Abstract
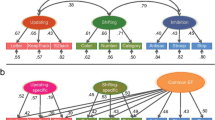
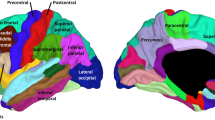
Previous studies have shown that language acquisition influences both the structure and function of the brain. However, whether the acquisition of a second language at different periods of life alters functional network organization in different ways remains unclear. Here, functional magnetic resonance imaging data from 27 English-speaking monolingual controls and 52 Spanish–English bilingual individuals, including 22 early bilinguals who began learning a second language before the age of ten and 30 late bilinguals who started learning a second language at age fourteen or later, were collected from the OpenNeuro database. Topological metrics of resting-state functional networks, including small-world attributes, network efficiency, and rich- and diverse-club regions, that characterize functional integration and segregation of the networks were computed via a graph theoretical approach. The results showed obvious increases in network efficiency in early bilinguals and late bilinguals relative to the monolingual controls; for example, the global efficiency of late bilinguals and early bilinguals was improved relative to that of monolingual controls, and the local efficiency of early bilinguals occupied an intermediate position between that of late bilinguals and monolingual controls. Obvious increases in rich-club and diverse-club functional connectivity were observed in the bilinguals relative to the monolingual controls. Three network metrics were positively correlated with Spanish proficiency test scores. These findings demonstrated that early and late acquisition of a second language had different impacts on the functional networks of the brain.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Imaging data were downloaded from the OpenNeuro database at the following link: https://openneuro.org/datasets/ds001747.
Code availability
The code used is available upon request.
References
Baggio, H. C., Segura, B., Junque, C., de Reus, M. A., Sala-Llonch, R., & Van den Heuvel, M. P. (2015). Rich club organization and cognitive performance in healthy older participants. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 27(9), 1801–1810. https://doi.org/10.1162/jocn_a_00821
Baker, S. T., Lubman, D. I., Yücel, M., Allen, N. B., Whittle, S., Fulcher, B. D., Zalesky, A., & Fornito, A. (2015). Developmental changes in brain network hub connectivity in late adolescence. Journal of Neuroscience, 35(24), 9078–9087. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5043-14.2015
Berken, J. A., Chai, X., Chen, J.-K., Gracco, V. L., & Klein, D. (2016). Effects of early and late bilingualism on resting-state functional connectivity. Journal of Neuroscience, 36(4), 1165–1172. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1960-15.2016
Bertolero, M. A., Yeo, B. T., & D’Esposito, M. (2015). The modular and integrative functional architecture of the human brain. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 112(49), E6798–E6807. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1510619112
Bertolero, M. A., Yeo, B. T. T., & D’Esposito, M. (2017). The diverse club. Nature Communications, 8(1), 1277. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-01189-w
Collin, G., Scholtens, L. H., Kahn, R. S., Hillegers, M. H., & van den Heuvel, M. P. (2017). Affected anatomical rich club and structural–functional coupling in young offspring of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder patients. Biological Psychiatry, 82(10), 746–755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2017.06.013
Cui, L.-B., Wei, Y., Xi, Y.-B., Griffa, A., De Lange, S. C., Kahn, R. S., Yin, H., & Van den Heuvel, M. P. (2019). Connectome-based patterns of first-episode medication-naïve patients with schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 45(6), 1291–1299. https://doi.org/10.1093/schbul/sbz014
Daianu, M., Mezher, A., Mendez, M. F., Jahanshad, N., Jimenez, E. E., & Thompson, P. M. (2016). Disrupted rich club network in behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia and early-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Human Brain Mapping, 37(3), 868–883. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.23069
DeLuca, V., Rothman, J., Bialystok, E., & Pliatsikas, C. (2019). Redefining bilingualism as a spectrum of experiences that differentially affects brain structure and function. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 116(15), 7565–7574. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1811513116
Dosenbach, N. U., Fair, D. A., Cohen, A. L., Schlaggar, B. L., & Petersen, S. E. (2008). A dual-networks architecture of top-down control. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 12(3), 99–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2008.01.001
Fan, L., Li, H., Zhuo, J., Zhang, Y., Wang, J., Chen, L., Yang, Z., Chu, C., Xie, S., Laird, A. R., Fox, P. T., Eickhoff, S. B., Yu, C., & Jiang, T. (2016). The human brainnetome atlas: A new brain atlas based on connectional architecture. Cerebral Cortex, 26(8), 3508–3526. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhw157%JCerebralCortex
Fan, X., Wu, Y., Cai, L., Ma, J., Pan, N., Xu, X., Sun, T., Jing, J., & Li, X. (2021). The differences in the whole-brain functional network between cantonese-mandarin bilinguals and mandarin monolinguals. Brain Sciences, 11(3), 310. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11030310
García-Pentón, L., Pérez Fernández, A., Iturria-Medina, Y., Gillon-Dowens, M., & Carreiras, M. (2014). Anatomical connectivity changes in the bilingual brain. NeuroImage, 84, 495–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.08.064
Giovannoli, J., Martella, D., Federico, F., Pirchio, S., & Casagrande, M. (2020). The Impact of Bilingualism on Executive Functions in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review Based on the PRISMA Method. Frontiers in Psychology, 11, 574789. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.574789
Gold, C. E. (2018). Exploring the resting state neural activity of monolinguals and late and early bilinguals. Brigham Young University. All Theses and Dissertations, pp. 6671. https://scholarsarchive.byu.edu/etd/6671
Grady, C. L., Luk, G., Craik, F. I., & Bialystok, E. (2015). Brain network activity in monolingual and bilingual older adults. Neuropsychologia, 66, 170–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2014.10.042
Grayson, D. S., Ray, S., Carpenter, S., Iyer, S., Dias, T. G. C., Stevens, C., Nigg, J. T., & Fair, D. A. (2014). Structural and functional rich club organization of the brain in children and adults. PLoS ONE, 9(2), e88297. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0088297
Griffa, A., & Van den Heuvel, M. P. (2018). Rich-club neurocircuitry: Function, evolution, and vulnerability. Dialogues in clinical neuroscience, 20(2), 121. https://doi.org/10.31887/DCNS.2018.20.2/agriffa
Guimera, R., & NunesAmaral, L. A. (2005). Functional cartography of complex metabolic networks. Nature, 433(7028), 895–900. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03288
Gullifer, J. W., Chai, X. J., Whitford, V., Pivneva, I., Baum, S., Klein, D., & Titone, D. J. N. (2018). Bilingual experience and resting-state brain connectivity: Impacts of L2 age of acquisition and social diversity of language use on control networks. Neuropsychologia, 117, 123–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2018.04.037
Hartanto, A., & Yang, H. (2019). Does early active bilingualism enhance inhibitory control and monitoring? A propensity-matching analysis. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 45(2), 60. https://psycnet.apa.org/doi/10.1037/xlm0000581
Itahashi, T., Yamada, T., Watanabe, H., Nakamura, M., Jimbo, D., Shioda, S., Toriizuka, K., Kato, N., & Hashimoto, R. (2014). Altered network topologies and hub organization in adults with autism: A resting-state fMRI study. PLoS ONE, 9(4), e94115. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0094115
Japee, S., Holiday, K., Satyshur, M. D., Mukai, I., & Ungerleider, L. G. (2015). A role of right middle frontal gyrus in reorienting of attention: A case study. Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience, 9, 23. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnsys.2015.00023
Kim, D.-J., Davis, E. P., Sandman, C. A., Sporns, O., O’Donnell, B. F., Buss, C., & Hetrick, W. P. (2016). Children’s intellectual ability is associated with structural network integrity. NeuroImage, 124, 550–556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.09.012
Klein, D., Mok, K., Chen, J.-K., & Watkins, K. E. (2014). Age of language learning shapes brain structure: A cortical thickness study of bilingual and monolingual individuals. Brain and Language, 131, 20–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bandl.2013.05.014
Liu, C., de Bruin, A., Jiao, L., Li, Z., & Wang, R. (2021). Second language learning tunes the language control network: A longitudinal fMRI study. Language, Cognition and Neuroscience, 36(4), 462–473. https://doi.org/10.1080/23273798.2020.1856898
Luk, G., De Sa, E. R. I. C., & Bialystok, E. (2011). Is there a relation between onset age of bilingualism and enhancement of cognitive control? Bilingualism: Language and cognition, 14(4), 588–595. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1366728911000010
Mai, N., Zhong, X., Chen, B., Peng, Q., Wu, Z., Zhang, W., Ouyang, C., & Ning, Y. (2017). Weight rich-club analysis in the white matter network of late-life depression with memory deficits. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 9, 279. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2017.00279
Mohades, S. G., Struys, E., Van Schuerbeek, P., Mondt, K., Van De Craen, P., & Luypaert, R. (2012). DTI reveals structural differences in white matter tracts between bilingual and monolingual children. Brain Research, 1435, 72–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2011.12.005
Nixon, P., Lazarova, J., Hodinott-Hill, I., Gough, P., & Passingham, R. (2004). The inferior frontal gyrus and phonological processing: An investigation using rTMS. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 16(2), 289–300. https://doi.org/10.1162/089892904322984571
Pintzka, C., Hansen, T. I., Evensmoen, H., & Håberg, A. (2015). Marked effects of intracranial volume correction methods on sex differences in neuroanatomical structures: A HUNT MRI study [Original Research]. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 9, 238. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2015.00238
Pliatsikas, C., DeLuca, V., & Voits, T. (2020). The many shades of bilingualism: Language experiences modulate adaptations in brain structure. Language Learning, 70(S2), 133–149. https://doi.org/10.1111/lang.12386
Rosvall, M., & Bergstrom, C. T. (2008). Maps of random walks on complex networks reveal community structure. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 105(4), 1118–1123. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0706851105
Sheffield, J. M., Repovs, G., Harms, M. P., Carter, C. S., Gold, J. M., MacDonald, A. W., III., Ragland, J. D., Silverstein, S. M., Godwin, D., & Barch, D. M. (2016). Evidence for accelerated decline of functional brain network efficiency in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 42(3), 753–761. https://doi.org/10.1093/schbul/sbv148
Sheng, Y., Yang, S., Rao, J., Zhang, Q., Li, J., Wang, D., & Zheng, W. (2023). Age of bilingual onset shapes the dynamics of functional connectivity and laterality in the resting-state. Brain Sciences, 13(9), 1231. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13091231
Shu, N., Duan, Y., Huang, J., Ren, Z., Liu, Z., Dong, H., Barkhof, F., Li, K., & Liu, Y. (2018). Progressive brain rich-club network disruption from clinically isolated syndrome towards multiple sclerosis. NeuroImage: Clinical, 19, 232–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2018.03.034
Szalárdy, O., Tóth, B., Farkas, D., György, E., & Winkler, I. (2019). Neuronal correlates of informational and energetic masking in the human brain in a multi-talker situation [Original Research]. Frontiers in Psychology, 10, 786. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00786
Thierry, G., Boulanouar, K., Kherif, F., Ranjeva, J.-P., & Démonet, J.-F. (1999). Temporal sorting of neural components underlying phonological processing. NeuroReport, 10(12), 2599–2603. https://doi.org/10.1097/00001756-199908200-00029*
Van Den Heuvel, M. P., & Sporns, O. (2011). Rich-club organization of the human connectome. Journal of Neuroscience, 31(44), 15775–15786. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3539-11.2011
van den Heuvel, M. P., Sporns, O., Collin, G., Scheewe, T., Mandl, R. C. W., Cahn, W., Goñi, J., Hulshoff Pol, H. E., & Kahn, R. S. (2013). Abnormal rich club organization and functional brain dynamics in schizophrenia. JAMA Psychiatry, 70(8), 783–792. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2013.1328
Verhelst, H., Vander Linden, C., De Pauw, T., Vingerhoets, G., & Caeyenberghs, K. (2018). Impaired rich club and increased local connectivity in children with traumatic brain injury: Local support for the rich? Human Brain Mapping, 39(7), 2800–2811. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.24041
Voevodskaya, O., Simmons, A., Nordenskjöld, R., Kullberg, J., Ahlström, H., Lind, L., Wahlund, L.-O., Larsson, E.-M., Westman, E., & Initiative, A. s. D. N. (2014). The effects of intracranial volume adjustment approaches on multiple regional MRI volumes in healthy aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 6, 264. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2014.00264
Wang, J., Wang, X., Xia, M., Liao, X., Evans, A., & He, Y. (2015). GRETNA: A graph theoretical network analysis toolbox for imaging connectomics. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 9, 386. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2015.00386
Wang, Y., Zhang, Y., Zhang, J., Wang, J., Xu, J., Li, J., Cui, G., & Zhang, J. (2018). Structural and functional abnormalities of the insular cortex in trigeminal neuralgia: A multimodal magnetic resonance imaging analysis. Pain, 159(3), 507–514. https://doi.org/10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001120
Weaver, B., & Wuensch, K. L. (2013). SPSS and SAS programs for comparing Pearson correlations and OLS regression coefficients. Behavior Research Methods, 45(3), 880–895. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13428-012-0289-7
Xue, C., Sun, H., Hu, G., Qi, W., Yue, Y., Rao, J., Yang, W., Xiao, C., & Chen, J. (2020). Disrupted patterns of rich-club and diverse-club organizations in subjective cognitive decline and amnestic mild cognitive impairment [Original Research]. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 14, 575652. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2020.575652
Yan, C.-G., Wang, X.-D., Zuo, X.-N., & Zang, Y.-F. (2016). DPABI: Data processing & analysis for (resting-state) brain imaging. Neuroinformatics, 14(3), 339–351. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-016-9299-4
Yao, Z., Zhang, Y., Lin, L., Zhou, Y., Xu, C., Jiang, T., & Initiative, A. s. D. N. (2010). Abnormal cortical networks in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS Computational Biology, 6(11), e1001006. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1001006
Zhang, M., Li, J., Chen, C., Xue, G., Lu, Z., Mei, L., Xue, H., Xue, F., He, Q., Chen, C., Wei, M., & Dong, Q. (2014). Resting-state functional connectivity and reading abilities in first and second languages. NeuroImage, 84, 546–553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.09.006
Zhang, Y., Han, K., Worth, R., & Liu, Z. (2020). Connecting concepts in the brain by mapping cortical representations of semantic relations. Nature Communications, 11(1), 1877. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-15804-w
Funding
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U21A20520), in part by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2019YFA0706200), in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62227807), and in part by the Science and Technology Program of Gansu Province (23YFGA0004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Author contributions included conception and study design (Jiajia Li and Chaofan Yao), data acquisition (Chaofan Yao), statistical analysis (Jiajia Li, Chaofan Yao and Yongchao Li), interpretation of results (Jiajia Li and Chaofan Yao), drafting the manuscript work or revising it critically for important intellectual content (Jiajia Li, Chaofan Yao, Yucen Sheng, Xia Liu, Ziyang Zhao, Yingying Shang, Jing Yang, Zhijun Yao, Bin Hu) and approval of final version to be published and agreement to be accountable for the integrity and accuracy of all aspects of the work (All authors).
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Not applicable.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All the authors provided consent for submission and publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Jiajia Li and Chaofan Yao contributed equally to this work and should be considered joint first authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Yao, C., Li, Y. et al. Effects of second language acquisition on brain functional networks at different developmental stages. Brain Imaging and Behavior (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-024-00865-y
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-024-00865-y