Abstract
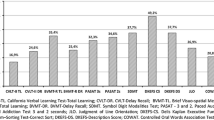
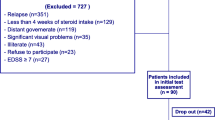
The prevalence of multiple sclerosis (MS) is on the rise globally, and recent epidemiological studies have observed increased rates in the Arab world (i.e., countries of North Africa and the Middle East where Arabic is the primary language). However, assessment of cognitive impairment and its relevant covariates (e.g., fatigue and depressive symptomatology) in the Arab world has not been rigorously reviewed. Thus, the objective of the present study was to systematically review the current use of cognitive assessment measures in observational and interventional studies of individuals with MS in the Arab world. A systematic review of studies that assessed cognitive function in adults with MS in the Arab world was conducted using PubMed, PsycINFO, CINAHL, The Cochrane Library, Embase, WHO Global Index Medicus, and Ovid Global Health. Studies that featured at least one objective cognitive measure were included. Eligible studies were reviewed for bias and study quality using the QUADAS-2 and NIH QAT. Study characteristics and finding were extracted by two independent reviewers, with results confirmed by a third reviewer. A total of 13 (N = 846) studies met inclusion criteria. Risk of bias and included measures varied across studies. Results demonstrated inconsistent availability and use of MS cognitive assessment tools across the Arab world. An Arabic version of the BICAMS was the only cognitive battery that was evaluated with regard to psychometric properties. The most common individual test include in reviewed studies was the SDMT. However, validation studies are still needed for this and a number of other measures. Other measures are still in the early stages of translation and cultural-linguistic norming. This review of cognitive assessment of individuals with MS in the Arab world was limited by variable study quality and measure selection. The present review provides a summary of the tests most commonly used in this region and recommendations for future investigation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou-Mrad, F., Tarabey, L., Zamrini, E., Pasquier, F., Chelune, G., Fadel, P., & Hayek, M. (2015). Sociolinguistic reflection on neuropsychological assessment: An insight into selected culturally adapted battery of Lebanese Arabic cognitive testing. Neurological Sciences, 36(10), 1813–1822. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-015-2257-3
Al-Araji, A., & Mohammed, A. I. (2005). Multiple sclerosis in Iraq: Does it have the same features encountered in Western countries? Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 234(1-2), 67–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2005.03.033
Al-Darmaki, F., & Yaaqeib, S. (2015). Psychology and mental health services in the UAE. Psychology International.
Alonso, A., & Hernán, M. A. (2008). Temporal trends in the incidence of multiple sclerosis. A Systematic Review, 71(2), 129–135. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000316802.35974.34
Alosaimi, F. D., AlMulhem, A., & Moscovici, M. (2017). The Relationship between Psychosocial Factors and Cognition in Multiple Sclerosis., 2017, 6847070. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6847070
Anderson, D., Ellenberg, J., Leventhal, C., Reingold, S., Rodriguez, M., & Silberberg, D. (1992). Revised estimate of the prevalence of multiple sclerosis in the United States. Annals of Neurology, 31(3), 333–336.
Becuş, T., & Popoviciu, L. (1994). Epidemiologic survey of multiple sclerosis in Mureş County, Romania. Romanian Journal of Neurology and Psychiatry= Revue Roumaine De Neurologie Et Psychiatrie, 32(2), 115–122.
Ben Aljia, L., Anissa, K., Rabiaa, D., Salma, N., Sofian, B., & BA, L. (2016). Fatigue, depression, and memory impairment in multiple sclerosis. European Journal of Neurology, 23(S2), 111–344. https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.13092
Benamer, H. T., Ahmed, E. S., Al-Din, A. S., & Grosset, D. G. (2009). Frequency and clinical patterns of multiple sclerosis in Arab countries: A systematic review. Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 278(1-2), 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2008.12.001
Benedict, R. H., Amato, M. P., Boringa, J., Brochet, B., Foley, F., Fredrikson, S., ... Penner, I. (2012). Brief international cognitive assessment for MS (BICAMS): International standards for validation. BMC Neurology, 12(1), 55.
Benedict, R. H., Cookfair, D., Gavett, R., Gunther, M., Munschauer, F., Garg, N., & Weinstock-Guttman, B. (2006). Validity of the minimal assessment of cognitive function in multiple sclerosis (MACFIMS). Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 12(04), 549–558.
Bohlega, S., Inshasi, J., Al Tahan, A. R., Madani, A. B., Qahtani, H., & Rieckmann, P. (2013). Multiple sclerosis in the Arabian gulf countries: A consensus statement. Journal of Neurology, 260(12), 2959–2963. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-013-6876-4
Charvet, L., Taub, E., Cersosimo, B., Rosicki, C., Melville, P., & Krupp, L. (2015). The Montreal cognitive assessment (MoCA) in multiple sclerosis: Relation to clinical features. J Mult Scler, 2(135), 2376–0389.1000135.
Chiaravalloti, N. D., & DeLuca, J. (2008). Cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurology, 7(12), 1139–1151.
Darwish, H., Haddad, R., Osman, S., Ghassan, S., Yamout, B., Tamim, H., & Khoury, S. (2017). Effect of vitamin D replacement on cognition in multiple sclerosis patients. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 45926. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep45926
Dean, G., Aksoy, H., Akalin, T., Middleton, L., & Kyriallis, K. (1997). Multiple sclerosis in the Turkish- and Greek-speaking communities of Cyprus. A United Nations (UNHCR) Bicommunal project. Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 145(2), 163–168.
El Ayoubi, N. K., Ghassan, S., Said, M., Allam, J., Darwish, H., & Khoury, S. J. (2016). Retinal measures correlate with cognitive and physical disability in early multiple sclerosis. Journal of Neurology, 263(11), 2287–2295.
El Ghoneimy, A. T., Hassan, A., Homos, M., Farghaly, M., & Dahshan, A. (2015). Thalamic involvement and its impact on disability and cognition in multiple sclerosis: A clinical and diffusion tensor imaging study. Egyptian Journal Of Neurology Psychiatry And Neurosurgery, 52(2), 139–145.
El-Ghoneimy, A. T., Gad, A. H., Samir, H., Shalaby, N., Ramzy, G., Farghaly, M., & Hegazy, M. I. (2009). Contribution of vitamin D to the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis and its effect on bone health. Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 285, S202.
El-Kholy, O. A., Ramadan, M., El-Sheikh, M., & Ali, M. (2012). Impairment in working memory in multiple sclerosis. Egyptian Journal of Psychiatry, 33(3), 117.
Fasfous, A. F., Al-Joudi, H. F., Puente, A. E., & Perez-Garcia, M. (2017). Neuropsychological measures in the Arab world: A systematic review. Neuropsychology Review, 27(2), 158–173.
Foley, F. W., Benedict, R. H. B., Gromisch, E. S., & DeLuca, J. (2012). The need for screening, assessment, and treatment for cognitive dysfunction in multiple sclerosis: Results of a multidisciplinary CMSC consensus conference, September 24, 2010. International Journal of MS Care, 14(2), 58–64. https://doi.org/10.7224/1537-2073-14.2.58
Goretti, B., Niccolai, C., Hakiki, B., Sturchio, A., Falautano, M., Minacapelli, E., ... Amato, M. P. (2014). The brief international cognitive assessment for multiple sclerosis (BICAMS): Normative values with gender, age and education corrections in the Italian population. BMC Neurology, 14(1), 171. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883-014-0171-6
Hamdy, S., Shaheen, H. A., Aboumousa, A. M., Farghaly, M., Ezzat, L. M., & Daker, L. (2013). Does the disease course or treatment type have impact on executive functions and cognition in multiple sclerosis patients? A clinical and 3 tesla MRI study. Egyptian Journal of Neurology, Psychiatry & Neurosurgery, 50(4).
Heydarpour, P., Khoshkish, S., Abtahi, S., Moradi-Lakeh, M., & Sahraian, M. A. (2015). Multiple sclerosis epidemiology in Middle East and North Africa: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neuroepidemiology, 44(4), 232–244. https://doi.org/10.1159/000431042
Hind, D., Kaklamanou, D., Beever, D., Webster, R., Lee, E., Barkham, M., & Cooper, C. (2016). The assessment of depression in people with multiple sclerosis: A systematic review of psychometric validation studies. BMC Psychiatry, 16(1), 278. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-016-0931-5
Kalb, R., Beier, M., Benedict, R. H., Charvet, L., Costello, K., Feinstein, A., ... DeLuca, J. (2018). Recommendations for cognitive screening and management in multiple sclerosis care. Multiple Sclerosis, 24(13), 1665–1680. https://doi.org/10.1177/1352458518803785
Kamel, R., El Kholy, S., & Hashem, H. (2004). Multiple sclerosis: Correlation of neuropsychological tests with EEG coherence analysis and MRI findings. Egyptian Journal Of Neurology Psychiatry And Neurosurgery, 41(1), 79–94.
Karni, A., Kahana, E., Zilber, N., Abramsky, O., Alter, M., & Karussis, D. (2003). The frequency of multiple sclerosis in jewish and Arab populations in greater Jerusalem. Neuroepidemiology, 22(1), 82–86. https://doi.org/10.1159/000067101
Khalil, H., Al-Shorman, A., El-Salem, K., Abdo, N., Alghwiri, A. A., Aburub, A., ... Al-Mustafa, F. (2017). Fear of falling in people with multiple sclerosis: Which clinical characteristics are important? Physical Therapy, 97, 698–706. https://doi.org/10.1093/ptj/pzx044
Kishk, N., Shalaby, N., Shehata, H., Hassan, A., Hegazy, M., Elmazny, A., ... Farghaly, M. (2017). Reliability of BICAMS (Arabic version) in Egyptian multiple sclerosis patients. Multiple Sclerosis Journal, 23, 155–156. https://doi.org/10.1177/1352458517731404
Kronfol, N. (2012). Access and barriers to health care delivery in Arab countries: A review.
Krupp, L. B., LaRocca, N. G., Muir-Nash, J., & Steinberg, A. D. (1989). The fatigue severity scale: Application to patients with multiple sclerosis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Archives of Neurology, 46(10), 1121–1123.
Langdon, D. W., Amato, M. P., Boringa, J., Brochet, B., Foley, F., Fredrikson, S., ... Penner, I. K. (2012). Recommendations for a brief international cognitive assessment for multiple sclerosis (BICAMS). Multiple Sclerosis Journal, 18(6), 891–898.
Makhani, N., Morrow, S., Fisk, J., Evans, C., Beland, S. G., Kulaga, S., ... Koch, M. (2013). Trends in multiple sclerosis incidence and prevalence in Africa, Asia, Australia and New Zealand: A systematic review. Multiple Sclerosis, 19, 344–345. https://doi.org/10.1177/1352458513502429
Manee, F. S., Nadar, M. S., Jassem, Z., & Chavan, S. R. (2017). Survey of cognitive rehabilitation practices in the state of Kuwait. Scandinavian Journal of Occupational Therapy, 24(2), 83–88.
Melcon, M. O., Correale, J., & Melcon, C. M. (2014). Is it time for a new global classification of multiple sclerosis? Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 344(1-2), 171–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2014.06.051
Moher, D., Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, J., & Altman, D. G. (2009). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Annals of Internal Medicine, 151(4), 264–269.
National Institutes of Health. (2014). Quality assessment tool for observational cohort and cross-sectional studies. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Avaliable from: www. nhlbi. nih. gov/health-pro/guidelines/indevelop/cardiovascular-risk-reduction/tools/cohort.[Accessed November 5, 2015].
Pugliatti, M., Sotgiu, S., & Rosati, G. (2002). The worldwide prevalence of multiple sclerosis. Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery, 104(3), 182–191.
Rao, S. M., Leo, G. J., Bernardin, L., & Unverzagt, F. (1991). Cognitive dysfunction in multiple sclerosis. I. Frequency, patterns, and prediction. Neurology, 41(5), 685–691.
Rosati, G. (2001). The prevalence of multiple sclerosis in the world: An update. Neurological Sciences, 22(2), 117–139.
Saadatnia, M., Etemadifar, M., & Maghzi, A. H. (2007). Multiple sclerosis in Isfahan, Iran. International Review of Neurobiology, 79, 357–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0074-7742(07)79016-5
Schiess, N., Huether, K., Fatafta, T., Fitzgerald, K. C., Calabresi, P. A., Blair, I., ... Szolics, M. (2016). How global MS prevalence is changing: A retrospective chart review in the United Arab Emirates. Multiple Sclerosis and Related Disorders, 9, 73–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msard.2016.07.005
Sharafaddinzadeh, N., Moghtaderi, A., Majdinasab, N., Dahmardeh, M., Kashipazha, D., & Shalbafan, B. (2013). The influence of ethnicity on the characteristics of multiple sclerosis: A local population study between Persians and Arabs. Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery, 115(8), 1271–1275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2012.11.027
Simpson, S., Blizzard, L., Otahal, P., Van der Mei, I., & Taylor, B. (2011). Latitude is significantly associated with the prevalence of multiple sclerosis: A meta-analysis. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry, 82(10), 1132–1141.
Sjonnesen, K., Berzins, S., Fiest, K. M., AG, M. B., Metz, L. M., Thombs, B. D., & Patten, S. B. (2012). Evaluation of the 9-item patient health questionnaire (PHQ-9) as an assessment instrument for symptoms of depression in patients with multiple sclerosis. Postgraduate Medicine, 124(5), 69–77. https://doi.org/10.3810/pgm.2012.09.2595
Vanotti, S., Smerbeck, A., Benedict, R. H. B., & Caceres, F. (2016). A new assessment tool for patients with multiple sclerosis from Spanish-speaking countries: Validation of the brief international cognitive assessment for MS (BICAMS) in Argentina. The Clinical Neuropsychologist, 30(7), 1023–1031. https://doi.org/10.1080/13854046.2016.1184317
Weinshenker, B. G. (1994). Natural history of multiple sclerosis. Annals of Neurology: Official Journal of the American Neurological Association and the Child Neurology Society, 36(S1), S6–S11.
Weinshenker, B. G., Bass, B., Rice, G. P., Noseworthy, J., Carriere, W., Baskerville, J., & Ebers, G. C. (1989). The natural history of multiple sclerosis: A geographically based study. I. Clinical course and disability. Brain, 112(Pt 1), 133–146.
Whiting, P., Savović, J., Higgins, J. P., Caldwell, D. M., Reeves, B. C., Shea, B., ... Churchill, R. (2016). ROBIS: A new tool to assess risk of bias in systematic reviews was developed. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, 69, 225–234.
Whiting, P. F., Rutjes, A. W., Westwood, M. E., Mallett, S., Deeks, J. J., Reitsma, J. B., ... Bossuyt, P. M. (2011). QUADAS-2: A revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Annals of Internal Medicine, 155(8), 529–536.
Yamout, B., Barada, W., Tohme, R. A., Mehio-Sibai, A., Khalifeh, R., & El-Hajj, T. (2008). Clinical characteristics of multiple sclerosis in Lebanon. Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 270(1-2), 88–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2008.02.009
Yamout, B., Hourani, R., Salti, H., Barada, W., El-Hajj, T., Al-Kutoubi, A., ... Khalil-Hamdan, R. (2010). Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in patients with multiple sclerosis: A pilot study. Journal of Neuroimmunology, 227(1–2), 185–189.
Yamout, B., Issa, Z., Herlopian, A., El Bejjani, M., Khalifa, A., Ghadieh, A., & Habib, R. (2013). Predictors of quality of life among multiple sclerosis patients: A comprehensive analysis. European Journal of Neurology, 20(5), 756–764.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge the 2017 review by Doctors Fasfous, al-Joudi, Puente, and Pérez-García, “Neuropsychological measures in the Arab world: A systematic review,” which contributed substantially to our current understanding of cognitive assessment in the Arab world. References included in Fasfous et al., 2017 were integral to identifying articles for the present review of MS-related cognitive assessment in the Arab world.
Funding
Abbey Hughes is currently funded on an NIH career development award through the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, National Center for Medical Rehabilitation Research (K23HD086154).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paul, S., Brown, A. & Hughes, A.J. Cognitive Assessment of Individuals with Multiple Sclerosis in the Arab World: a Systematic Review. Neuropsychol Rev 29, 259–269 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11065-019-09408-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11065-019-09408-5