Abstract
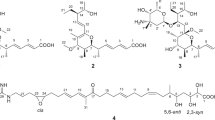
Two new azaphilone derivatives, comazaphilones G and H (1 and 2), together with eight known analogues (3–10), were isolated from an endophytic fungus Penicillium variabile. Their structures were established on the basis of extensive spectroscopic analysis. Compounds 1, 2 and 4–10 were tested their nitric oxide inhibitory activities in lipopolysaccharide-activated RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. Compounds 1, 2 and 4–9 showed significant nitric oxide inhibitory activities with IC50 values ranged from 4.35 ± 0.05 to 40.52 ± 0.47 μM.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gao SS, Li XM, Zhang Y, Li CS, Cui CM, Wang BG. Comazaphilones A- F, azaphilone derivatives from the marine sediment-derived fungus Penicillium commune QSD-17. J Nat Prod. 2011;74:256–61.
Chen C, Wang J, Zhu H, Wang J, Xue Y, Wei G, et al. Chaephilones A and B, two new azaphilone derivatives isolated from Chaetomium globosum. Chem Biodivers. 2016;13:422–6.
Chen W, Chen R, Liu Q, He Y, He K, Ding X, et al. Orange, red, yellow: biosynthesis of azaphilone pigments in Monascus fungi. Chem Sci. 2017;8:4917–25.
Yamada T, Jinno M, Kikuchi T, Kajimoto T, Numata A, Tanaka R. Three new azaphilones produced by a marine fish-derived Chaetomium globosum. J Antibiot. 2012;65:413.
Zhao DL, Shao CL, Zhang Q, Wang KL, Guan FF, Shi T, et al. Azaphilone and Diphenyl Ether Derivatives from a Gorgonian-Derived Strain of the Fungus Penicillium pinophilum. J Nat Prod. 2015;78:2310–4.
Luo JG, Xu Ym, Sandberg DC, Arnold AE, Gunatilaka AL. Montagnuphilones A-G, Azaphilones from Montagnulaceae sp. DM0194, a Fungal Endophyte of Submerged Roots of Persicaria amphibia. J Nat Prod. 2017;80:76–81.
Yang SW, Chan TM, Terracciano J, Loebenberg D, Patel M, Gullo V, et al. Sch 1385568, a new azaphilone from Aspergillus sp. J Antibiot. 2009;62:401.
Li W, Yang XQ, Yang YB, Zhao LX, Xu LH, Ding ZT. A new anthracycline from endophytic Streptomyces sp. YIM66403. J Antibiot. 2015;68:216–9.
Yin TP, Cai L, Fang HX, Fang YS, Li ZJ, Ding ZT. Diterpenoid alkaloids from Aconitum vilmorinianum. Phytochemistry. 2015;116:314–9.
Li LQ, Yang YG, Zeng Y, Zou C, Zhao PJ. A new azaphilone, kasanosin C, from an endophytic Talaromyces sp. T1BF. Molecules. 2010;15:3993–7.
Takeuchi T, Mizushina Y, Takaichi S, Inoue N, Kuramochi K, Shimura S, et al. Total synthesis of (+)-Sch 725680: inhibitor of mammalian A–, B–, and Y–family DNA polymerases. Org Lett. 2012;14:4303–5.
Wu HY, Wang WG, Jiang HY, Du X, Li XN, Pu JX, et al. Cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory ent-kaurane diterpenoids from Isodon wikstroemioides. Fitoterapia. 2014;98:192–8.
Quang DN, Harinantenaina L, Nishizawa T, Hashimoto T, Kohchi C, Soma GI, et al. Inhibition of nitric oxide production in RAW 264.7 cells by azaphilones from xylariaceous fungi. Biol Pharm Bull. 2006;29:34–7.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from Yunnan Provincial Science and Technology Department-Kunming Medical University Applied Basic Research Joint Special Fund Project [Nos. 2017FE468(-136), 2017FE468(-172)], grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 31860095, 81860632), a grant from the Scientific Research Foundation of Yunnan Provincial Department of Education (No. 2019J1191), and a grant from the Science and Technology Project of Zunyi City in China (No. ZSKHSZ(2017)05).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shao, Y., Yan, H., Yin, T. et al. New azaphilones from Penicillium variabile, a fungal endophyte from roots of Aconitum vilmorinianum. J Antibiot 73, 77–81 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41429-019-0250-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41429-019-0250-4
This article is cited by
-
A new steroid with potent antimicrobial activities and two new polyketides from Penicillium variabile EN-394, a fungus obtained from the marine red alga Rhodomela confervoides
The Journal of Antibiotics (2024)
-
Molecular characterization of fungal endophyte diversity isolated from Aconitum heterophyllum: a critically endangered medicinal plant of Kashmir Himalaya
International Microbiology (2023)
-
Current status of research on endophytes of traditional Tibetan medicinal plant and their metabolites
3 Biotech (2023)
-
Biotransformation ability of endophytic fungi: from species evolution to industrial applications
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology (2021)