Abstract
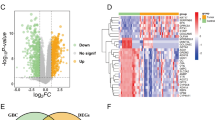
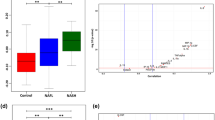
In recent years, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has become a more serious public health issue worldwide. This study strived to investigate the molecular mechanism of pathogenesis of NAFLD and explore promising diagnostic and therapeutic targets for NAFLD. Raw data from GSE130970 were downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus database. We used the dataset to analyze the expression levels of cuproptosis-related genes in NAFLD patients and healthy controls to identify the differentially expressed cuproptosis-related genes (DECRGs). The relationship and potential mechanism between DECRGs and clinicopathological factors were examined by enrichment analysis and two consensus clustering methods. We screened key DECRGs based on Random Forest (RF), and then verified the key DECRGs in NAFLD patients, high-fat diet (HFD)–fed mice, and palmitic acid–induced AML12 cells. ROC analysis showed good diagnostic function of DECRGs in normal and NAFLD liver tissue. Two consensus clusters indicated the important role of cuproptosis in the development of NAFLD. We screened for key DECRGs (DLD, DLAT) based on RF and found a close relationship between the DECRGs and clinicopathological factors. We collected clinical blood samples to verify the differences in gene expression levels by qPCR. In addition, we further verified the expression levels of DLD and DLAT in HFD mice and AML12 cells, which showed the same results. This study provides a novel perspective on the pathogenesis of NAFLD. We identified two cuproptosis-related genes that are closely related to NAFLD. These genes may play a significant role in the molecular pathogenesis of NAFLD, which may be useful to make progress in the diagnosis and treatment of NAFLD.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found below: GSE130970; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
References
Sanyal AJ (2019) Past, present and future perspectives in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 16:377–386. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41575-019-0144-8
Younossi ZM, Koenig AB, Abdelatif D, Fazel Y, Henry L, Wymer M (2016) Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology 64:73–84. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.28431
Abdelmalek MF (2021) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: another leap forward. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 18:85–86. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41575-020-00406-0
Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, Charlton M, Cusi K, Rinella M, Harrison SA, Brunt EM, Sanyal AJ (2018) The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: practice guidance from the American association for the study of liver diseases. Hepatology 67:328–357. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.29367
Galluzzi L, Vitale I, Aaronson SA, Abrams JM, Adam D, Agostinis P, Alnemri ES, Altucci L, Amelio I, Andrews DW, Annicchiarico-Petruzzelli M, Antonov AV, Arama E, Baehrecke EH, Barlev NA, Bazan NG, Bernassola F, Bertrand MJM, Bianchi K, Blagosklonny MV, Blomgren K, Borner C, Boya P, Brenner C, Campanella M, Candi E, Carmona-Gutierrez D, Cecconi F, Chan FKM, Chandel NS, Cheng EH, Chipuk JE, Cidlowski JA, Ciechanover A, Cohen GM, Conrad M, Cubillos-Ruiz JR, Czabotar PE, D’Angiolella V, Dawson TM, Dawson VL, De Laurenzi V, De Maria R, Debatin K-M, DeBerardinis RJ, Deshmukh M, Di Daniele N, Di Virgilio F, Dixit VM, Dixon SJ, Duckett CS, Dynlacht BD, El-Deiry WS, Elrod JW, Fimia GM, Fulda S, García-Sáez AJ, Garg AD, Garrido C, Gavathiotis E, Golstein P, Gottlieb E, Green DR, Greene LA, Gronemeyer H, Gross A, Hajnoczky G, Hardwick JM, Harris IS, Hengartner MO, Hetz C, Ichijo H, Jäättelä M, Joseph B, Jost PJ, Juin PP, Kaiser WJ, Karin M, Kaufmann T, Kepp O, Kimchi A, Kitsis RN, Klionsky DJ, Knight RA, Kumar S, Lee SW, Lemasters JJ, Levine B, Linkermann A, Lipton SA, Lockshin RA, López-Otín C, Lowe SW, Luedde T, Lugli E, MacFarlane M, Madeo F, Malewicz M, Malorni W, Manic G, Marine J-C, Martin SJ, Martinou J-C, Medema JP, Mehlen P, Meier P, Melino S, Miao EA, Molkentin JD, Moll UM, Muñoz-Pinedo C, Nagata S, Nuñez G, Oberst A, Oren M, Overholtzer M, Pagano M, Panaretakis T, Pasparakis M, Penninger JM, Pereira DM, Pervaiz S, Peter ME, Piacentini M, Pinton P, Prehn JHM, Puthalakath H, Rabinovich GA, Rehm M, Rizzuto R, Rodrigues CMP, Rubinsztein DC, Rudel T, Ryan KM, Sayan E, Scorrano L, Shao F, Shi Y, Silke J, Simon H-U, Sistigu A, Stockwell BR, Strasser A, Szabadkai G, Tait SWG, Tang D, Tavernarakis N, Thorburn A, Tsujimoto Y, Turk B, Vanden Berghe T, Vandenabeele P, Vander Heiden MG, Villunger A, Virgin HW, Vousden KH, Vucic D, Wagner EF, Walczak H, Wallach D, Wang Y, Wells JA, Wood W, Yuan J, Zakeri Z, Zhivotovsky B, Zitvogel L, Melino G, Kroemer G (2018) Molecular mechanisms of cell death: recommendations of the nomenclature committee on cell death 2018. Cell Death Differ 25:486–541. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-017-0012-4
Tan Y, Chen Q, Li X, Zeng Z, Xiong W, Li G, Li X, Yang J, Xiang B, Yi M (2021) Pyroptosis: a new paradigm of cell death for fighting against cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 40:153. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-021-01959-x
Tsvetkov P, Coy S, Petrova B, Dreishpoon M, Verma A, Abdusamad M, Rossen J, Joesch-Cohen L, Humeidi R, Spangler RD, Eaton JK, Frenkel E, Kocak M, Corsello SM, Lutsenko S, Kanarek N, Santagata S, Golub TR (2022) Copper induces cell death by targeting lipoylated TCA cycle proteins. Science 375:1254–1261. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abf0529
Chen L, Min J, Wang F (2022) Copper homeostasis and cuproptosis in health and disease. Signal Transduct Target Ther 7:378. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-022-01229-y
Ma C, Han L, Zhu Z, Heng Pang C, Pan G (2022) Mineral metabolism and ferroptosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases. Biochem Pharmacol 205:115242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2022.115242
Hoang SA, Oseini A, Feaver RE, Cole BK, Asgharpour A, Vincent R, Siddiqui M, Lawson MJ, Day NC, Taylor JM, Wamhoff BR, Mirshahi F, Contos MJ, Idowu M, Sanyal AJ (2019) Gene expression predicts histological severity and reveals distinct molecular profiles of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Sci Rep 9:12541. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-48746-5
Clough E, Barrett T (2016) The gene expression omnibus database. Methods Mol Biol 1418:93–110. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-3578-9_5
Robin X, Turck N, Hainard A, Tiberti N, Lisacek F, Sanchez J-C, Müller M (2011) pROC: an open-source package for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinformatics 12:77. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-12-77
Wilkerson MD, Hayes DN (2010) ConsensusClusterPlus: a class discovery tool with confidence assessments and item tracking. Bioinformatics 26:1572–1573. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq170
Ringnér M (2008) What is principal component analysis? Nat Biotechnol 26:303–304. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0308-303
Hänzelmann S, Castelo R, Guinney J (2013) GSVA: gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-seq data. BMC Bioinformatics 14:7. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-14-7
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW, Shi W, Smyth GK (2015) limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res 43:e47. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv007
Kanehisa M, Goto S (2000) KEGG: kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 28:27–30. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/28.1.27
da Huang W, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA (2009) Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc 4:44–57. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2008.211
Warde-Farley D, Donaldson SL, Comes O, Zuberi K, Badrawi R, Chao P, Franz M, Grouios C, Kazi F, Lopes CT, Maitland A, Mostafavi S, Montojo J, Shao Q, Wright G, Bader GD, Morris Q (2010) The GeneMANIA prediction server: biological network integration for gene prioritization and predicting gene function. Nucleic Acids Res 38:W214–W220. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkq537
Qin Z, Xi Y, Zhang S, Tu G, Yan A (2019) Classification of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors using support vector machine and random forest methods. J Chem Inf Model 59:1988–2008. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jcim.8b00876
Lau JK, Zhang X, Yu J (2017) Animal models of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: current perspectives and recent advances. J Pathol 241:36–44. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.4829
Van Herck MA, Vonghia L, Francque SM (2017) Animal models of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-a starter’s guide. Nutrients. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9101072
Friedman SL, Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Rinella M, Sanyal AJ (2018) Mechanisms of NAFLD development and therapeutic strategies. Nat Med 24:908–922. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-018-0104-9
He F, Ru X, Wen T (2020) NRF2, a transcription factor for stress response and beyond. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21134777
Mohs A, Otto T, Schneider KM, Peltzer M, Boekschoten M, Holland CH, Hudert CA, Kalveram L, Wiegand S, Saez-Rodriguez J, Longerich T, Hengstler JG, Trautwein C (2021) Hepatocyte-specific NRF2 activation controls fibrogenesis and carcinogenesis in steatohepatitis. J Hepatol 74:638–648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2020.09.037
Cai Y, He Q, Liu W, Liang Q, Peng B, Li J, Zhang W, Kang F, Hong Q, Yan Y, Peng J, Xu Z, Bai N (2022) Comprehensive analysis of the potential cuproptosis-related biomarker LIAS that regulates prognosis and immunotherapy of pan-cancers. Front Oncol 12:952129. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.952129
Chen Y (2022) Identification and validation of cuproptosis-related prognostic signature and associated regulatory axis in uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma. Front Genet 13:912037. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2022.912037
Huster D, Kühne A, Bhattacharjee A, Raines L, Jantsch V, Noe J, Schirrmeister W, Sommerer I, Sabri O, Berr F, Mössner J, Stieger B, Caca K, Lutsenko S (2012) Diverse functional properties of Wilson disease ATP7B variants. Gastroenterology. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2011.12.048
Jiang X, Ji S, Yuan F, Li T, Cui S, Wang W, Ye X, Wang R, Chen Y, Zhu S (2023) Pyruvate dehydrogenase B regulates myogenic differentiation via the FoxP1-Arih2 axis. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 14:606–621. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.13166
Wu C, Liu X, Zhong L, Zhou Y, Long L, Yi T, Chen S, Li Y, Chen Y, Shen L, Zeng Q, Tang S (2023) Identification of cuproptosis-related genes in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2023:9245667. https://doi.org/10.1155/2023/9245667
Chen S, Liu X, Peng C, Tan C, Sun H, Liu H, Zhang Y, Wu P, Cui C, Liu C, Yang D, Li Z, Lu J, Guan J, Ke X, Wang R, Bo X, Xu X, Han J, Liu J (2021) The phytochemical hyperforin triggers thermogenesis in adipose tissue via a Dlat-AMPK signaling axis to curb obesity. Cell Metab. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2021.02.007
Acknowledgements
The authors all would like to thank the GEO database and the authors who provided their platforms and contributors for uploading their meaningful datasets. We thank LetPub (www.letpub.com) for its linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. ZR2022MH182 and Grant No. ZR2021QH119), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 82300892).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JL carried out experiments and wrote the manuscript, YZ, XM, RL, CX downloaded, arranged, analyzed, and validated the data. MD, QH designed the experiment and reviewed and approved the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database belongs to public databases. Patients / participants provided written informed consent to participate in this study. Individual written informed consent has been obtained for publishing any potentially identifiable images or data contained in this article, our study is based on open-source data with no ethical issues and other conflicts of interest. This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of Qilu Hospital of Shandong University.(KYLL-202210–070-1). All animal experimental protocols were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Qilu Hospital of Shandong University.(DWLL-2022–090).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Zhang, Y., Ma, X. et al. Identification and validation of cuproptosis-related genes for diagnosis and therapy in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Mol Cell Biochem (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-024-04957-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-024-04957-7