Abstract
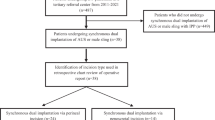
There is limited scientific literature regarding the management outcomes for end-stage erectile dysfunction (ED) following radical cystoprostatectomy (RCP). This study aims to evaluate the surgical outcomes of penile prosthesis (PP) implantation. A retrospective analysis over 17 years (2004–2017) was performed from the clinical records of patients in four tertiary referral centres, whom previously had undergone RCP, followed by PP implantation for end-stage ED. Outcome measures include both intra and postoperative complications, operative duration, a 5-point Likert hematoma scale as well as length of hospital stay. Additionally, a matched-pair cohort analysis was performed, dividing patients in 2 groups according to the type of urinary diversion (neobladder versus ileal conduit/cutaneous ureterostomy). The median time elapsed between RCP and PP implantation was 38 months (IQR 20–56). The median follow-up was 18 months (IQR 12–156). A 3-piece inflatable PP was implanted in 43 patients (91.5%) whereas a semirigid device was implanted in the remainder. Reservoir position was extra-peritoneal (utilising a separate abdominal incision) in 24 patients (54.8%), while an ectopic high-submuscular placement was preferred in the remainder. PP infection and mechanical failure occurred in 1 (2.1%) and 3 cases (6.3%) respectively. The comparative analysis of surgical outcomes did not show any statistically significant difference between the two groups. Our evidence suggests that PP implantation in patients with refractory ED following RCP may represent a safe and effective procedure associated with a low incidence of complications. The main limitation of this study is represented by the non-randomised, retrospective nature as well as the lack of patients’ functional outcomes and the limited follow-up.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Witjes JA, Lebret T, Compérat EM, Cowan NC, De Santis M, Bruins HM, et al. Updated 2016 EAU Guidelines on Muscle-invasive and Metastatic Bladder Cancer. Eur Urol 2017;71:462–75.
Hernández V, Espinos EL, Dunn J, Maclennan S, Lam T, Yuan Y, et al. Oncological and functional outcomes of sexual function–preserving cystectomy compared with standard radical cystectomy in men: a systematic review. Urol Oncol Semin Orig Investig. 2017;35:539.e17–539.e29.
Zippe CD, Raina R, Massanyi EZ, Agarwal A, Jones JS, Ulchaker J, et al. Sexual function after male radical cystectomy in a sexually active population. Urology. 2004;64:682–5.
Hatzimouratidis K, Amar E, Eardley I, Giuliano F, Hatzichristou D, Montorsi F, et al. Guidelines on male sexual dysfunction: erectile dysfunction and premature ejaculation. Eur Urol. 2010;57:804–14.
Loh-Doyle J, Patil MB, Sawkar H, Wayne K, Boyd SD. 3-piece inflatable penile prosthesis placement following radical cystoprostatectomy and urinary diversion: technique and outcomes. J Sex Med. 2018:15;907–13.
Rolle L, Falcone M, Ceruti C, Timpano M, Sedigh O, Ralph DJ, et al. A prospective multicentric international study on the surgical outcomes and patients’ satisfaction rates of the “sliding” technique for end-stage Peyronie’s disease with severe shortening of the penis and erectile dysfunction. BJU Int. 2016;117:814–20.
Chung E, Ralph D, Kagioglu A, Garaffa G, Shamsodini A, Bivalacqua T, et al. Evidence-based management guidelines on Peyronie’s disease. J Sex Med. 2016;13:905–23.
Morey AF, Cefalu CA, Hudak SJ. High submuscular placement of urologic prosthetic balloons and reservoirs via transscrotal approach. J Sex Med. 2013;10:603–10.
De Luca V, Pescatori ES, Taher B, Zambolin T, Giambroni L, Frego E, et al. Damage to the erectile function following radical pelvic surgery: prevalence of veno-occlusive dysfunction. Eur Urol. 1996;29:36–40.
Hekal IA, Mosbah A, El-Bahnasawy MS, El-Assmy A, Shaaban A. Penile haemodynamic changes in post-radical cystectomy patients. Int J Androl. 2011;34:27–32.
Berookhim BM, Nelson CJ, Kunzel B, Mulhall JP, Narus JB. Prospective analysis of penile length changes after radical prostatectomy. BJU Int. 2014;113(5 B):131–6.
Davila HH, Weber T, Burday D, Thurman S, Carrion R, Salup R, et al. Total or partial prostate sparing cystectomy for invasive bladder cancer: long-term implications on erectile function. BJU Int. 2007;100:1026–9.
Kessler TM, Burkhard FC, Perimenis P, Danuser H, Thalmann GN, Hochreiter WW, et al. Attempted nerve sparing surgery and age have a significant effect on urinary continence and erectile function after radical cystoprostatectomy and ileal orthotopic bladder substitution. J Urol. 2004;172(4 Pt 1):1323–7.
Schlegel PN, Walsh PC. Neuroanatomical approach to radical cystoprostatectomy with preservation of sexual function. J Urol. 1987;138:1402–6.
Hekal IA, El-Bahnasawy MS, Mosbah A, El-Assmy A, Shaaban A. Recoverability of erectile function in post–radical cystectomy patients: subjective and objective evaluations. Eur Urol. 2009;55:275–83.
Novara G, Catto JWF, Wilson T, Annerstedt M, Chan K, Murphy DG, et al. Systematic review and cumulative analysis of perioperative outcomes and complications after robot-assisted radical cystectomy. Eur Urol. 2015;67:376–401.
Yuh B, Wilson T, Bochner B, Chan K, Palou J, Stenzl A, et al. Systematic review and cumulative analysis of oncologic and functional outcomes after robot-assisted radical cystectomy. Eur Urol. 2015;67:402–22.
Bochner BH, Dalbagni G, Sjoberg DD, Silberstein J, Keren Paz GE, Donat SM, et al. Comparing open radical cystectomy and robot-assisted laparoscopic radical cystectomy: a randomized clinical trial. Eur Urol. 2015;67:1042–50.
Menard J, Tremeaux JC, Faix A, Pierrevelcin J, Staerman F. Erectile function and sexual satisfaction before and after penile prosthesis implantation in radical prostatectomy patients: a comparison with patients with vasculogenic erectile dysfunction. J Sex Med. 2011;8:3479–86.
Osterberg EC, Maganty A, Ramasamy R, Eid JF. Pharmacologically induced erect penile length and stretched penile lengh are both good predictors of post-inflatable prosthesis penile length. Int J Impot Res. 2014;26:128–31.
Karpman E, Sadeghi-Nejad H, Henry G, Khera M, Morey AF. Current opinions on alternative reservoir placement for inflatable penile prosthesis among members of the sexual medicine society of North America. J Sex Med. 2013;10:2115–20.
Stember DS, Garber BB, Perito PE. Outcomes of abdominal wall reservoir placement in inflatable penile prosthesis implantation: a safe and efficacious alternative to the space of retzius. J Sex Med. 2014;11:605–12.
Gross MS, Stember DS, Garber BB, Perito PE. A retrospective analysis of risk factors for IPP reservoir entry into the peritoneum after abdominal wall placement. Int J Impot Res. 2017;29:215–8.
Dadhich P, Hockenberry M, Kirby EW, Lipshultz L. Penile prosthesis in the management of erectile dysfunction following cancer therapy. Transl Androl Urol. 2017;6(Supplement 5):S883–889.
Tran CN, Boncher N, Montague DK, Angermeier KW. Erosion of inflatable penile prosthesis reservoir into neobladder. J Sex Med. 2013;10:2343–6.
Acknowledgements
We would like to express a great appreciation to all physicians involved in this study for the interest and efforts in data collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Falcone, M., Pucci, L., Garaffa, G. et al. An outcomes analysis of penile prosthesis implantation following radical cystoprostatectomy and urinary diversion: a multicentric retrospective cohort study. Int J Impot Res 32, 126–132 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-019-0171-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-019-0171-6
This article is cited by
-
Surgical tips in difficult penile prosthetic surgery: a narrative review
International Journal of Impotence Research (2023)
-
Development and content validation of a competency-based assessment tool for penile prosthesis surgery
International Journal of Impotence Research (2022)