Abstract
Purpose
Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (MI-TLIF) is commonly used to treat degenerative lumbar spinal disorders. It facilitates a full-scale spinal decompression and interbody fusion with minimal neural retraction using the tubular retractor system. Despite the benefits of surgical efficiency and minimalism, this technique requires a long learning curve. There is currently no consensus on the learning curve characteristics and proper training methods for MI-TLIF. Thus, this systematic review aimed to discuss the cutoff point at which technical proficiency is achieved and ways to enhance the learning process.
Methods
Major databases, including PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library, were searched for learning curve studies that have evaluated the clinical outcome and learning progress of MI-TLIF using quantitative data. The qualities of the selected studies were assessed using the Newcastle‒Ottawa scale. The plateau points in the “learning curve” were analyzed according to various outcome measures.
Results
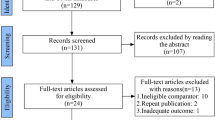
Nine full-text articles, representing 753 cases, were included from 9743 screened studies. The most commonly used outcome measures were the operative time, followed by the complication rate. The mean cutoff point for the operative time was 31.33 ± 11.98 (range 13‒45) cases.
Conclusion
The plateau point in the learning curve for MI-TLIF may differ according to the outcome measures used. Most studies have demonstrated the learning progress based on simple task efficiency, rather than patient outcomes. Moreover, the learning rate may be affected by the patients’ and technical conditions. Therefore, great care is required in interpreting the learning curve and cutoff point for MI-TLIF proficiency.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harms J, Rolinger H (1982) Die operative Behandlung der Spondylolisthese durch dorsale Aufrichtung und ventrale Verblockung [A one-stager procedure in operative treatment of spondylolistheses: dorsal traction-reposition and anterior fusion (author’s transl)]. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb 120:343–347. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2008-1051624
Karikari IO, Isaacs RE (2010) Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a review of techniques and outcomes. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 35:S294–S301. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e3182022ddc
Tsahtsarlis A, Wood M (2012) Minimally invasive transforaminal lumber interbody fusion and degenerative lumbar spine disease. Eur Spine J 21:2300–2305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-012-2376-y
Qin R, Wu T, Liu H, Zhou B, Zhou P, Zhang X (2020) Minimally invasive versus traditional open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for the treatment of low-grade degenerative spondylolisthesis: a retrospective study. Sci Rep 10:21851. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-78984-x
Seng C, Siddiqui MA, Wong KP, Zhang K, Yeo W, Tan SB, Yue WM (2013) Five-year outcomes of minimally invasive versus open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a matched-pair comparison study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 38:2049–2055. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e3182a8212d
Phan K, Rao PJ, Kam AC, Mobbs RJ (2015) Minimally invasive versus open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for treatment of degenerative lumbar disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Spine J 24:1017–1030. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-015-3903-4
Foley KT, Lefkowitz MA (2002) Advances in minimally invasive spine surgery. Clin Neurosurg 49:499–517
Peng CW, Yue WM, Poh SY, Yeo W, Tan SB (2009) Clinical and radiological outcomes of minimally invasive versus open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 34:1385–1389. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181a4e3be
Schizas C, Tzinieris N, Tsiridis E, Kosmopoulos V (2009) Minimally invasive versus open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: evaluating initial experience. Int Orthop 33:1683–1688. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-008-0687-8
Rouben D, Casnellie M, Ferguson M (2011) Long-term durability of minimal invasive posterior transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a clinical and radiographic follow-up. J Spinal Disord Tech 24:288–296. https://doi.org/10.1097/BSD.0b013e3181f9a60a
Scheufler KM, Dohmen H, Vougioukas VI (2007) Percutaneous transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for the treatment of degenerative lumbar instability. Neurosurgery 60(4 Suppl 2):203–212. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000255388.03088.B7 (discussion 212-213)
Dhall SS, Wang MY, Mummaneni PV (2008) Clinical and radiographic comparison of mini-open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in 42 patients with long-term follow-up. J Neurosurg Spine 9:560–565. https://doi.org/10.3171/SPI.2008.9.08142
Shunwu F, Xing Z, Fengdong Z, Xiangqian F (2010) Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for the treatment of degenerative lumbar diseases. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 35:1615–1620. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181c70fe3
Lau D, Lee JG, Han SJ, Lu DC, Chou D (2011) Complications and perioperative factors associated with learning the technique of minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF). J Clin Neurosci 18:624–627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2010.09.004
Stang A (2010) Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol 25:603–605. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-010-9491-z
Wells GA, Shea B, O’Connell D, J Peterson, V Welch, M Losos, P Tugwell (2021) The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality if nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses. http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.htm. Accessed 10 Jan 2021
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 327:557–560
Neal CJ, Rosner MK (2010) Resident learning curve for minimal-access transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in a military training program. Neurosurg Focus 28:E21. https://doi.org/10.3171/2010.1.FOCUS1011
Lee JC, Jang HD, Shin BJ (2012) Learning curve and clinical outcomes of minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: our experience in 86 consecutive cases. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 37:1548–1557. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e318252d44b
Silva PS, Pereira P, Monteiro P, Silva PA, Vaz R (2013) Learning curve and complications of minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. Neurosurg Focus 35:E7. https://doi.org/10.3171/2013.5.FOCUS13157
Lee KH, Yeo W, Soeharno H, Yue WM (2014) Learning curve of a complex surgical technique: minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (MIS TLIF). J Spinal Disord Tech 27:E234-240. https://doi.org/10.1097/BSD.0000000000000089
Nandyala SV, Fineberg SJ, Pelton M, Singh K (2014) Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: one surgeon’s learning curve. Spine J 14:1460–1465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spinee.2013.08.045
Park Y, Lee SB, Seok SO, Jo BW, Ha JW (2015) Perioperative surgical complications and learning curve associated with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a single-institute experience. Clin Orthop Surg 7:91–96. https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2015.7.1.91
Xu YF, Le XF, Tian W, Liu B, Li Q, Zhang GL, Liu YJ, Yuan Q, He D, Mao JP, Xiao B, Lang Z, Han XG, Jin PH (2018) Computer-assisted, minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: one surgeon’s learning curve a STROBE-compliant article. Medicine (Baltimore) 97:e11423. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000011423
Kumar A, Merrill RK, Overley SC, Leven DM, Meaike JJ, Vaishnav A, Gang C, Qureshi SA (2019) Radiation exposure in minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: the effect of the learning curve. Int J Spine Surg 13:39–45. https://doi.org/10.14444/6006
Kovari VZ, Kuti A, Konya K, Szel I, Szekely AK, Szalay K (2020) Comparison of single-level open and minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusions presenting a learning curve. Biomed Res Int 2020:3798537. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/3798537
Yap CH, Colson ME, Watters DA (2007) Cumulative sum techniques for surgeons: a brief review. ANZ J Surg 77:583–586
Biau DJ, Williams SM, Schlup MM, Nizard RS, Porcher R (2008) Quantitative and individualized assessment of the learning curve using LC-CUSUM. Br J Surg 95:925–929. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.6056
Ramsay CR, Grant AM, Wallace SA, Garthwaite PH, Monk AF, Russell IT (2000) Assessment of the learning curve in health technologies. A systematic review. Int J Technol Assess Health Care 16:1095–1108
Hoppe DJ, de Sa D, Simunovic N, Bhandari M, Safran MR, Larson CM, Ayeni OR (2014) The learning curve for hip arthroscopy: a systematic review. Arthroscopy 30:389–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arthro.2013.11.012
Ahn Y, Lee S, Son S, Kim H, Kim JE (2020) Learning curve for transforaminal percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy: a systematic review. World Neurosurg 143:471–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2020.08.044
Sánchez-Santos R, Estévez S, Tomé C, González S, Brox A, Nicolás R, Crego R, Piñón M, Masdevall C, Torres A (2012) Training programs influence in the learning curve of laparoscopic gastric bypass for morbid obesity: a systematic review. Obes Surg 22:34–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-011-0398-x
Sclafani JA, Kim CW (2014) Complications associated with the initial learning curve of minimally invasive spine surgery: a systematic review. Clin Orthop Relat Res 472:1711–1717. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-014-3495-z
Simonson DC, Roukis TS (2015) Incidence of complications during the surgeon learning curve period for primary total ankle replacement: a systematic review. Clin Podiatr Med Surg 32:473–482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpm.2015.06.011
Xie L, Wu WJ, Liang Y (2016) Comparison between minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion and conventional open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: an updated meta-analysis. Chin Med J (Engl) 129:1969–1986. https://doi.org/10.4103/0366-6999.187847
Serban D, Calina N, Tender G (2017) Standard versus minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a prospective randomized study. Biomed Res Int 2017:7236970. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7236970
Droeghaag R, Hermans SMM, Caelers IJMH, Evers SMAA, van Hemert WLW, van Santbrink H (2021) Cost-effectiveness of open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (OTLIF) versus minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (MITLIF): a systematic review and meta-analysis. Spine J 21:945–954. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spinee.2021.01.018
Sharif S, Afsar A (2018) Learning curve and minimally invasive spine surgery. World Neurosurg 119:472–478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2018.06.094
Kimchi G, Orlev A, Hadanny A, Knoller N, Harel R (2020) Minimally invasive spine surgery: the learning curve of a single surgeon. Global Spine J 10:1022–1026. https://doi.org/10.1177/2192568219880872
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Ah Jin Jeon and Eun Young Park for their valuable support and technical assistance.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors. This study was certified as exempt by the institutional review board (GFIRB2021-422).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ahn, Y., Lee, S., Kim, WK. et al. Learning curve for minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a systematic review. Eur Spine J 31, 3551–3559 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-022-07397-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-022-07397-3