Abstract
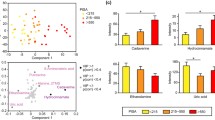
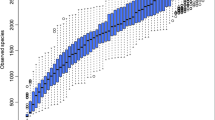
The onset and progression of periodontitis involves complicated interactions between the dysbiotic oral microbiota and disrupted host immune-inflammatory response, which can be mirrored by the changes in salivary metabolites profile. This pilot study sought to examine the saliva microbiome and metabolome in the Chinese population by the combined approach of 16s rRNA sequencing and high-throughput targeted metabolomics to discover potential cues for host-microbe metabolic interactions. Unstimulated whole saliva samples were collected from eighteen Stage III and IV periodontitis patients and thirteen healthy subjects. Full-mouth periodontal parameters were recorded. The taxonomic composition of microbiota was obtained by 16s rRNA sequencing, and the metabolites were identified and measured by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry-based metabolomic analysis. The oral microbiota composition displayed marked changes where the abundance of 93 microbial taxa differed significantly between the periodontitis and healthy group. Targeted metabolomics identified 103 differential metabolites between the patients and healthy individuals. Functional enrichment analysis demonstrated the upregulation of protein digestion and absorption, histidine metabolism, and nicotinate and nicotinamide metabolism pathways in the dysbiotic microbiota, while the ferroptosis, tryptophan metabolism, glutathione metabolism, and carbon metabolism pathways were upregulated in the patients. Correlation analysis confirmed positive relationships between the clinical parameters, pathogen abundances, and disease-related metabolite levels. The integral analysis of the saliva microbiome and metabolome yielded an accurate presentation of the dysbiotic oral microbiome and functional alterations in host-microbe metabolism. The microbial and metabolic profiling of the saliva could be a potential tool in the diagnosis, prognosis evaluation, and pathogenesis study of periodontitis.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Hajishengallis, G. 2014. Immunomicrobial pathogenesis of periodontitis: Keystones, pathobionts, and host response. Trends in Immunology 35: 3–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2013.09.001.
Schenkein, H.A., P.N. Papapanou, R. Genco, and M. Sanz. 2000. Mechanisms underlying the association between periodontitis and atherosclerotic disease. Periodontology 2020 83: 90–106. https://doi.org/10.1111/prd.12304.
Kamer, A.R., R.G. Craig, R. Niederman, J. Fortea, and M.J. de Leon. 2000. Periodontal disease as a possible cause for Alzheimer’s disease. Periodontology 2020 83: 242–271. https://doi.org/10.1111/prd.12327.
Genco, R.J., and M. Sanz. 2000. Clinical and public health implications of periodontal and systemic diseases: An overview. Periodontology 2020 83: 7–13. https://doi.org/10.1111/prd.12344.
Meyle, J., and I. Chapple. 2000. Molecular aspects of the pathogenesis of periodontitis. Periodontology 2015 69: 7–17. https://doi.org/10.1111/prd.12104.
Curtis, M.A., P.I. Diaz, and T.E. Van Dyke. 2000. The role of the microbiota in periodontal disease. Periodontology 2020 83: 14–25. https://doi.org/10.1111/prd.12296.
Zhou, T., W. Xu, Q. Wang, C. Jiang, H. Li, Y. Chao and Y. Sun. 2023. The effect of the "Oral-Gut" axis on periodontitis in inflammatory bowel disease: A review of microbe and immune mechanism associations. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology 13: 1132420. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2023.1132420.
Ding, J., C. Zhao, and L. Gao. 2023. Metabolism of periodontal pathobionts: Their regulatory roles in the dysbiotic microbiota. Molecular Oral Microbiology 38: 181–188. https://doi.org/10.1111/omi.12409.
Belstrom, D. 2020. The salivary microbiota in health and disease. Journal of Oral Microbiology 12: 1723975. https://doi.org/10.1080/20002297.2020.1723975.
Romano, F., G. Meoni, V. Manavella, G. Baima, L. Tenori, S. Cacciatore, and M. Aimetti. 2018. Analysis of salivary phenotypes of generalized aggressive and chronic periodontitis through nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolomics. Journal of Periodontology 89: 1452–1460. https://doi.org/10.1002/JPER.18-0097.
Hirtz, C., R. O'Flynn, P.M. Voisin, D. Deville de Periere, S. Lehmann, S. Guedes, F. Amado, R. Ferreira, F. Trindade and R. Vitorino. 2021. The potential impact of salivary peptides in periodontitis. Critical Reviews in Clinical Laboratory Sciences 58:479–492. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408363.2021.1907298.
Katsiki, P., K. Nazmi, B.G. Loos, M.L. Laine, K. Schaap, E. Hepdenizli, F.J. Bikker, H.S. Brand, E.C.I. Veerman, and E.A. Nicu. 2021. Comparing periodontitis biomarkers in saliva, oral rinse and gingival crevicular fluid: A pilot study. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 48: 1250–1259. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.13479.
Lundmark, A., Y.O.O. Hu, M. Huss, G. Johannsen, A.F. Andersson, and T. Yucel-Lindberg. 2019. Identification of salivary microbiota and its association with host inflammatory mediators in periodontitis. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology 9: 216. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2019.00216.
Kim, S., H.J. Kim, Y. Song, H.A. Lee, S. Kim, and J. Chung. 2021. Metabolic phenotyping of saliva to identify possible biomarkers of periodontitis using proton nuclear magnetic resonance. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 48: 1240–1249. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.13516.
Li, Y., F. Qian, X. Cheng, D. Wang, Y. Wang, Y. Pan, L. Chen, W. Wang, and Y. Tian. 2023. Dysbiosis of oral microbiota and metabolite profiles associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Microbiology Spectrum 11.
Salminen, A., U.K. Gursoy, S. Paju, K. Hyvarinen, P. Mantyla, K. Buhlin, E. Kononen, M.S. Nieminen, T. Sorsa, J. Sinisalo, and P.J. Pussinen. 2014. Salivary biomarkers of bacterial burden, inflammatory response, and tissue destruction in periodontitis. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 41: 442–450. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.12234.
Balci, N., S. Kurgan, A. Cekici, T. Cakir, and M.A. Serdar. 2021. Free amino acid composition of saliva in patients with healthy periodontium and periodontitis. Clinical Oral Investigations. 25: 4175–4183. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-021-03977-7.
Guney, Z., S. Kurgan, C. Onder, C. Mammadov, M.A. Serdar, and M. Gunhan. 2023. Asymmetric and symmetric dimethylarginine gingival crevicular fluid levels in periodontitis. Journal of Periodontal Research 58: 256–261. https://doi.org/10.1111/jre.13087.
R Core Team. 2020. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. https://www.R-project.org/.
Bolyen, E., J.R. Rideout, M.R. Dillon, N.A. Bokulich, C.C. Abnet, G.A. Al-Ghalith, H. Alexander, E.J. Alm, M. Arumugam, F. Asnicar, Y. Bai, J.E. Bisanz, K. Bittinger, A. Brejnrod, C.J. Brislawn, C.T. Brown, B.J. Callahan, A.M. Caraballo-Rodriguez, J. Chase, E.K. Cope, R. Da Silva, C. Diener, P.C. Dorrestein, G.M. Douglas, D.M. Durall, C. Duvallet, C.F. Edwardson, M. Ernst, M. Estaki, J. Fouquier, J.M. Gauglitz, S.M. Gibbons, D.L. Gibson, A. Gonzalez, K. Gorlick, J. Guo, B. Hillmann, S. Holmes, H. Holste, C. Huttenhower, G.A. Huttley, S. Janssen, A.K. Jarmusch, L. Jiang, B.D. Kaehler, K.B. Kang, C.R. Keefe, P. Keim, S.T. Kelley, D. Knights, I. Koester, T. Kosciolek, J. Kreps, M.G.I. Langille, J. Lee, R. Ley, Y.X. Liu, E. Loftfield, C. Lozupone, M. Maher, C. Marotz, B.D. Martin, D. McDonald, L.J. McIver, A.V. Melnik, J.L. Metcalf, S.C. Morgan, J.T. Morton, A.T. Naimey, J.A. Navas-Molina, L.F. Nothias, S.B. Orchanian, T. Pearson, S.L. Peoples, D. Petras, M.L. Preuss, E. Pruesse, L.B. Rasmussen, A. Rivers, M.S. Robeson 2nd., P. Rosenthal, N. Segata, M. Shaffer, A. Shiffer, R. Sinha, S.J. Song, J.R. Spear, A.D. Swafford, L.R. Thompson, P.J. Torres, P. Trinh, A. Tripathi, P.J. Turnbaugh, S. Ul-Hasan, J.J.J. van der Hooft, F. Vargas, Y. Vazquez-Baeza, E. Vogtmann, M. von Hippel, W. Walters, Y. Wan, M. Wang, J. Warren, K.C. Weber, C.H.D. Williamson, A.D. Willis, Z.Z. Xu, J.R. Zaneveld, Y. Zhang, Q. Zhu, R. Knight, and J.G. Caporaso. 2019. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nature Biotechnology 37: 852–857. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-019-0209-9.
Callahan, B.J., P.J. McMurdie, M.J. Rosen, A.W. Han, A.J. Johnson, and S.P. Holmes. 2016. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nature Methods 13: 581–583. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3869.
Cole, J.R., Q. Wang, J.A. Fish, B. Chai, D.M. McGarrell, Y. Sun, C.T. Brown, A. Porras-Alfaro, C.R. Kuske, and J.M. Tiedje. 2014. Ribosomal database project: Data and tools for high throughput rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Research 42: D633–D642. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt1244.
Schloss, P.D., S.L. Westcott, T. Ryabin, J.R. Hall, M. Hartmann, E.B. Hollister, R.A. Lesniewski, B.B. Oakley, D.H. Parks, C.J. Robinson, J.W. Sahl, B. Stres, G.G. Thallinger, D.J. Van Horn, and C.F. Weber. 2009. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Applied and Environment Microbiology 75: 7537–7541. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01541-09.
Caporaso, J.G., J. Kuczynski, J. Stombaugh, K. Bittinger, F.D. Bushman, E.K. Costello, N. Fierer, A.G. Pena, J.K. Goodrich, J.I. Gordon, G.A. Huttley, S.T. Kelley, D. Knights, J.E. Koenig, R.E. Ley, C.A. Lozupone, D. McDonald, B.D. Muegge, M. Pirrung, J. Reeder, J.R. Sevinsky, P.J. Turnbaugh, W.A. Walters, J. Widmann, T. Yatsunenko, J. Zaneveld, and R. Knight. 2010. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nature Methods 7: 335–336. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.f.303.
Segata, N., J. Izard, L. Waldron, D. Gevers, L. Miropolsky, W.S. Garrett, and C. Huttenhower. 2011. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biology 12: R60. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2011-12-6-r60.
Langille, M.G., J. Zaneveld, J.G. Caporaso, D. McDonald, D. Knights, J.A. Reyes, J.C. Clemente, D.E. Burkepile, R.L. Vega Thurber, R. Knight, R.G. Beiko, and C. Huttenhower. 2013. Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nature Biotechnology 31: 814–821. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2676.
Wen, B., Z. Mei, C. Zeng, and S. Liu. 2017. metaX: A flexible and comprehensive software for processing metabolomics data. BMC Bioinformatics 18: 183. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-017-1579-y.
Takahashi, N. 2015. Oral microbiome metabolism: From “who are they?” to “what are they doing?” Journal of Dental Research 94: 1628–1637. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034515606045.
Melguizo-Rodriguez, L., V.J. Costela-Ruiz, F.J. Manzano-Moreno, C. Ruiz and R. Illescas-Montes. 2020. Salivary biomarkers and their application in the diagnosis and monitoring of the most common oral pathologies. International Journal of Molecular Science. 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21145173.
Nguyen, T., L. Sedghi, S. Ganther, E. Malone, P. Kamarajan, and Y.L. Kapila. 2000. Host-microbe interactions: Profiles in the transcriptome, the proteome, and the metabolome. Periodontology 2020 82: 115–128. https://doi.org/10.1111/prd.12316.
Bostanci, N., M. Grant, K. Bao, A. Silbereisen, F. Hetrodt, D. Manoil, and G.N. Belibasakis. 2000. Metaproteome and metabolome of oral microbial communities. Periodontology 2021 85: 46–81. https://doi.org/10.1111/prd.12351.
Shi, B., M. Chang, J. Martin, M. Mitreva, R. Lux, P. Klokkevold, E. Sodergren, G.M. Weinstock, S.K. Haake and H. Li. 2015. Dynamic changes in the subgingival microbiome and their potential for diagnosis and prognosis of periodontitis. mBio. 6:e01926–14. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.01926-14.
Hajishengallis, G., and R.J. Lamont. 2012. Beyond the red complex and into more complexity: The polymicrobial synergy and dysbiosis (PSD) model of periodontal disease etiology. Molecular Oral Microbiology 27: 409–419. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2041-1014.2012.00663.x.
Abusleme, L., A.K. Dupuy, N. Dutzan, N. Silva, J.A. Burleson, L.D. Strausbaugh, J. Gamonal, and P.I. Diaz. 2013. The subgingival microbiome in health and periodontitis and its relationship with community biomass and inflammation. ISME Journal 7: 1016–1025. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2012.174.
Overmyer, K.A., T.W. Rhoads, A.E. Merrill, Z. Ye, M.S. Westphall, A. Acharya, S.K. Shukla, and J.J. Coon. 2021. Proteomics, lipidomics, metabolomics, and 16S DNA sequencing of dental plaque from patients with diabetes and periodontal disease. Molecular and Cellular Proteomics 20: 100126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcpro.2021.100126.
Ozeki, M., T. Nozaki, J. Aoki, T. Bamba, K.R. Jensen, S. Murakami, and M. Toyoda. 2016. Metabolomic analysis of gingival crevicular fluid using gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Mass Spectrom (Tokyo) 5: A0047. https://doi.org/10.5702/massspectrometry.A0047.
Chen, H.W., W. Zhou, Y. Liao, S.C. Hu, T.L. Chen, and Z.C. Song. 2018. Analysis of metabolic profiles of generalized aggressive periodontitis. Journal of Periodontal Research 53: 894–901. https://doi.org/10.1111/jre.12579.
Garcia-Villaescusa, A., J.M. Morales-Tatay, D. Monleon-Salvado, J.M. Gonzalez-Darder, C. Bellot-Arcis, J.M. Montiel-Company, and J.M. Almerich-Silla. 2018. Using NMR in saliva to identify possible biomarkers of glioblastoma and chronic periodontitis. PLoS ONE 13: e0188710. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0188710.
Sedghi, L., V. DiMassa, A. Harrington, S.V. Lynch, and Y.L. Kapila. 2000. The oral microbiome: Role of key organisms and complex networks in oral health and disease. Periodontology 2021 87: 107–131. https://doi.org/10.1111/prd.12393.
Vital, M., A.C. Howe and J.M. Tiedje. 2014. Revealing the bacterial butyrate synthesis pathways by analyzing (meta)genomic data. mBio. 5:e00889. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.00889-14.
Tsuda, H., K. Ochiai, N. Suzuki, and K. Otsuka. 2010. Butyrate, a bacterial metabolite, induces apoptosis and autophagic cell death in gingival epithelial cells. Journal of Periodontal Research 45: 626–634. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0765.2010.01277.x.
Shirasugi, M., K. Nishioka, T. Yamamoto, T. Nakaya, and N. Kanamura. 2017. Normal human gingival fibroblasts undergo cytostasis and apoptosis after long-term exposure to butyric acid. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 482: 1122–1128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.11.168.
Mayrand, D., and S.C. Holt. 1988. Biology of asaccharolytic black-pigmented Bacteroides species. Microbiological Reviews 52: 134–152. https://doi.org/10.1128/mr.52.1.134-152.1988.
Slots, J., and R.J. Genco. 1984. Black-pigmented Bacteroides species, Capnocytophaga species, and Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans in human periodontal disease: Virulence factors in colonization, survival, and tissue destruction. Journal of Dental Research 63: 412–421. https://doi.org/10.1177/00220345840630031101.
Zhao, Y., J. Li, W. Guo, H. Li and L. Lei. 2020. Periodontitis-level butyrate-induced ferroptosis in periodontal ligament fibroblasts by activation of ferritinophagy. Cell Death Discovery. 6. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-020-00356-1.
Cai, J., L. Sun, and F.J. Gonzalez. 2022. Gut microbiota-derived bile acids in intestinal immunity, inflammation, and tumorigenesis. Cell Host & Microbe 30: 289–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2022.02.004.
Wahlstrom, A., S.I. Sayin, H.U. Marschall, and F. Backhed. 2016. Intestinal crosstalk between bile acids and microbiota and its impact on host metabolism. Cell Metabolism 24: 41–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2016.05.005.
Yang, R., W. Yu, L. Lin, M. Jin, S. Hu, B. Jiang, C. Mao, G. Li, J. Tang, Y. Gu, H. Chen, and E. Lu. 2023. Profiling of bile acids and activated receptor S1PR2 in gingival tissues of periodontitis patients. Journal of Periodontology 94: 564–574. https://doi.org/10.1002/JPER.22-0398.
Talebian, R., L. Panahipour, and R. Gruber. 2020. Ursodeoxycholic acid attenuates the expression of proinflammatory cytokines in periodontal cells. Journal of Periodontology 91: 1098–1104. https://doi.org/10.1002/JPER.19-0013.
Cao, S., X. Meng, Y. Li, L. Sun, L. Jiang, H. Xuan, and X. Chen. 2021. Bile acids elevated in chronic periaortitis could activate farnesoid-X-receptor to suppress IL-6 production by macrophages. Frontiers in Immunology 12: 632864. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.632864.
Bhargava, P., M.D. Smith, L. Mische, E. Harrington, K.C. Fitzgerald, K. Martin, S. Kim, A.A. Reyes, J. Gonzalez-Cardona, C. Volsko, A. Tripathi, S. Singh, K. Varanasi, H.N. Lord, K. Meyers, M. Taylor, M. Gharagozloo, E.S. Sotirchos, B. Nourbakhsh, R. Dutta, E.M. Mowry, E. Waubant, and P.A. Calabresi. 2020. Bile acid metabolism is altered in multiple sclerosis and supplementation ameliorates neuroinflammation. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 130: 3467–3482. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI129401.
Winston, J.A., and C.M. Theriot. 2020. Diversification of host bile acids by members of the gut microbiota. Gut Microbes. 11: 158–171. https://doi.org/10.1080/19490976.2019.1674124.
Collins, S.L., J.G. Stine, J.E. Bisanz, C.D. Okafor, and A.D. Patterson. 2023. Bile acids and the gut microbiota: Metabolic interactions and impacts on disease. Nature Reviews Microbiology 21: 236–247. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-022-00805-x.
Jones, B.V., M. Begley, C. Hill, C.G. Gahan, and J.R. Marchesi. 2008. Functional and comparative metagenomic analysis of bile salt hydrolase activity in the human gut microbiome. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA. 105: 13580–13585. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0804437105.
Sayin, S.I., A. Wahlstrom, J. Felin, S. Jantti, H.U. Marschall, K. Bamberg, B. Angelin, T. Hyotylainen, M. Oresic, and F. Backhed. 2013. Gut microbiota regulates bile acid metabolism by reducing the levels of tauro-beta-muricholic acid, a naturally occurring FXR antagonist. Cell Metabolism 17: 225–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2013.01.003.
Nakagawa, M., and K.D. Setchell. 1990. Bile acid metabolism in early life: Studies of amniotic fluid. Journal of Lipid Research 31: 1089–1098.
Shoda, J., R. Mahara, T. Osuga, M. Tohma, S. Ohnishi, H. Miyazaki, N. Tanaka, and Y. Matsuzaki. 1988. Similarity of unusual bile acids in human umbilical cord blood and amniotic fluid from newborns and in sera and urine from adult patients with cholestatic liver diseases. Journal of Lipid Research 29: 847–858.
Bove, K.E., C.C. Daugherty, W. Tyson, G. Mierau, J.E. Heubi, W.F. Balistreri, and K.D. Setchell. 2000. Bile acid synthetic defects and liver disease. Pediatric and Developmental Pathology 3: 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s100240050001.
Zohrer, E., K. Meinel, G. Fauler, V.A. Moser, T. Greimel, J. Zobl, A. Schlagenhauf, and J. Jahnel. 2018. Neonatal sepsis leads to early rise of rare serum bile acid tauro-omega-muricholic acid (TOMCA). Pediatric Research 84: 66–70. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-018-0007-y.
Liu, K., H. Meng, and J. Hou. 2012. Activity of 25-hydroxylase in human gingival fibroblasts and periodontal ligament cells. PLoS ONE 7: e52053. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0052053.
Geier, B., E.M. Sogin, D. Michellod, M. Janda, M. Kompauer, B. Spengler, N. Dubilier, and M. Liebeke. 2020. Spatial metabolomics of in situ host-microbe interactions at the micrometre scale. Nature Microbiology 5: 498–510. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-019-0664-6.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 82170959) and the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (2022A1515010855).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L.G. and C.J.Z. conceived the research design and supervised the entire study. C.Z. and L.T. collected clinical information. J.D. and J.L. analyzed the data, drew the figures and drafted the manuscript. L.G. and C.J.Z. revised the manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Medical Ethics Committee of Hospital of Stomatology, Sun Yat-sen University (Issuing number: KQEC-2022–16-01), and with the Helsinki Declaration. Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, J., Li, J., Zhang, C. et al. High-Throughput Combined Analysis of Saliva Microbiota and Metabolomic Profile in Chinese Periodontitis Patients: A Pilot Study. Inflammation (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-023-01948-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-023-01948-6