spatial multiplexing of heralded single-photon sources. Nat. Commun. 4, 2582 (2014).
Senellart, P., Solomon, G. & White, A. High-performance semiconductor quantum-dot single-photon sources. Nat. Nanotechnol. 12, 1026–1039 (2017).
He, Y.-M. et al. On-demand semiconductor single-photon source with near-unity indistinguishability. Nat. Nanotechnol. 8, 213–217 (2013).
Ding, X. et al. On-demand single photons with high extraction efficiency and near-unity indistinguishability from a resonantly driven quantum dot in a micropillar. Phys. Rev. Lett. 116, 020401 (2016).
Somaschi, N. et al. Near-optimal single-photon sources in the solid state. Nat. Photon. 10, 340–345 (2016).
Arcari, M. et al. Near-unity coupling efficiency of a quantum emitter to a photonic crystal waveguide. Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 093603 (2014).
Lenzini, F. et al. Active demultiplexing of single photons from a solid-state source. Laser. Rev. 11, 1600297 (2017).
Wang, H. et al. High-efficiency multiphoton boson sampling. Nat. Photon. 11, 361–365 (2017).
Wang, H. et al. Toward scalable boson sampling with photon loss. Phys. Rev. Lett. 120, 230502 (2018).
Loredo, J. C. et al. Boson sampling with single-photon Fock states from a bright solid-state source. Phys. Rev. Lett. 118, 130503 (2017).
Hadfield, R. H. Single-photon detectors for optical quantum information applications. Nat. Photon. 3, 696–705 (2009).
Najafi, F. et al. On-chip detection of non-classical light by scalable integration of single-photon detectors. Nat. Commun. 6, 5873 (2015).
Gerrits, T. et al. On-chip, photon-number-resolving, telecommunication-band detectors for scalable photonic information processing. Phys. Rev. A 84, 060301 (2011).
Sahin, D. et al. Waveguide photon-number-resolving detectors for quantum photonic integrated circuits. Appl. Phys. Lett. 103, 111116 (2013).
Martinez, N. J. D. et al. Single photon detection in a waveguidecoupled Ge-on-Si lateral avalanche photodiode. Opt. Express 25, 16130–16139 (2017).
Vines, P. et al. High performance planar germanium-on-silicon single-photon avalanche diode detectors. Nat. Commun. 10, 1086 (2019).
Honjo, T., Inoue, K. & Takahashi, H. Differential-phase-shift quantum key distribution experiment with a planar light-wave circuit Mach–Zehnder interferometer. Opt. Lett. 29, 2797–2799 (2004).
Ma, C. et al. Silicon photonic transmitter for polarization-encoded quantum key distribution. Optica 3, 1274–1278 (2016).
Sibson, P. et al. Integrated silicon photonics for high-speed quantum key distribution. Optica 4, 172–177 (2017).
Bunandar, D. et al. Metropolitan quantum key distribution with silicon photonics. Phys. Rev. X 8, 021009 (2018).
Thompson, M. G. Large-scale integrated quantum photonic technologies for communications and computation. In Optical Fiber Communication Conference (OFC) W3D.3 (Optical Society of America, 2019).
Ding, Y. et al. High-dimensional quantum key distribution based on multicore fiber using silicon photonic integrated circuits. npj Quantum Inf. 3, 25 (2017).
Semenenko, H., Sibson, P., Thompson, M. G. & Erven, C. Interference between independent photonic integrated devices for quantum key distribution. Opt. Lett. 44, 275–278 (2019).
Agnesi, C. et al. Hong-Ou-Mandel interference between independent III–V on silicon waveguide integrated lasers. Opt. Lett. 44, 271–274 (2019).
Autebert, C. et al. Integrated AlGaAs source of highly indistinguishable and energy-time entangled photons. Optica 3, 143–146 (2016).
Grassani, D. et al. Micrometer-scale integrated silicon source of time-energy entangled photons. Optica 2, 88–94 (2015).
Wang, J. et al. Chip-to-chip quantum photonic interconnect by path-polarization interconversion. Optica 3, 407–413 (2016).
Roger, T. et al. Real-time interferometric quantum random number generation on chip. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 36, B137–B142 (2019).
Raffaelli, F. et al. A homodyne detector integrated onto a photonic chip for measuring quantum states and generating random numbers. Quantum Sci. Technol. 3, 025003 (2018).
Politi, A., Matthews, J. C. F. & O’Brien, J. L. Shor’s quantum factoring algorithm on a photonic chip. Science 325, 1221 (2009).
Carolan, J. et al. Universal linear optics. Science 349, 711–716 (2015).
Metcalf, B. J. et al. Quantum teleportation on a photonic chip. Nat. Photon. 8, 770–774 (2014).
Peruzzo, A. et al. A variational eigenvalue solver on a photonic quantum processor. Nat. Commun. 5, 4213 (2013).
Flamini, F. et al. Thermally reconfigurable quantum photonic circuits at telecom wavelength by femtosecond laser micromachining. Light Sci. Appl. 4, e354 (2015).
Qiang, X. et al. Large-scale silicon quantum photonics implementing arbitrary two-qubit processing. Nat. Photon. 12, 534–539 (2018).
Sparrow, C. et al. Simulating the vibrational quantum dynamics of molecules using photonics. Nature 557, 660–667 (2018).
Taballione, C. et al. 8x8 reconfigurable quantum photonic processor based on silicon nitride waveguides. Opt. Express 19, 26842–26857 (2019).
Silverstone, J. W. et al. Qubit entanglement between ring-resonator photon-pair sources on a silicon chip. Nat. Commun. 6, 7948 (2015).
Ciampini, M. A. et al. Path-polarization hyperentangled and cluster states of photons on a chip. Light Sci. Appl. 5, e16064 (2016).
Reimer, C. et al. High-dimensional one-way quantum processing implemented on d-level cluster states. Nat. Phys. 15, 148–153 (2019).
Adcock, J. C., Vigliar, C., Santagati, R., Silverstone, J. W. & Thompson, M. G. Programmable four-photon graph states on a silicon chip. Nat. Commun. 10, 3528 (2019).
Harrow, A. W. & Montanaro, A. Quantum computational supremacy. Nature 549, 203–209 (2017).
Spagnolo, N. et al. Three-photon bosonic coalescence in an integrated tritter. Nat. Commun. 4, 1606 (2013).
Metcalf, B. J. et al. Multiphoton quantum interference in a multiport integrated photonic device. Nat. Commun. 4, 1356 (2013).
Crespi, A. et al. Integrated multimode interferometers with arbitrary designs for photonic boson sampling. Nat. Photon. 7, 545–549 (2013).
Tillmann, M. et al. Experimental boson sampling. Nat. Photon. 7, 540–544 (2013).
Spring, J. B. et al. Boson sampling on a photonic chip. Science 339, 798–801 (2013).
Carolan, J. et al. On the experimental verification of quantum complexity in linear optics. Nat. Photon. 8, 621–626 (2014).
Broome, M. A. et al. Photonic boson sampling in a tunable circuit. Science 339, 794–798 (2013).
Tillmann, M. et al. Generalized multiphoton quantum interference. Phys. Rev. X 5, 041015 (2015).
Bentivegna, M. et al. Experimental scattershot boson sampling. Sci. Adv. 1, e1400255 (2015).
Paesani, S. et al. Generation and sampling of quantum states of light in a silicon chip. Nat. Phys. 15, 925–929 (2019).
Zhong, H.-S. et al. Experimental Gaussian Boson sampling. Sci. Bull. 64, 511–515 (2019).
Aaronson, S. & Arkhipov, A. Boson sampling is far from uniform. Quantum Inf. Comput. 14, 1383–1423 (2014).
Spagnolo, N. et al. Experimental validation of photonic boson sampling. Nat. Photon. 8, 615–620 (2014).
Giordani, T. et al. Experimental statistical signature of many-body quantum interference. Nat. Photon. 12, 173–178 (2018).
Agresti, I. et al. Pattern recognition techniques for Boson sampling validation. Phys. Rev. X 9, 011013 (2019).
Neville, A. et al. Classical boson sampling algorithms with superior performance to near-term experiments. Nat. Phys. 13, 1153–1157 (2017).
Sansoni, L. et al. Two-particle bosonic-fermionic quantum walk via integrated photonics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 010502 (2012).
Crespi, A. et al. Anderson localization of entangled photons in an integrated quantum walk. Nat. Photon. 7, 322–328 (2013).
Pitsios, I. et al. Photonic simulation of entanglement growth and engineering after a spin chain quench. Nat. Commun. 8, 1569 (2017).
Peruzzo, A. et al. Quantum walks of correlated photons. Science 329, 1500–1503 (2010).
Crespi, A. et al. Particle statistics affects quantum decay and Fano interference. Phys. Rev. Lett. 114, 090201 (2015).
Caruso, F., Crespi, A., Ciriolo, A. G., Sciarrino, F. & Osellame, R. Fast escape of a quantum walker from an integrated photonic maze. Nat. Commun. 7, 1682 (2016).
Biggerstaff, D. N. et al. Enhancing coherent transport in a photonic network using controllable decoherence. Nat. Commun. 7, 11282 (2016).
Tang, H. et al. Experimental quantum fast hitting on hexagonal graphs. Nat. Photon. 12, 754–758 (2018).
Poulios, K. et al. Quantum walks of correlated photon pairs in two-dimensional waveguide arrays. Phys. Rev. Lett. 112, 143604 (2014).
Paesani, S. et al. Experimental Bayesian quantum phase estimation on a silicon photonic chip. Phys. Rev. Lett. 118, 100503 (2017).
Santagati, R. et al. Witnessing eigenstates for quantum simulation of Hamiltonian spectra. Sci. Adv. 4, eaap9646 (2018).
Huh, J., Guerreschi, G. G., Peropadre, B., McClean, J. R. & Aspuru-Guzik, A. Boson sampling for molecular vibronic spectra. Nat. Photon. 9, 615–620 (2015).
Wang, J. et al. Experimental quantum Hamiltonian learning. Nat. Phys. 13, 551–555 (2017).
Seok, T. J., Kwon, K., Henriksson, J., Luo, J. & Wu, M. C. 240×240 wafer-scale silicon photonic switches. In Optical Fiber Communication Conference (OFC) 2019 Th1E.5 (Optical Society of America, 2019).
Wang, C. et al. Integrated lithium niobate electro-optic modulators operating at CMOS-compatible voltages. Nature 562, 101–104 (2018).
He, M. et al. High-performance hybrid silicon and lithium niobite Mach-Zehnder modulators for 100 Gbit s−1 and beyond. Nat. Photon. 13, 359–364 (2019).
Abel, S. et al. Large Pockels effect in micro- and nanostructured barium titanate integrated on silicon. Nat. Mater. 18, 42–47 (2019).
Li, G. et al. Ultralow-loss, high-density SOI optical waveguide routing for macrochip interconnects. Opt. Express 20, 12035–12039 (2012).
Zhang, M., Wang, C., Cheng, R., Shams-Ansari, A. & Loncar, M. Monolithic ultra-high-Q lithium niobate microring resonator. Optica 4, 1536–1537 (2017).
Wu, R. et al. Long low-loss-litium niobate on insulator waveguides with sub-nanometer surface roughness. Nanomaterials 8, 910 (2018).
Bauters, J. F. et al. Planar waveguides with less than 0.1 dB/m propagation loss fabricated with wafer bonding. Opt. Express 19, 24090–24101 (2011).
Lee, H., Chen, T., Li, J., Painter, O. & Vahala, K. J. Ultra-low-loss optical delay line on a silicon chip. Nat. Commun. 3, 867 (2012).
Digeronimo, G. E. et al. Integration of single-photon sources and detectors on GaAs. Photonics 3, 55 (2016).
Khasminskaya, S. et al. Fully integrated quantum photonic circuit with an electrically driven light source. Nat. Photon. 10, 727–732 (2016).
Ong, J., Kumar, R. & Mookherjea, S. Ultra-high-contrast and tunable-bandwidth filter using cascaded high-order silicon microring filters. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 25, 1543–1546 (2013).
Piekarek, M. et al. High-extinction ratio integrated photonic filters for silicon quantum photonics. Opt. Lett. 42, 815–818 (2017).
Eltes, F. et al. An integrated cryogenic optical modulator. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/1904.10902 (2019).
Miller, D. A. B. Perfect optics with imperfect components. Optica 2, 747–750 (2015).
Carolan, J. et al. Scalable feedback control of single photon sources for photonic quantum technologies. Optica 6, 335–340 (2019).
Biamonte, J. et al. Quantum machine learning. Nature 549, 195–202 (2017).
Acknowledgements
We thank C.-Y. Lu for discussions on quantum dot sources and J. Bulmer for discussions on photonic quantum information processing. J.W. acknowledges support from the Natural Science Foundation of China (61975001), National Key Research & Development (R&D) Program of China (2018YFB1107205), Beijing Natural Science Foundation (Z190005), Beijing Academy of Quantum Information Sciences (Y18G21) and the Key R&D Program of Guangdong Province (2018B030329001). F.S. acknowledges support from the H2020-FETPROACT-2014 Grant QUCHIP (Quantum Simulation on a Photonic Chip; grant agreement no. 641039). A.L. acknowledges support from an EPSRC (Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council) Early Career Fellowship EP/N003470/1. M.G.T. acknowledges support from an ERC (European Research Council) starter grant (ERC-2014-STG 640079) and an EPSRC Early Career Fellowship (EP/K033085/1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
M.T. is involved in developing quantum photonic technologies at PsiQuantum Corporation.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Sciarrino, F., Laing, A. et al. Integrated photonic quantum technologies. Nat. Photonics 14, 273–284 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-019-0532-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-019-0532-1
This article is cited by
-
An elementary review on basic principles and developments of qubits for quantum computing
Nano Convergence (2024)
-
Non-Hermitian topological phase transitions controlled by nonlinearity
Nature Physics (2024)
-
Inverse design of high-dimensional quantum optical circuits in a complex medium
Nature Physics (2024)
-
Quantum interference of pulsed time-bin entanglement generated from silicon ring resonator
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Logical rotation of non-separable states via uniformly self-assembled chiral superstructures
Nature Communications (2024)