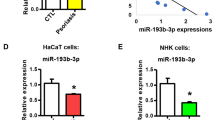
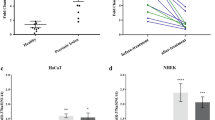
Abstract
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease characterized by abnormal keratinocyte proliferation and inflammation. MiRNAs and serum exosomes participate in the pathogenesis of many diseases. The objective of this study is to explore the function of miR-6785-5p in psoriatic keratinocytes and its upstream and downstream mechanisms. For our study, we employed qRT-PCR and fluorescence in situ hybridization to evaluate miR-6785-5p in psoriatic keratinocytes and conducted a microRNA microarray for identifying differentially expressed miRNAs in patient serum exosomes. We then cocultured keratinocytes with these exosomes, using immunofluorescence staining and qRT-PCR to assess uptake and miR-6785-5p overexpression. We explored miR-6785-5p’s role through transfection with specific mimics and inhibitors and confirmed MNK2 as its target using a luciferase assay. MNK2’s function was further examined using siRNA technology. Lastly, we applied an imiquimod-induced psoriasis mouse model, also employing siRNA, to investigate MNK2’s role in psoriasis. MiR-6785-5p demonstrates a notable overexpression in the keratinocytes of psoriasis patients as well as in their serum exosomes. These keratinocytes actively uptake the miR-6785-5p-enriched serum exosomes. Functionally, miR-6785-5p appears to alleviate psoriasis-like skin damage, observable both in vitro and in vivo, by downregulating MNK2 expression. Psoriasis keratinocytes uptake serum exosomes highly expressing miR-6785-5p. MiR-6785-5p inhibits the abnormal proliferation and inflammatory state of keratinocytes by reducing MNK2 expression and interfering with the MNK2/p-eIF4E axis.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Griffiths, C.E.M., A.W. Armstrong, J.E. Gudjonsson, and J.N.W.N. Barker. 2021. Psoriasis. Lancet. 397 (10281): 1301–1315. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32549-6.
Griffiths, C.E., and J.N. Barker. 2007. Pathogenesis and clinical features of psoriasis. Lancet 370 (9583): 263–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61128-3.
Zhou, X., Y. Chen, L. Cui, Y. Shi, and C. Guo. 2022. Advances in the pathogenesis of psoriasis: From keratinocyte perspective. Cell Death & Disease 13 (1): 81. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-022-04523-3.
Lu, T.X., and M.E. Rothenberg. 2018. MicroRNA. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 141 (4): 1202–1207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2017.08.034.
Fabian, M.R., and N. Sonenberg. 2012. The mechanics of miRNA-mediated gene silencing: A look under the hood of miRISC. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology 19 (6): 586–593. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2296.
Srivastava, A., L. Luo, W. Lohcharoenkal, et al. 2021. Cross-talk between IFN-γ and TWEAK through miR-149 amplifies skin inflammation in psoriasis. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 147 (6): 2225–2235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2020.12.657.
Wu, R., J. Zeng, J. Yuan, et al. 2018. MicroRNA-210 overexpression promotes psoriasis-like inflammation by inducing Th1 and Th17 cell differentiation. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 128 (6): 2551–2568. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI97426.
Huang, C., W. Zhong, X. Ren, et al. 2021. MiR-193b-3p-ERBB4 axis regulates psoriasis pathogenesis via modulating cellular proliferation and inflammatory-mediator production of keratinocytes. Cell Death & Disease 12 (11): 963. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-021-04230-5.
Chakraborty, C., A.R. Sharma, G. Sharma, and S.S. Lee. 2020. Therapeutic advances of miRNAs: A preclinical and clinical update. Journal of Advanced Research 28: 127–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2020.08.012.
Kalluri, R., and V.S. LeBleu. 2020. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 367 (eaau6478): 6977. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aau6977.
Yang, D., W. Zhang, H. Zhang, et al. 2020. Progress, opportunity, and perspective on exosome isolation - efforts for efficient exosome-based theranostics. Theranostics. 10 (8): 3684–3707. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.41580.
Tenchov, R., J.M. Sasso, X. Wang, W.S. Liaw, C.A. Chen, and Q.A. Zhou. 2022. Exosomes─nature’s lipid nanoparticles, a rising star in drug delivery and diagnostics. ACS Nano 16 (11): 17802–17846. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.2c08774.
Jiang, M., H. Fang, S. Shao, et al. 2019. Keratinocyte exosomes activate neutrophils and enhance skin inflammation in psoriasis. The FASEB Journal 33 (12): 13241–13253. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201900642R.
Shao, S., H. Fang, J. Zhang, et al. 2019. Neutrophil exosomes enhance the skin autoinflammation in generalized pustular psoriasis via activating keratinocytes. The FASEB Journal 33 (6): 6813–6828. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201802090RR.
Zhang, B., R.C. Lai, W.K. Sim, A.B.H. Choo, E.B. Lane, and S.K. Lim. 2021. Topical application of mesenchymal stem cell exosomes alleviates the imiquimod induced psoriasis-like inflammation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22 (2): 720. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020720.
Jiang, M., H. Fang, E. Dang, et al. 2021. Small extracellular vesicles containing miR-381-3p from keratinocytes promote T helper type 1 and T helper type 17 polarization in psoriasis. The Journal of Investigative Dermatology 141 (3): 563–574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jid.2020.07.009.
Alvarez-Erviti, L., Y. Seow, H. Yin, C. Betts, S. Lakhal, and M.J. Wood. 2011. Delivery of siRNA to the mouse brain by systemic injection of targeted exosomes. Nature Biotechnology 29 (4): 341–345. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1807.
Maimon, A., M. Mogilevsky, A. Shilo, et al. 2014. Mnk2 alternative splicing modulates the p38-MAPK pathway and impacts Ras-induced transformation. Cell Reports 7 (2): 501–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2014.03.041.
Yang, X., W. Zhong, and R. Cao. 2020. Phosphorylation of the mRNA cap-binding protein eIF4E and cancer. Cellular Signalling 73: 109689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2020.109689.
Piserà, A., A. Campo, and S. Campo. 2018. Structure and functions of the translation initiation factor eIF4E and its role in cancer development and treatment. Journal of Genetics and Genomics 45 (1): 13–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgg.2018.01.003.
Culjkovic, B., K. Tan, S. Orolicki, A. Amri, S. Meloche, and K.L. Borden. 2008. The eIF4E RNA regulon promotes the Akt signaling pathway. Journal of Cell Biology 181 (1): 51–63. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200707018.
Ueda, T., R. Watanabe-Fukunaga, H. Fukuyama, S. Nagata, and R. Fukunaga. 2004. Mnk2 and Mnk1 are essential for constitutive and inducible phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 4E but not for cell growth or development. Molecular and Cellular Biology 24 (15): 6539–6549. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.24.15.6539-6549.2004.
Xu, W., S. Kannan, C.S. Verma, and K. Nacro. 2022. Update on the development of MNK inhibitors as therapeutic agents. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 65 (2): 983–1007. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c00368.
Zhu, L., H.T. Sun, S. Wang, et al. 2020. Isolation and characterization of exosomes for cancer research. Journal of Hematology & Oncology 13 (1): 152. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-020-00987-y.
Gao, J., F. Chen, H. Fang, J. Mi, Q. Qi, and M. Yang. 2020. Daphnetin inhibits proliferation and inflammatory response in human HaCaT keratinocytes and ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin lesion in mice. Biological Research 53 (1): 48. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40659-020-00316-0.
Rabeony, H., I. Petit-Paris, J. Garnier, et al. 2014. Inhibition of keratinocyte differentiation by the synergistic effect of IL-17A, IL-22, IL-1α, TNFα and oncostatin M. PLoS ONE 9 (7): e101937. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0101937.
Varghese, F., A.B. Bukhari, R. Malhotra, and A. De. 2014. IHC Profiler: An open source plugin for the quantitative evaluation and automated scoring of immunohistochemistry images of human tissue samples. PLoS ONE 9 (5): e96801. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0096801.
Moos, S., A.N. Mohebiany, A. Waisman, and F.C. Kurschus. 2019. Imiquimod-induced psoriasis in mice depends on the IL-17 signaling of keratinocytes. The Journal of Investigative Dermatology 139 (5): 1110–1117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jid.2019.01.006.
Korman, N.J. 2020. Management of psoriasis as a systemic disease: What is the evidence? British Journal of Dermatology 182 (4): 840–848. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjd.18245.
Blauvelt, A., and A. Chiricozzi. 2018. The immunologic role of IL-17 in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis pathogenesis. Clinical Reviews in Allergy and Immunology 55 (3): 379–390. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-018-8702-3.
Shuai, Y., Z. Ma, W. Liu, et al. 2020. TEAD4 modulated LncRNA MNX1-AS1 contributes to gastric cancer progression partly through suppressing BTG2 and activating BCL2. Molecular Cancer 19 (1): 6. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-1104-1.
Xiong, Y., M. Pang, Y. Du, et al. 2022. The LINC01929/miR-6875-5p/ADAMTS12 axis in the ceRNA network regulates the development of advanced bladder cancer. Frontiers in Oncology 12: 856560. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.856560.
Chuang, H.C., M.H. Chen, Y.M. Chen, et al. 2021. BPI overexpression suppresses Treg differentiation and induces exosome-mediated inflammation in systemic lupus erythematosus. Theranostics. 11 (20): 9953–9966. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.63743.
Zhang, Y., L. Chen, X. Ye, et al. 2021. Expression and mechanism of exosome-mediated A FOXM1 related long noncoding RNA in gastric cancer. J Nanobiotechnology. 19 (1): 133. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-021-00873-w.
Wei, X.B., W.Q. Jiang, J.H. Zeng, et al. 2022. Exosome-derived lncRNA NEAT1 exacerbates sepsis-associated encephalopathy by promoting ferroptosis through regulating miR-9-5p/TFRC and GOT1 axis. Molecular Neurobiology 59 (3): 1954–1969. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-022-02738-1.
Ding, Y., P. Gong, J. Jiang, et al. 2022. Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells primed by inflammatory cytokines alleviate psoriasis-like inflammation via the TSG-6-neutrophil axis. Cell Death & Disease 13 (11): 996. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-022-05445-w.
Xu, Y., S. Liao, L. Wang, et al. 2021. Galeterone sensitizes breast cancer to chemotherapy via targeting MNK/eIF4E and β-catenin. Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology 87 (1): 85–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-020-04195-w.
Guo, Z., G. Peng, E. Li, et al. 2017. MAP kinase-interacting serine/threonine kinase 2 promotes proliferation, metastasis, and predicts poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Science and Reports 7 (1): 10612. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-10397-9.
Gao, J., L. Teng, S. Yang, et al. 2021. MNK as a potential pharmacological target for suppressing LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice. Biochemical Pharmacology 186: 114499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114499.
Acknowledgements
We sincerely thank all patients with psoriasis and healthy controls for participating in this study. And we show our best honour to the experimental mice for their sacrifice.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Numbers: 81972937, 82173419, and 82003344), the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2023QH333), and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2023M742110).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ruijie Wang first proposed the article topic. Ruijie Wang, Qing Sun, and Jianjun Yan designed the experiments. Ruijie Wang, Yingjian Huang, and Kaixin Shao performed the experiments. Ruijie Wang, Yingjian Huang, and Jianjun Yan analysed the data. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Ruijie Wang, and all the authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
This work was supported by the Ethics Committee of Shandong University (Ethics Committee No. KYLL-2017(KS)-152) and fulfilled the Declaration of Helsinki Principles.
Consent to Participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, R., Huang, Y., Shao, K. et al. High Expression of miR-6785-5p in the Serum Exosomes of Psoriasis Patients Alleviates Psoriasis-Like Skin Damage by Interfering with the MNK2/p-eIF4E Axis in Keratinocytes. Inflammation (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-024-01995-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-024-01995-7