Abstract
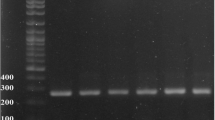
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) transmission in livestock, community, and healthcare settings poses a significant public health concern both locally and globally. This study aimed to investigate the occurrence, molecular detection, and antibiogram of the MRSA strain in fresh beef, contact surfaces, and butchers’ knives from the four major abattoirs (Karu, Gwagwalada, Deidei, and Kubwa) located in the Federal Capital Territory, Nigeria. A multi-stage sampling technique was used to collect 400 swab samples from butchers’ knives (132), fresh beef (136), and contact surfaces (132). Presumptive colonies on mannitol salt agar were subjected to culture, isolation, and biotyping. The antibiogram was carried out via a Kirby-Bauer disk containing eight antibiotics. MRSA was phenotypically confirmed by oxacillin-resistant screening agar base (ORSAB) and genotypically by PCR to detect the presence of the mecA gene. Out of the 400 samples, 47.24% of fresh beef, 37% of contact surfaces, and 64.33% of butchers’ knife swabs were Staphylococcus aureus positive. Thirty-two Staphylococcus aureus-positive isolates were confirmed to be MRSA, 50% fresh beef, 28.12% contact surfaces, and 21.87% butcher’s knife swabs. MRSA isolates displayed multidrug-resistant traits, with a high resistance of 90.62% against cloxacillin, and a highest susceptibility of 100% to co-trimaxole. The antibiogram showed MRSA strains to be multidrug resistant. Molecular characterisation of the MRSA detected the presence of the mecA gene at a band size of 163 bp in all isolates. Strict hygiene of butchers, and working equipment in meat processing and marketing should be of top priority.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Abdelazeem RM, Khalil NS, Ibrahim A (2019) Effect of Body Wash with Tea Tree Oil on the Prevention of Methicillin–Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in critically ill patients at a university hospital in Egypt. Iris J Nurs Care 1:2
Anueyiagu KN, Isiyaku AW (2015) Isolation and identification of Staphylococcus aureus from bovine milk and its antibiotic susceptibility. Int J Liv Prod 6:74–77
Bhutia KO, Singh TS, Biswas S, Adhikari L (2012) Evaluation of phenotypic with genotypic methods for species identification and detection of methicillin resistant in Staphylococcus aureus. Int J Appl Basic Med Res 2:84–91
Cella E, Sutcliffe CG, Tso C, Paul E, Ritchie N, Colelay J, Azarian T (2022) Carriage prevalence and genomic epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus among native American children and adults in the Southwestern USA. Microb Genom 8:000806
Cheesbrough (2016) District Laboratory Practice in Tropical Countries Part II, vol 65. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge UK, pp 38–39
Chen F, Ye J, Chio C, Liu W, Shi J, Qin W (2020) A simplified quick microbial genomic DNA extraction via freeze–thawing cycles. Mol Biol Rep 47:703–709
Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) (2021) Performance standards for antimicrobial disk and dilution susceptibility tests for bacteria isolated from animals, approved Standard, 5th Edition. VET01
Foster TJ (2017) Antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Current status and future prospects. FEMS Microbiol Rev 41(3):430–449
Gaddafi MS, Yakubu Y, Bello MB, Bitrus AA, Musawa AI, Garba B, Emeka AJ (2022) Occurrence and antibiotic resistance profiles of Methicillin-resistant (MRSA) in layer chickens in Kebbi, Nigeria. Folia Vet 66:37–45
Gulani IA, Geidam YA, Adamu L, Lawal JR, Abadam FA (2016) Prevalence and phenotypic detection of methicillin resistance Staphylococcus aureus between ruminants butchered for humanoid intake and animal handlers in Maiduguri, Nigeria. J Adv Vet Anim Res 3:152–159
Ivbule M, Miklaševičs E, Čupāne L, Bērziņa L, Bālinš A, Valdovska A (2017) Presence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in slaughterhouse environment, pigs, carcasses, and workers. J Vet Res 61:267
Jaradat ZW, Ababneh QO, Sha’aban ST, Alkofahi AA, Assaleh D, Al Shara A (2020) Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus and public fomites: a review. Pathog Glob Health 114:426–450
Karygianni L, Ren Z, Koo H, Thurnheer T (2020) Biofilm matrixome: extracellular components in structured microbial communities. Trends Microb 28:668–681
Magiorakos AP, Srinivasan A, Carey RB, Carmeli Y, Falagas ME, Giske CG, Harbarth S, Hindler JF, Kahlmeter G, Olsson-Liljequist B, Paterson DL (2012) Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: an international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin Microb Inf 18:268–281
Mlynarczyk-Bonikowska B, Kowalewski C, Krolak-Ulinska A, Marusza W (2022) Molecular mechanisms of drug resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Int J Mol Sci 23:8088
Ndip RN, Ndip LM, Smith SI, Kfusi JA, Kaah KN, Nkengum WP, Nkie ES (2021) Prevalence and characterization of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus from Meat Retail shops and Meat handlers in the Buea Municipality, Cameroon. Int J Trop Dis Health 13–27
Neopane P, Nepal HP, Shrestha R, Uehara O, Abiko Y (2018) In vitro biofilm formation by Staphylococcus aureus isolated from wounds of hospital-admitted patients and their association with antimicrobial resistance. Int J Gen Med 18:25–32
Ochei B, Kolhatkar J (2016) Medical Laboratory Science-Theory and Practice. Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing Company Ltd, New Delhi, pp 648–657
Odetokun IA, Maurischat S, Adetunji VO, Fetsch A (2022) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from municipal abattoirs in Nigeria: showing highly similar clones and possible transmission from slaughter animals to humans. Foodborne Pathog Dis 19(1):56–61
Olatoye IO (2010) The incidence and antibiotics susceptibility of Escherichia coli O157:H7 from beef in Ibadan Municipal. Nigeria Afr J Biotech 9:1196–1199
Olonitola OS, INabo HI, Olayinka BO, Bugo ID (2007) Nasal carriage of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by primary school pupils in a university staff school, Zaria, Nigeria. Int J Biolog Chem Sci 1:71–75
Omoruyi IM, Obodo IC, Obukohwo EO, Otoide FE (2020) Virulent gene detection and antibiogramic profile of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from birds of a poultry farm. Ife J Sci 22:045–055
Pauly N, Wichmann-Schauer H, Ballhausen B, Reyes NT, Fetsch A, Tenhagen BA (2019) Detection and quantification of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in fresh broiler meat at retail in Germany. Int J Food Microb 292:8–12
Plata KB, Riosa S, Singh CR, Rosato RR, Rosato AE (2013) Targeting of PBP1 by β-lactams determines recA/SOS response activation in heterogeneous MRSA clinical strains. PLoS ONE 8:e61083
Pokharel S, Shrestha P, Adhikari B (2020) Antimicrobial use in food animals and human health: time to implement ‘One health’ approach. Antimicrob Resist Inf Cont 9:1–5
Rodrigues MX, Silva NCC, Trevilin JH, Cruzado MMB, Mui TS, Duarte FRS, Porto E (2017) Antibiotic resistance and molecular characterization of Staphylococcus species from mastitic milk. Afr J Microbiol Res 11:84–91
Saiful AJ, Mastura M, Zarizal S, Mazurah MI, Shuhaimi M, Ali AM (2006) Detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus using mecA/nuc genes and antibiotic susceptibility profile of Malaysian clinical isolates. World J Microb Biotech 22:1289–1294
Salamandane A, Correia J, Muetanene BA, dos Santos M, Malfeito-Ferreira M, Brito L (2023) Methicillin Resistance of Food-Borne Biofilm-forming Staphylococci. Appl Sci 13:7725
Schumacher I (2020) Strategies to assess and minimize the Biological risk of Antibiotic Resistance. Antimicrobial resistance in the environment. Keen P.L and montforts (ED).1st Edn. John Wiley and Sons Inc, New Jersey, USA, pp 251–264
Shoaib M, Aqib AI, Muzammil I, Majeed N, Bhutta ZA, Kulyar MF, Fatima M, Zaheer C, Fatima N, Muneer A, Murtaza M (2023) MRSA compendium of epidemiology, transmission, pathophysiology, treatment, and prevention within one health framework. Front Microbiol 13:1067284.
Tessema F (2016) Prevalence and drug resistance patterns of Staphylococcus aureus in lactating dairy cows‟ milk in Wolayta Sodo, Ethiopia. EC Vet Sci 2:226–230
Thrusfield M (2018) Veterinary epidemiology. London, 3rd edn. Blackwell Science Ltd., London, UK, pp 228–246
Usman RZ, Mustapha BM, Mohammed FI (2016) Isolation and identification of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) from traditionally fermented milk nono and yoghurt in Kaduna Metropolis, Nigeria. Food Sci Qua Manag 2:1–21
Acknowledgements
The authors appreciate the laboratory staff for their technical assistance during this research.
Funding
None to be declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dauda Dauda Ibrahim: Conceptualization, Project administration, Investigation, Validation, Writing – original draft. Simon Ikechukwu Enem: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. Godwin Egwu: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. David Dantong: Investigation, Formal Analysis. Kelvin Olutimilehin Jolayemi: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Visualization. Mohammed Sani Gaddafi: Investigation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
None.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ibrahim, D.D., Enem, S.I., Egwu, G. et al. An emerging zoonosis: molecular detection of multidrug-methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus from butchers’ knives, livestock products and contact surfaces. Vet Res Commun 48, 1697–1705 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-024-10346-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-024-10346-8