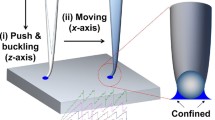
Abstract
We developed a simple method to investigate rheological properties of soft surfaces, such as polymeric liquids and colloidal suspensions, by capturing the images of a metal micro-needle inserted into the surface. At contact, a meniscus-like deformation is formed on the surface. By relating the shape of the deformation to the balance of applied forces, local elasticity and viscosity just inside the surface are obtained. With a facile setup and rapid measurement process, the present method can be implemented to variety of systems, for instance, drying sessile drops and small volume of liquid confined in a capillary.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author T.K. The data are not publicly available due to the confidential affairs.
References
A.F. Routh, Rep. Prog. Phys. 76, 046603 (2013)
D.E. Bornside, C.W. Macosko, L.E. Scriven, J. Appl. Phys. 66, 5185 (1989)
M.E. Knipschildt, G.G. Andersen, Robinson: modern dairy technology (Springer, Boston, 1994), p.159
P. Coussot, Rheometry of pastes, suspensions, and granular materials (Wiley, New Jersey, 2005), p.185
P. Coussot, Eur. Phys. J. B 15, 557 (2000)
P.-G. de Gennes, Eur. Phys. J. E 7, 31 (2002)
L. Daubersies, J.-B. Salmon, Phys. Rev. E 84, 031406 (2011)
E. Keita, P. Faure, S. Rodts, P. Coussot, Phys. Rev. E 87, 062303 (2013)
M. Okada, Y. Sumino, H. Ito, H. Kitahata, Phys. Rev. E 102, 042603 (2020)
Y. Sumino, H. Kitahata, H. Seto, S. Nakata, K. Yoshikawa, J. Phys. Chem. B 113, 15709 (2009)
T. Okuzono, K. Ozawa, M. Doi, Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 136103 (2006)
L. Pauchard, C. Allain, Eurphys. Lett. 62, 897 (2003)
T. Kajiya, E. Nishitani, T. Yamaue, M. Doi, Phys. Rev. E 73, 011601 (2006)
F. Boulogne, F. Giorgiutti-Dauphiné, L. Pauchard, Soft Matter 9, 750 (2013)
S. Arai, M. Doi, Eur. Phys. J. E 36, 63 (2013)
S. Mitani, K. Sakai, AIP Conf. Proc. 1027, 1153 (2008)
Y. Yoshitake, S. Mitani, K. Sakai, K. Takagi, Phys. Rev. E 78, 041405 (2008)
Y. Shimokawa, T. Kajiya, K. Sakai, M. Doi, Phys. Rev. E 84, 051803 (2011)
R. Wunenburger, A. Casner, J.-P. Delville, Phys. Rev. E 73, 036315 (2006)
M.T. Valentine, P.D. Kaplan, D. Thota, J.C. Crocker, T. Gisler, R.K. Prud’homme, M. Beck, D.A. Weitz, Phys. Rev. E 64, 061506 (2001)
C. van der Wel, D.J. Kraft, J. Phys. Condens. Matter 29, 044001 (2017)
E.M. Furst, T.M. Squires, Microrheology (Oxford, New York, 2017), p.198
T. Narita, K. Mayumi, G. Ducouret, P. Hébraud, Macromolecules 46, 4174 (2013)
X. Xiong, S. Guo, Z. Xu, P. Sheng, P. Tong, Phys. Rev. E 80, 061604 (2009)
J.D. de Baubigny, M. Benzaquen, L. Fabié, M. Delmas, J.-P. Aimé, M. Legros, T. Ondarçuhu, Langmuir 31, 9790 (2015)
J.T. Pham, F. Schellenberger, M. Kappl, H.-J. Butt, Phys. Rev. Mater. 1, 015602 (2017)
K. Guevorkian, M.-J. Colbert, M. Durth, S. Dufour, F.B. Wyart, Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 218101 (2010)
N.R. Chevalier, Ph. Dantan, E. Gazquez, A.J.M. Cornelissen, V. Fleury, Eur. Phys. J. E 39, 10 (2016)
B. Andreotti, O. Bäumchen, F. Boulogne, K.E. Daniels, E.R. Dufresne, H. Perrin, T. Salez, J.H. Snoeijer, R.W. Style, Soft Matter 12, 2993 (2016)
M.E.R. Shanahan, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 20, 945 (1987)
R.W. Style, C. Hyland, R. Boltyanskiy, J.S. Wettlaufer, E.R. Dufresne, Nat. Commun. 4, 2728 (2013)
L. Dorogin, B.N.J. Persson, Soft Matter 14, 1142 (2018)
L. Limat, Eur. Phys. J. E 35, 134 (2012)
C. Clanet, D. Quéré, J. Fluid Mech. 460, 131 (2002)
M.-J. Vega, D. Seveno, G. Lemaur, M.-H. Adão, J. De Coninck, Langmuir 21, 9584 (2005)
P.-G. de Gennes, F.B. Wyart, D. Quéré, Capillarity and wetting phenomena (Springer, New York, 2004), p.107
E.W. Washburn, Phys. Rev. 17, 273 (1921)
C. Monteux, A. Tay, T. Narita, Y. de Wilde, F. Lequeux, Soft Matter 5, 3713 (2009)
C. Arnold, F. Thalmann, C. Marques, P. Marie, Y. Holl, J. Phys. Chem. B 114, 9135 (2010)
J.H. Snoeijer, A. Pandey, M.A. Herrada, J. Eggers, Proc. R. Soc. A 476, 20200419 (2020)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. T. Ogura for technical supports of fluorescence microscopy, and Dr. S. Ohira for careful reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
T.K. and H.N. devised the study. T.K. performed the experiment and analysis. K.M. and H.N. fabricated the micro-needles by electrochemical etching. T.K., D.S. and Y.M. made the theoretical discussion and wrote the manuscript. All authors contributed in completing the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kajiya, T., Sawai, D., Miyata, K. et al. Simple method to measure rheological properties of soft surfaces by a micro-needle contact. Eur. Phys. J. E 45, 76 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/s10189-022-00227-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/s10189-022-00227-w