Abstract
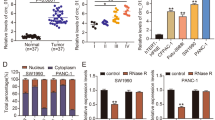
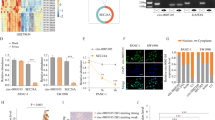
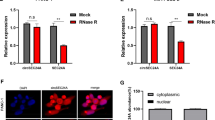
Aberrant expression of circular RNAs (circRNAs) is important in carcinogenesis, however, many differentially expressed circRNAs have not been functionally characterized. This study aimed to unveil the role of circRNA-dual specificity phosphatase 22 (circDUSP22) in pancreatic cancer (PaCa). Expression analyses of circDUSP22, miR-1178-3p and BCL2 interacting protein 3 (BNIP3) were carried out using quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) or western blotting. Cell growth was assessed by MTT, EdU and colony formation assays. Cell cycle distribution and cell apoptosis were investigated using flow cytometry assay. The assumed binding relationship between miR-1178-3p and circDUSP22 or BNIP3 was testified by dual-luciferase reporter and pull-down assays. The effect of circDUSP22 in vivo was identified by animal studies. The decreased expression of circDUSP22 was observed in PaCa samples and cells. CircDUSP22 ectopic expression in vitro blocked PaCa cell proliferation, arrested cell cycle and provoked cell apoptosis. CircDUSP22 targeted miR-1178-3p, whose expression was reinforced in PaCa. The inhibitory cell growth caused by circDUSP22 ectopic expression was reversed by miR-1178-3p enrichment. In addition, miR-1178-3p targeted BNIP3, whose expression was declined in PaCa. The inhibitory cell growth caused by circDUSP22 ectopic expression was reversed by BNIP3 knockdown. CircDUSP22 overexpression in vivo decelerated tumor growth. CircDUSP22 upregulation blocked PaCa development partly by targeting miR-1178-3p and increasing BNIP3, implying the potential implication of circDUSP22 in targeted therapy of PaCa.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
Bharti A, Kar AG, Singh D, Ansari MA, Tewari M, Narayan G, Singh S (2022) Frequent promoter hypermethylation and down regulation of BNIP3: an early event during gallbladder cancer progression. Dig Liver Dis. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dld.2022.01.121
Bi J, Liu H, Dong W, Xie W, He Q, Cai Z, Huang J, Lin T (2019) Circular RNA circ-ZKSCAN1 inhibits bladder cancer progression through miR-1178-3p/p21 axis and acts as a prognostic factor of recurrence. Mol Cancer 18:133. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-1060-9
Cao Z, Xu J, Huang H, Shen P, You L, Zhou L, Zheng L, Zhang T, Zhao Y (2015) MiR-1178 promotes the proliferation, G1/S transition, migration and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells by targeting CHIP. PLoS ONE 10:e0116934. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0116934
Chen B, Huang S (2018) Circular RNA: an emerging non-coding RNA as a regulator and biomarker in cancer. Cancer Lett 418:41–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2018.01.011
Erkan M, Kleeff J, Esposito I, Giese T, Ketterer K, Buchler MW, Giese NA, Friess H (2005) Loss of BNIP3 expression is a late event in pancreatic cancer contributing to chemoresistance and worsened prognosis. Oncogene 24:4421–4432. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208642
Ferlay J, Partensky C, Bray F (2016) More deaths from pancreatic cancer than breast cancer in the EU by 2017. Acta Oncol 55:1158–1160. https://doi.org/10.1080/0284186X.2016.1197419
Guo S, Xu X, Ouyang Y, Wang Y, Yang J, Yin L, Ge J, Wang H (2018) Microarray expression profile analysis of circular RNAs in pancreatic cancer. Mol Med Rep 17:7661–7671. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2018.8827
Hsiao KY, Sun HS, Tsai SJ (2017) Circular RNA—new member of noncoding RNA with novel functions. Exp Biol Med (maywood) 242:1136–1141. https://doi.org/10.1177/1535370217708978
Hu C, Xia R, Zhang X, Li T, Ye Y, Li G, He R, Li Z, Lin Q, Zheng S, Chen R (2022) circFARP1 enables cancer-associated fibroblasts to promote gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer via the LIF/STAT3 axis. Mol Cancer 21:24. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-022-01501-3
Huang J, Lok V, Ngai CH, Zhang L, Yuan J, Lao XQ, Ng K, Chong C, Zheng ZJ, Wong MCS (2021) Worldwide burden of, risk factors for, and trends in pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology 160:744–754. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2020.10.007
Jia J, Yang X, Zhao Q, Ying F, Cai E, Sun S, He X (2020) BNIP3 contributes to cisplatin-induced apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells. FEBS Open Bio 10:1463–1473. https://doi.org/10.1002/2211-5463.12881
Kong Y, Li Y, Luo Y, Zhu J, Zheng H, Gao B, Guo X, Li Z, Chen R, Chen C (2020) circNFIB1 inhibits lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis via the miR-486-5p/PIK3R1/VEGF-C axis in pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer 19:82. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-020-01205-6
Lee S, Vasudevan S (2013) Post-transcriptional stimulation of gene expression by microRNAs. Adv Exp Med Biol 768:97–126. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-5107-5_7
Li Z, Yanfang W, Li J, Jiang P, Peng T, Chen K, Zhao X, Zhang Y, Zhen P, Zhu J, Li X (2018) Tumor-released exosomal circular RNA PDE8A promotes invasive growth via the miR-338/MACC1/MET pathway in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett 432:237–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2018.04.035
Li S, Teng S, Xu J, Su G, Zhang Y, Zhao J, Zhang S, Wang H, Qin W, Lu ZJ, Guo Y, Zhu Q, Wang D (2019) Microarray is an efficient tool for circRNA profiling. Brief Bioinform 20:1420–1433. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bby006
Li X, Zhou S, Fan T, Feng X (2020) lncRNA DGCR 5/miR27a3p/BNIP3 promotes cell apoptosis in pancreatic cancer by regulating the p38 MAPK pathway. Int J Mol Med 46:729–739. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2020.4632
Liu H, Bi J, Dong W, Yang M, Shi J, Jiang N, Lin T, Huang J (2018) Invasion-related circular RNA circFNDC3B inhibits bladder cancer progression through the miR-1178-3p/G3BP2/SRC/FAK axis. Mol Cancer 17:161. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0908-8
Maisonneuve P, Lowenfels AB (2010) Epidemiology of pancreatic cancer: an update. Dig Dis 28:645–656. https://doi.org/10.1159/000320068
Niu Y, Lin Z, Wan A, Chen H, Liang H, Sun L, Wang Y, Li X, Xiong XF, Wei B, Wu X, Wan G (2019) RNA N6-methyladenosine demethylase FTO promotes breast tumor progression through inhibiting BNIP3. Mol Cancer 18:46. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-1004-4
Qu S, Hao X, Song W, Niu K, Yang X, Zhang X, Shang R, Wang Q, Li H, Liu Z (2019) Circular RNA circRHOT1 is upregulated and promotes cell proliferation and invasion in pancreatic cancer. Epigenomics 11:53–63. https://doi.org/10.2217/epi-2018-0051
Rong Z, Shi S, Tan Z, Xu J, Meng Q, Hua J, Liu J, Zhang B, Wang W, Yu X, Liang C (2021) Circular RNA CircEYA3 induces energy production to promote pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma progression through the miR-1294/c-Myc axis. Mol Cancer 20:106. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-021-01400-z
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71:209–249. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Tao M, Zheng M, Xu Y, Ma S, Zhang W, Ju S (2021) CircRNAs and their regulatory roles in cancers. Mol Med 27:94. https://doi.org/10.1186/s10020-021-00359-3
Zeng Z, Zhao Y, Chen Q, Zhu S, Niu Y, Ye Z, Hu P, Chen D, Xu P, Chen J, Hu C, Hu Y, Xu F, Tang J, Wang F, Han S, Huang M, Wang C, Zhao G (2021) Hypoxic exosomal HIF-1alpha-stabilizing circZNF91 promotes chemoresistance of normoxic pancreatic cancer cells via enhancing glycolysis. Oncogene 40:5505–5517. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-021-01960-w
Zhou WY, Cai ZR, Liu J, Wang DS, Ju HQ, Xu RH (2020) Circular RNA: metabolism, functions and interactions with proteins. Mol Cancer 19:172. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-020-01286-3
Acknowledgements
None
Funding
This work was supported by Study on the correlation between miRNA-10a expression and serum TNF-α and IL-6 levels in patients with inflammatory bowel disease and its value in diagnosis and disease assessment (No.MSZ19184).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YS designed and performed the research; MS, YY, JQ analyzed the data; YS wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Ethical Approval
This study was permitted by the Ethics Committee of Nantong First People’s Hospital.
Consent to Participate
Written informed consents were obtained from all participants.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Y., Shen, M., Yang, Y. et al. CircDUSP22 Overexpression Restrains Pancreatic Cancer Development via Modulating miR-1178-3p and Downstream BNIP3. Biochem Genet 61, 651–668 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-022-10275-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-022-10275-8