Abstract
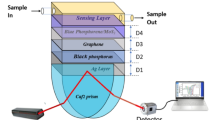
In this paper, the effect of different structures and flakes of phosphorene (Ph), germanene (Ge), and borophene (B) sandwiched between MoS2 layers on the surface plasmon resonance (SPR) biosensor structure is simulated and investigated in the Lumerical software environment. The main structure is based on the Kretschmann structure, utilizing the BK7 prism, a 30 nm gold (Au) layer, and an MoS2 and (Ph, Ge, B) hybrid structure as the top layer. The reflectance curves of the proposed SPR biosensors were obtained, analyzed, and compared for different refractive index modes, specifically n = 1.33 for a neutral aqueous medium and n = 1.339 for a bacterial medium. The results demonstrate that the minimum reflectance occurs for a 30 nm Au layer at an SPR resonance angle of θ = 71.95°. However, when different configurations of (Ph, Ge, B) with varying thicknesses are sandwiched between MoS2 layers on the Au layer, the resonance angle increases. The minimum reflectance values for a monolayer of phosphorene, a triple layer of germanene, and a triple layer of borophene sandwiched between MoS2 double layers on the Au layer are 0.027, 0.002, and 0.004, respectively. The triple layer of germanene exhibits the highest sensitivity of 152°/RIU for Δn = 0.009 with a detection accuracy of 0.090. The simulation results of the proposed structures present new opportunities for enhancing the sensitivity and performance of SPR biosensors.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No data was used for the research described in the article.
References
Váradi, L., et al.: Methods for the detection and identification of pathogenic bacteria: past, present, and future. Chem. Soc. Rev. 46(16), 4818–4832 (2017)
Ryan, K., Ray, C.: Principles of laboratory diagnosis of infectious diseases. In: Sherris Medical Microbiology, New York, p. 225 (1994).
James, T., Mannoor, M.S., Ivanov, D.V.: BioMEMS–advancing the frontiers of medicine. Sensors 8(9), 6077–6107 (2008)
Sabri, N., et al.: Toward optical sensors: review and applications. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 423, 012064 (2013)
Ho, A.H.-P., et al.: SPR Biosensors 5. Channels. 15, p. 37 (2017)
Wang, Y., et al.: Investigation of phase SPR biosensor for efficient targeted drug screening with high sensitivity and stability. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 209, 313–322 (2015)
Nurrohman, D.T., Chiu, N.-F.: Surface plasmon resonance biosensor performance analysis on 2D material based on graphene and transition metal dichalcogenides. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 9(11), 115023 (2020)
Sahoo, P.R., et al.: Surface plasmon resonance based biosensor: a new platform for rapid diagnosis of livestock diseases. Vet. World 9(12), 1338 (2016)
Zhang, C., et al.: U-bent fiber optic SPR sensor based on graphene/AgNPs. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 251, 127–133 (2017)
Hossain, M.B., et al.: High performance refractive index SPR sensor modeling employing graphene tri sheets. Results Phys. 15, 102719 (2019)
Sheng, X., et al.: Optimization of tunable symmetric SPR sensor based on Ag-graphene. Optik 184, 339–347 (2019)
Zhao, A., Wang, B.: Two-dimensional graphene-like Xenes as potential topological materials. APL Mater. 8(3), 030701 (2020)
Hu, H., et al.: Recent advances in two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides for biological sensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 142, 111573 (2019)
AlaguVibisha, G., et al.: Sensitivity enhancement of surface plasmon resonance sensor using hybrid configuration of 2D materials over bimetallic layer of Cu–Ni. Opt. Commun. 463, 125337 (2020)
Tao, W., et al.: Emerging two-dimensional monoelemental materials (Xenes) for biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 48(11), 2891–2912 (2019)
Pielnhofer, F., et al.: Designing 3D topological insulators by 2D-Xene (X= Ge, Sn) sheet functionalization in GaGeTe-type structures. J. Mater. Chem. C 5(19), 4752–4762 (2017)
Kumar, A., Kumar, A., Srivastava, S.: A study on surface plasmon resonance biosensor for the detection of CEA biomarker using 2D materials graphene, Mxene and MoS2. Optik 258, 168885 (2022)
Deepa, C., Rajeshkumar, L., Ramesh, M.: Preparation, synthesis, properties and characterization of graphene-based 2D nano-materials for biosensors and bioelectronics. J. Market. Res. 19, 2657–2694 (2022)
Raether, H.: Surface plasmons on smooth surfaces. In: Surface Plasmons on Smooth and Rough Surfaces and on Gratings, pp. 4–39. Springer, New york (1988)
Choi, K., et al.: Analytic design and visualization of multiple surface plasmon resonance excitation using angular spectrum decomposition for a Gaussian input beam. Opt. Express 13(22), 8866–8874 (2005)
Khorasani, S., Rashidian, B.: Modified transfer matrix method for conducting interfaces. J. Opt. A: Pure Appl. Opt. 4(3), 251 (2002)
Sreekanth, K.V., et al.: Sensitivity enhanced biosensor using graphene-based one-dimensional photonic crystal. Sens. Actuators, B Chem. 182, 424–428 (2013)
Rahman, M.S., et al.: Design and numerical analysis of highly sensitive Au-MoS2-graphene based hybrid surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Opt. Commun. 396, 36–43 (2017)
Abasi, T., Boochani, A., Masharian, S.: Metallic and intra-band investigation of optical properties for Borophene nano-sheet: a DFT study. Int. Nano Lett. 10(1), 33–41 (2020)
Pamungkas, M.A., Salim, M.F., Afifah, D.N.: Effects of sodium and chlorine doping on optical properties of germanene: density functional theory calculation. IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 299, 012045 (2018)
Ross, A.M., et al.: Anisotropic complex refractive indices of atomically thin materials: determination of the optical constants of few-layer black phosphorus. Materials 13(24), 5736 (2020)
Vahed, H., Nadri, C.: Sensitivity enhancement of SPR optical biosensor based on Graphene–MoS2 structure with nanocomposite layer. Opt. Mater. 88, 161–166 (2019)
Homola, J.: Surface plasmon resonance sensors for detection of chemical and biological species. Chem. Rev. 108(2), 462–493 (2008)
Ramanujam, J., Singh, U.P.: Copper indium gallium selenide based solar cells–a review. Energy Environ. Sci. 10(6), 1306–1319 (2017)
Fotovvati, B., Namdari, N., Dehghanghadikolaei, A.: On coating techniques for surface protection: a review. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 3(1), 28 (2019)
Weber, W., McCarthy, S.: Surface-plasmon resonance as a sensitive optical probe of metal-film properties. Phys. Rev. B 12(12), 5643 (1975)
Ordal, M.A., et al.: Optical properties of the metals al, co, cu, au, fe, pb, ni, pd, pt, ag, ti, and w in the infrared and far infrared. Appl. Opt. 22(7), 1099–1119 (1983)
Sadowski, J.W., Lekkala, J., Vikholm, I.: Biosensors based on surface plasmons excited in non-noble metals. Biosens. Bioelectron. 6(5), 439–444 (1991)
Sharma, N.K.: Performances of different metals in optical fibre-based surface plasmon resonance sensor. Pramana 78, 417–427 (2012)
Wu, L., et al.: Highly sensitive graphene biosensors based on surface plasmon resonance. Opt. Express 18(14), 14395–14400 (2010)
Maharana, P.K., Jha, R.: Chalcogenide prism and graphene multilayer based surface plasmon resonance affinity biosensor for high performance. Sens. Actuators, B Chem. 169, 161–166 (2012)
Komlev, A., Dyukin, R., Shutova, E.: The method of controlling the thickness of the deposited film on the basis of the surface plasmon resonance effect. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 872, 012042 (2017)
Maurya, J., Prajapati, Y., Tripathi, R.: Effect of molybdenum disulfide layer on surface plasmon resonance biosensor for the detection of bacteria. Silicon 10(2), 245–256 (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Davami, A., Aarabi, M. Effect of MoS2 and (phosphorene, germanene, borophene) hybrid structure on the performance of an SPR biosensor for detection of bacteria. Opt Rev (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10043-024-00875-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10043-024-00875-7