Abstract
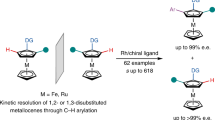
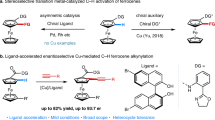
Planar chiral ferrocenes are widely studied structures in asymmetric catalysis, materials science and medicinal chemistry. Although synthetic methods for 1,2-disubstituted planar chiral ferrocenes are well known, methods for the direct construction of 1,3-disubstituted planar chiral ferrocenes remain elusive. Here we report a modular platform for the construction of planar chirality in 1,3-disubstituted ferrocenes/ruthenocenes via an enantioselective relay remote C–H activation strategy. This method demonstrates a mechanism for remote enantiocontrol via enantiodetermining initial C‒H activation at the C2 position, enabled by a chiral mono-N-protected natural amino-acid ligand, and subsequent relay to the remote C3 position by a bridgehead-substituted norbornene mediator. A wide variety of 1,3-disubstituted planar chiral metallocenes are prepared with high enantioselectivity (96‒99% e.e.). The reaction shows good functional-group tolerance and high step-economy, and aryl iodides/bromides are compatible as coupling partners. The resulting metallocenes can be readily derivatized to yield planar chiral ligands and catalysts for asymmetric catalysis as well as building blocks for other applications.

This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Crystallographic data for the structures reported in this Article have been deposited at the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre, under deposition nos. CCDC 2116139 (3a-2), 2117209 (3b) and 2116140 (8). Copies of the data can be obtained free of charge via https://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/structures/. All other characterization data and detailed experimental procedures are available in the Supplementary Information.
References
Carreira, E. M. & Kvaerno, L. Classics in Stereoselective Synthesis (Wiley, 2009).
Lopez, R. & Palomo, C. Planar chirality: a mine for catalysis and structure discovery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 61, e202113504 (2021).
Ogasawara, M. Enantioselective preparation of planar-chiral transition metal complexes by asymmetric olefin-metathesis reactions in metal coordination spheres. Chem. Rec. 21, 3509–3519 (2021).
Gagnon, C. et al. Biocatalytic synthesis of planar chiral macrocycles. Science 367, 917–921 (2020).
Zhou, Q.-L. Privileged Chiral Ligands and Catalysts (Wiley, 2011).
Ye, B. & Cramer, N. Chiral cyclopentadienyl ligands as stereocontrolling element in asymmetric C-H functionalization. Science 338, 504–506 (2012).
Togni, A. & Hayashi, T. Ferrocenes (Wiley, 1995).
Dai, L.-X. & Hou, X.-L. Chiral Ferrocenes in Asymmetric Catalysis (Wiley, 2010).
Fu, G. C. Applications of planar-chiral heterocycles as ligands in asymmetric catalysis. Acc. Chem. Res. 39, 853–860 (2006).
Caniparoli, U., Escofet, I. & Echavarren, A. M. Planar chiral 1,3-disubstituted ferrocenyl phosphine gold(I) catalysts. ACS Catal. 12, 3317–3322 (2022).
Štěpnička, P. Ferrocenes (Wiley, 2008).
Muraoka, T., Kinbara, K., Kobayashi, Y. & Aida, T. Light-driven open-close motion of chiral molecular scissors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125, 5612–5613 (2003).
Muraoka, T., Kinbara, K. & Aida, T. Mechanical twisting of a guest by a photoresponsive host. Nature 440, 512–515 (2006).
Chuard, T. et al. Planar chirality: a fascinating symmetry breaking which leads to ferroelectricity in ferrocenyl liquid crystals. Chem. Commun. 2000, 2109–2110 (2000).
Brettar, J. et al. Ferrocene-containing optically active liquid-crystalline side-chain polysiloxanes with planar chirality. Adv. Funct. Mater. 16, 260–267 (2006).
Patra, M. & Gasser, G. The medicinal chemistry of ferrocene and its derivatives. Nat. Rev. Chem. 1, 0066 (2017).
Ogasawara, M., Arae, S., Watanabe, S., Nakajima, K. & Takahashi, T. Kinetic resolution of planar-chiral ferrocenylphosphine derivatives by molybdenum-catalyzed asymmetric ring-closing metathesis and their application in asymmetric catalysis. ACS Catal. 6, 1308–1315 (2016).
Ogasawara, M., Watanabe, S., Nakajima, K. & Takahashi, T. Enantioselective synthesis of planar-chiral phosphaferrocenes by molybdenum-catalyzed asymmetric interannular ring-closing metathesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 2136–2137 (2010).
Zhu, D.-Y., Chen, P. & Xia, J.-B. Synthesis of planar chiral ferrocenes by transition-metal-catalyzed enantioselective C-H activation. ChemCatChem 8, 68–73 (2016).
Gao, D.-W., Gu, Q., Zheng, C. & You, S.-L. Synthesis of planar chiral ferrocenes via transition-metal-catalyzed direct C-H bond functionalization. Acc. Chem. Res. 50, 351–365 (2017).
Liu, C.-X., Gu, Q. & You, S.-L. Asymmetric C-H bond functionalization of ferrocenes: new opportunities and challenges. Trends Chem. 2, 737–749 (2020).
Steurer, M., Tiedl, K., Wang, Y. & Weissensteiner, W. Stereoselective synthesis of chiral, non-racemic 1,2,3-tri- and 1,3-disubstituted ferrocene derivatives. Chem. Commun. 2005, 4929–4931 (2005).
Ferber, B., Top, S., Welter, R. & Jaouen, G. A new efficient route to chiral 1,3-disubstituted ferrocenes: application to the syntheses of (Rp)- and (Sp)-17α-[(3′-formylferrocenyl)ethynyl]estradiol. Chem. Eur. J. 12, 2081–2086 (2006).
Steurer, M., Wang, Y., Mereiter, K. & Weissensteiner, W. Bromide-mediated ortho-deprotonation in the synthesis of chiral, nonracemic ferrocene derivatives. Organometallics 26, 3850–3859 (2007).
Leow, D., Li, G., Mei, T.-S. & Yu, J.-Q. Activation of remote meta-C–H bonds assisted by an end-on template. Nature 486, 518–522 (2012).
Wang, X.-C. et al. Ligand-enabled meta-C−H activation using a transient mediator. Nature 519, 334–338 (2015).
Bisht, R., Hoque, M. E. & Chattopadhyay, B. Amide effects in C-H activation: noncovalent interactions with L-shaped ligand for meta borylation of aromatic amides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 57, 15762–15766 (2018).
Meng, G. et al. Achieving site-selectivity for C-H activation processes based on distance and geometry: a carpenter’s approach. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142, 10571–10591 (2020).
Chaturvedi, J., Haldar, C., Bisht, R., Pandey, G. & Chattopadhyay, B. Meta selective C-H borylation of sterically biased and unbiased substrates directed by electrostatic interaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 143, 7604–7611 (2021).
Dutta, U., Maiti, S., Bhattacharya, T. & Maiti, D. Arene diversification through distal C(sp2)-H functionalization. Science 372, eabd5992 (2021).
Catellani, M., Frignani, F. & Rangoni, A. A complex catalytic cycle leading to a regioselective synthesis of o,o′-disubstituted vinylarenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 36, 119–122 (1997).
Wang, J. & Dong, G. Palladium/norbornene cooperative catalysis. Chem. Rev. 119, 7478–7528 (2019).
Shi, H., Herron, A. N., Shao, Y., Shao, Q. & Yu, J.-Q. Enantioselective remote meta-C−H arylation and alkylation via a chiral transient mediator. Nature 558, 581–585 (2018).
Hill, D. E., Yu, J.-Q. & Blackmond, D. G. Insights into the role of transient chiral mediators and pyridone ligands in asymmetric Pd-catalyzed C-H functionalization. J. Org. Chem. 85, 13674–13679 (2020).
Genov, G. R., Douthwaite, J. L., Lahdenpera, A. S. K., Gibson, D. C. & Phipps, R. J. Enantioselective remote C-H activation directed by a chiral cation. Science 367, 1246–1251 (2020).
Gaunt, J. C. & Shaw, B. L. Transition metal-carbon bonds: XL. Palladium(II) complexes of [(dimethylamino)methyl]-ferrocene. J. Organometal. Chem. 102, 511–516 (1975).
Sokolov, V. I., Troitskaya, L. L. & Reutov, O. A. Asymmetric induction in the course of internal palladation of enantiomeric 1-dimethylaminoethylferrocene. J. Organometal. Chem. 133, C28–C30 (1977).
Sokolov, V. I., Troitskaya, L. L. & Reutov, O. A. Asymmetric cyclopalladation of dimethylaminomethylferrocene. J. Organometal. Chem. 182, 537–546 (1979).
Sokolov, V. I., Troitskaya, L. L. & Khrushchova, N. S. Asymmetric cyclopalladation in the ferrocene series as a tool for enantioselective synthesis. Preparation of some analogues of natural products. J. Organometal. Chem. 250, 439–446 (1983).
Shi, B.-F., Maugel, N., Zhang, Y.-H. & Yu, J.-Q. Pd(II)-catalyzed enantioselective activation of C(sp2)-H and C(sp3)-H bonds using monoprotected amino acids as chiral ligands. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 47, 4882–4886 (2008).
Shao, Q., Wu, K., Zhuang, Z., Qian, S. & Yu, J.-Q. From Pd(OAc)2 to chiral catalysts: the discovery and development of bifunctional mono-N-protected amino acid ligands for diverse C-H functionalization reactions. Acc. Chem. Res. 53, 833–851 (2020).
Wang, J., Li, R., Dong, Z., Liu, P. & Dong, G. Complementary site-selectivity in arene functionalization enabled by overcoming the ortho constraint in palladium/norbornene catalysis. Nat. Chem. 10, 866–872 (2018).
Li, R. & Dong, G. Structurally modified norbornenes: a key factor to modulate reaction selectivity in the palladium/norbornene cooperative catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142, 17859–17875 (2020).
Shen, P.-X., Wang, X.-C., Wang, P., Zhu, R.-Y. & Yu, J.-Q. Ligand-enabled meta-C-H alkylation and arylation using a modified norbornene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137, 11574–11577 (2015).
Ding, Q. et al. Ligand-enabled meta-selective C-H arylation of nosyl-protected phenethylamines, benzylamines and 2-aryl anilines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139, 417–425 (2017).
Pi, C. et al. Redox of ferrocene controlled asymmetric dehydrogenative Heck reaction via palladium-catalyzed dual C-H bond activation. Chem. Sci. 4, 2675–2679 (2013).
Gao, D.-W., Shi, Y.-C., Gu, Q., Zhao, Z.-L. & You, S.-L. Enantioselective synthesis of planar chiral ferrocenes via palladium-catalyzed direct coupling with arylboronic acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 86–89 (2013).
Delacroix, O., Picart-Goetgheluck, S., Maciejewski, L. & Brocard, J. Synthesis of chiral ferrocenyl aminoalcohols involving a diastereospecific oxidation: use in asymmetric catalysis. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 10, 4417–4425 (1999).
Gao, D.-W., Gu, Q. & You, S.-L. An enantioselective oxidative C-H/C-H cross-coupling reaction: highly efficient method to prepare planar chiral ferrocenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 2544–2547 (2016).
Acknowledgements
This paper is dedicated to the 130th anniversary of Wuhan University. We thank H. Cong (WHU), X.-G. Meng (CCNU) and Y.-Q. Zhou (SCU) for X-ray crystallographic analysis assistance. We gratefully acknowledge D. Ma (SIOC), L.-Q. Lu (CCNU), W.-B. Liu, G. Yin and Q. Lu (WHU) for helpful discussions, X. Qi (WHU) for calculation studies, W. Reid (J-STAR Research Inc.) for assistance with the preparation of the manuscript and H. Li (ZMU) for technical assistance. This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (no. 2022YFA1503703), National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 21801193, 21871213 and 22071189), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (grant no. BK20210119, H.-G.C.), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2042021kf0214 and 2042020kf0039) and start-up funding from Wuhan University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L.Z., L.L., J.H., C.J. and Z.L. prepared the substrates and NBE mediators, performed the reaction optimization, substrate scope exploration and synthetic applications under the supervision of H.-G.C., J.-Q.Y. and Q.Z. S.D. performed the density functional theory calculations. H.-G.C., K.W., J.-Q.Y. and Q.Z. co-wrote the manuscript. All authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Chemistry thanks the anonymous reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Figs. 1–9 and Tables 1–11.
Supplementary Data 1
Crystallographic data for compound 3a-2. CCDC reference 2116139.
Supplementary Data 2
Crystallographic data for compound 3b. CCDC reference 2117209.
Supplementary Data 3
Crystallographic data for compound 8. CCDC reference 2116140.
Supplementary Data 4
Cartesian coordinates (Å) and energies of optimized structures.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, L., Cheng, HG., Li, L. et al. Synthesis of planar chiral ferrocenes via enantioselective remote C–H activation. Nat. Chem. 15, 815–823 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41557-023-01176-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41557-023-01176-3
This article is cited by
-
Stereoselective assembly of C-oligosaccharides via modular difunctionalization of glycals
Nature Communications (2024)