Abstract
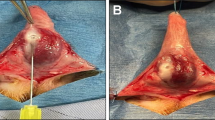
The aim of the present study was to evaluate the histological, histochemical, and stereological changes caused by mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) on the tunica albuginea of rat penises submitted to an injection of transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) for the induction of Peyronie’s disease (PD). Twenty adult male Wistar rats were divided into four groups: Control group; TGF-β group (TGF-β injection); MMF-7d group (treated with MMF 7 days after induction with TGF-β); and MMF-30d group (treated with MMF 30 days after induction with TGF-β). The steorological evaluation included the relative volume of different types of connective fibres of the tunica albuginea. The histochemical analysis revealed the fragmentation and degradation of elastin in the tunica albuginea. This process was partially reversed in the MMF-7d group and a situation very close to normality was observed in the MMF-30d group. In the collagen III/collagen I ratio it was observed increase in this ratio in the TGF-β (59.4 ± 5.53) and MMF-7d (49 ± 18.2) groups and a decrease in the MMF-30d group (28.7 ± 4), approaching normality. The injection of TGF-β promoted fibrotic alterations in the penile tunica albuginea in Wistar rats corresponding to PD. In this model, MMF acts as a regenerating anti-fibrotic agent.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Joice GA, Burnett AL. Nonsurgical interventions for Peyronie’s disease: update as of 2016. World J Mens Health. 2016;34:65–72.
Talib RA, Ibrahim MA, Cangüven Ö. Nonsurgical treatment options in Peyronie’s Disease: 2016 update. Turk J Urol. 2016;42:217–23.
Al-Thakafi S, Al-Hathal N. Peyronie’s disease: a literature review on epidemiology, genetics, pathophysiology, diagnosis and work-up. Transl Androl Urol. 2016;5:280–9.
Tal R, Heck M, Teloken P, Siegrist T, Nelson CJ, Mulhall JP. Peyronie’s disease following radical prostatectomy: incidence and predictors. J Sex Med. 2010;7:1254–61.
Antoniassi TS, Spessoto LCF, Gonçalves Filho JR, Cavalcante VMM, da Silva EA, Facio MFW, et al. Risk factors for Peyronie’s disease in patients submitted to the Nesbit procedure. Int J Sci. 2016;5:131–3.
Bilgutay AN, Pastuszak AW. Peyronie’s disease: a review of etiology, diagnosis and management. Curr Sex Health Rep. 2015;7:117–31.
Gonzalez-Cadavid NF, Rajfer J. Mechanisms of disease: new insights into the cellular and molecular pathology of Peyronie’s disease. Nat Clin Pract Urol. 2005;2:291–7.
Gonzalez-Cadavid NF, Rajfer J. Experimental models of Peyronie’s disease. Implications for new therapies. J Sex Med. 2009;6:303–13.
El-Sakka AI, Hassoba HM, Chui RM, Bhatnagar RS, Dahiya R, Lue TF. An animal model of Peyronie’s-like condition associated with an increase of transforming growth factor beta mRNA and protein expression. J Urol. 1997;158:2284–90.
Somers KD, Sismour EN, Wright GL Jr, Devine CJ Jr, Gilbert DA, Horton CE. Isolation and characterization of collagen in Peyronie’s Disease. J Urol. 1989;141:629–31.
Luangkhot R, Rutchik S, Agarwal V, Puglia K, Bhargava G, Melman A. Collagen alterations in the corpus cavernosum of men with sexual dysfunction. J Urol. 1992;148:467–71.
Hellstrom WJ, Bivalacqua TJ. Peyronie’s disease: etiology, medical, and surgical therapy. J Androl. 2000;21:347–54.
Castiglione F, Hedlund P, Van der Aa F, Bivalacqua TJ, Rigatti P, Van Poppel H, et al. Intratunical injection of human adipose tissue-derived stem cells prevents fibrosis and is associated with improved erectile function in a rat model of Peyronie’s disease. Eur Urol. 2013;63:551–60.
Roos N, Poulalhon N, Farge D, Madelaine I, Mauviel A, Verrecchia F. In vitro evidence for a direct antifibrotic role of the immunosuppressive drug mycophenolate mofetil. J Pharm Exp Ther. 2007;321:583–9.
Scheel PJ Jr, Piccini J, Rahman MH, Lawler LJ. Combined prednisone and mycophenolate mofetil treatment for retroperitoneal fibrosis. J Urol. 2007;178:140–3.
Scheel PJ Jr, Sozio SM, Feeley N. Medical management of retroperitoneal fibrosis. Trans Am Clin Clim Assoc. 2012;123:283–90.
Hussein AA, Alwall A, Lue TF. All about Peyronie’s disease. Asian J Urol. 2015;2:70–8.
El-Sakka AI, Hassan MU, Nunes L, Bhatnagar RS, Yen TS, Lue TF. Histological and ultrastructural alterations in an animal model of Peyronie’s disease. Br J Urol. 1998;81:445–52.
Tzouvelekis A, Bouros E, Oikonomou A, Ntolios P, Zacharis G, Kolios G, et al. Effect and safety of mycophenolate mofetil in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Pulm Med. 2011;2011:849035.
American Veterinary Medical Association. Guideline for the Euthanasia of animals: ed. 2013; p.48. https://www.avma.org/KB/Policies/Documents/euthanasia.pdf.
Behmer AO, Tolosa EMC, Neto AGF. Manual de práticas para histologia normal e patológica. São Paulo: EDART-EDUSP; 1976. p. 329.
de Carvalho HF, Taboga SR. Fluorescence and confocal laser scanning microscopy imaging of elastic fibers in hematoxylin-eosin stained sections. Histochem Cell Biol. 1996;106:587–92.
Weibel ER. Principles and methods for the morphometric study of the lung and other organs. Lab Invest. 1978;12:131–55.
Bilgutay AN, Pastuszak AW. Peyronie’s disease: what’s around the bend? Indian J Urol. 2016;32:6–14.
Gokce A, Abd Elmageed ZY, Lasker GF, Bouljihad M, Kim H, Trost LW, et al. Adipose tissue-derived stem cell therapy for prevention and treatment of erectile dysfunction in a rat model of Peyronie’s disease. Andrology. 2014;2:244–51.
Levine LA, Larsen SM. Surgery for Peyronie’s disease. Asian J Androl. 2013;15:27–34.
Hellstrom WJG, Tan RBW, Liu G. Safety profile of collagenase Clostridium histolyticum stratified by degree of penile curvature in patients with Peyronie’s disease. Urology. 2017;S0090-4295:30477–6.
Gelbard M, Goldstein I, Hellstrom WJ, McMahon CG, Smith T, Tursi J, et al. Clinical efficacy, safety and tolerability of collagenase Clostridium histolyticum for the treatment of Peyronie disease in 2 large double-blind, randomized, placebo controlled phase 3 studies. J Urol. 2013;190:199–207.
Yan S, Yap T, Minhas S. Collagenase clostridium histolyticum intralesional injections for the treatment of Peyronie’s disease: a safety profile. Transl Androl Urol. 2017;6:123–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Antoniassi, T., Júnior, F.N.F., Spessoto, L.C.F. et al. Anti-fibrotic effect of mycophenolate mofetil on Peyronie’s disease experimentally induced with TGF-β. Int J Impot Res 32, 201–206 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-019-0138-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-019-0138-7
This article is cited by
-
Is classifying SSc-ILD drugs as either immunosuppressive or anti-fibrotic misleading?
Nature Reviews Rheumatology (2023)
-
Management of the Acute Phase of Peyronie’s Disease: a Contemporary Review
Current Sexual Health Reports (2019)