Abstract
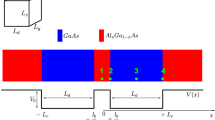
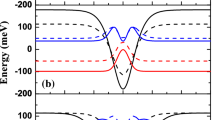
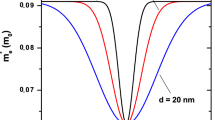
The present work focuses on the theoretical calculations of the ground-state binding energy of a shallow impurity, the impurity-related photoionization cross-section (PICS), and impurity-related polarizability under the combined effects of an electric field and hydrostatic pressure using a variational approach within the parabolic-band and effective-mass approximations. The low heterostructure is made up of two GaAs quantum dots separated by a Al\(_{0.3}\)Ga\(_{0.7}\)As central barrier. The applied electric field is considered to be directed along the growth-direction. As a general, the binding energy is obtained as a function of the impurity position and the electric field intensity. The PICS is calculated as a function of photon energy, for various impurity positions, with changes in hydrostatic pressure and/or electric field strength to prove their impact on their magnitude and shifting. Calculations are without accounting for the \(\Gamma -X\) effect of the GaAs/Al\(_{0.3}\)Ga\(_{0.7}\)As and for a specific nanostructure size. In addition, we have shown how variations in hydrostatic pressure and electric field affect the polarizability of impurities at three distinct places in the nanostructure.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
This manuscript has no associated data or the data will not be deposited. [Author’s comment: All the files with tables, figures, and codes are available. The corresponding author will provide all the files in case they are requested.]
References
S. Nizamoglu, H.V. Demir, Hybrid white light sources based on layer-by-layer assembly of nanocrystals on near-UV emitting diodes, Nanotechnology 18, 405702 (pp4) (2007). https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/18/40/405702
T. Suzuki, T. Mitsuyu, K. Nishi, H. Ohyama, T. Tomimasu, S. Noda, T. Asano, A. Sasaki, Observation of ultrafast all-optical modulation based on intersubband transition in \(n\)-doped quantum wells by using free electron laser. Appl. Phys. Lett. 69, 4136 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.117838
R.C. Miller, D.A. Kleinman, A.C. Gossard, Energy-gap discontinuities and effective masses for GaAs-Al\(_{x}\)Ga\(_{1-x}\)As quantum wells. Phys. Rev. B 29, 7085–7087 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.29.7085
S. Noda, T. Uemura, T. Yamashita, A. Sasaki, All-optical modulation using an \(n\)-doped quantum-well structure. J. Appl. Phys. 68, 6529–6531 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.346830
J. López-Gondar, J. d’Albuquerque e Castro, L.E. Oliveira, Electric-field effects on shallow impurity states in GaAs-(Ga,Al)As quantum wells, Phys. Rev. B 42, 7069-7077 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.42.7069
G. Bastard, Hydrogenic impurity states in a quantum well: A simple model. Phys. Rev. B 24, 4714–4722 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.24.4714
J.W. Brown, H.N. Spector, Hydrogen impurities in quantum well wires. J. Appl. Phys. 59, 1179 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.336555
R. Khordad, H. Bahramiyan, Study of impurity position effect in pyramid and cone like quantum dots. Eur. Phys. J. Appl. Phys. 67, 20402 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1051/epjap/2014140080
T.G. Emam, Effect of temperature on the binding energy of a shallow hydrogenic impurity in a quantum well wire. Can. J. Phys. 87, 1159–1161 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1139/P09-083
A.M. Elabsy, Effect of temperature on the binding energy of a confined impurity to a spherical semiconductor quantum dot. Phys. Scri. 59, 328–330 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1238/physica.regular.059a00328
E.B. Al, E. Kasapoglu, S. Sakiroglu, H. Sari, I. Sökmen, C.A. Duque, Binding energies and optical absorption of donor impurities in spherical quantum dot under applied magnetic field. Physica E 119, 114011 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physe.2020.114011
A. Bilekkaya, Ş Aktaş, S.E. Okan, F.K. Boz, Electric and magnetic field effects on the binding energy of a hydrogenic impurity in quantum well wires with different shapes. Superlattice Microst. 44, 96–105 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2008.02.010
C. Dane, H. Akbas, S. Minez, A. Guleroglu, Electric field effect in a GaAs/AlAs spherical quantum dot. Physica E 41, 278–281 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physe.2008.07.016
H.C. Liu, Quantum dot infrared photodetector. Opto-Electron. Rev 11, 1–5 (2003)
S. Nizamoglu, T. Ozel, E. Sari, and H. V. Demir, White light generation using CdSe/ZnS core-shell nanocrystals hybridized with InGaN/GaN light emitting diodes, Nanotechnology 18, 065709 (5pp) (2007). https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/18/6/065709
J. Gorman, D.G. Hasko, D.A. Williams, Charge-qubit operation of an isolated double quantum dot, Phys. Rev, Lett. 95, 090502 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.95.090502
J.R. Petta, A.C. Johnson, J.M. Taylor, E.A. Laird, A. Yacoby, M.D. Lukin, C.M. Marcus, M.P. Hanson, A.C. Gossard, Coherent manipulation of coupled electron spins in semiconductor quantum dots. Science 309, 2180 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1116955
J.R. Petta, A.C. Johnson, C.M. Marcus, M.P. Hanson, A.C. Gossard, Manipulation of a single charge in a double quantum dot. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 1–4 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.93.186802
S. Selsto, M. Forre, Coherent single-electron transport between coupled quantum dots. Phys. Rev. B 74, 1–6 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.74.195327
M. Forre, J.P. Hansen, V. Popsueva, A. Dubois, Fast single-electron transport in a double quantum dot. Phys. Rev. B 74, 165304 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.74.165304
A. Fountoulakis, Andreas F. Terzis, E. Paspalakis, Coherent single-electron transfer in coupled quantum dots, J. Appl. Phys. 106, 074305 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3232226
C.A. Duque, A. Montes, A.L. Morales, Binding energy and polarizability in GaAs-(Ga, Al)As quantum-well wires. Physica B 302–303, 84–87 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-4526(01)00410-0
Z.G. Bai, J.J. Liu, Stress effects on the binding energy of shallow-donor impurities in symmetrical GaAs/AlGaAs double quantum-well wires, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 19, 346218 (pp13) (2007). https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/19/34/346218
A.L. Morales, N. Raigoza, E. Reyes-Gómez, J.M. Osorio-Guillén, C.A. Duque, Impurity-related polarizability and photoionization-cross section in GaAs-Ga\(_{1-x}\)Al\(_x\) As double quantum wells under electric fields and hydrostatic pressure. Superlattice Microst. 45, 590–597 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2009.03.001
M. Takikawa, K. Kelting, G. Brunthaler, M. Takechi, J. Komeno, Photoionization of deep traps in AlGaAs/GaAs quantum wells. J. Appl. Phys. 65, 3937 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.343359
A. Sali, M. Fliyou, H. Satori, H. Loumrhari, Photoionization of impurities in quantum-well wires, Phys. Stat. Sol. (B) 211, 661 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1521-3951(199902)211:2¡661::AID-PSSB661¿3.0.CO;2-Q
A. Sali, H. Satori, M. Fliyou, H. Loumrhari, The photoionization cross-section of impurities in quantum dots. Phys. Stat. Sol. (B) 232, 209–219 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1002/1521-3951(200208)232:2¡209::AID-PSSB209¿3.0.CO;2-O
E. Iqraoun, A. Sali, K. El-Bakkari, M.E. Mora-Ramos, C.A. Duque, Binding energy, polarizability, and diamagnetic response of shallow donor impurity in zinc blende GaN quantum dots, Micro and Nanostructures 163, 107142 (pp12) (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2021.107142
A. Fakkahi, A. Sali, M. Jaouane, R. Arraoui, A. Ed-Dahmouny, Study of photoionization cross section and binding energy of shallow donor impurity in multilayered spherical quantum dot, Physica E 143, 115351 (pp7) (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physe.2022.115351
M. Jaouane, A. Sali, A. Fakkahi, R. Arraoui, F. Ungan, The effects of temperature and pressure on the optical properties of a donor impurity in (In,Ga)N/GaN multilayer cylindrical quantum dots, Micro and Nanostructures 163, 107146 (pp12) (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/10.1016/j.spmi.2021.107146
Aindrila Bera, Anuja Ghosh, Surajit Saha, Sk. Md. Arif, Manas Ghosh, Modulation of static dipole polarizability of impurity doped quantum dots in presence of noise, J. Alloys Compd. 742, 142-150 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.01.274
Aindrila Bera, Manas Ghosh, Dipole moment and polarizability of impurity doped quantum dots driven by noise: Influence of hydrostatic pressure and temperature. Physica B 515, 18–22 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2017.03.047
A.L. Morales, A. Montes, S.Y. López, N. Raigoza, C.A. Duque, Donor-related density of states and polarizability in a GaAs-(Ga, Al)As quantum-well under hydrostatic pressure and applied electric field. Phys. Stat. Sol. Conferences 656, 652–656 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1002/pssc.200306176
A. Zounoubi, K. El Messaoudi, I. Zorkani, A. Jorio, Magnetic field and finite barrier-height effects on the polarizability of a shallow donor in a GaAs quantum wire. Superlattice Microst. 30, 189–200 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1006/spmi.2001.1006
I. Karabulut, M.E. Mora-Ramos, C.A. Duque, Nonlinear optical rectification and optical absorption in GaAs-Ga\(_{1-x}\)Al\(_x\)As asymmetric double quantum wells: Combined effects of applied electric and magnetic fields and hydrostatic pressure. J. Lumin. 131, 1502–1509 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2011.03.044
E. Kasapoglu, The hydrostatic pressure and temperature effects on donor impurities in GaAs/Ga\(_{1-x}\)Al\(_x\)As double quantum well under the external fields. Phys. Lett. A 373, 140–143 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.881393
W. Belaid, H. El Ghazi, I. Zorkani, A. Jorio, Pressure-related binding energy in (In, Ga)N/GaN double quantum wells under internal composition effects. Sol. Sta. Comm. 327, 114193 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssc.2021.114193
A.L. Morales, N. Raigoza, C.A. Duque, Donor-related optical absorption spectra for a GaAs-Ga\(_{0.7}\)Al\(_{0.3}\)As double quantum well under hydrostatic pressure and applied electric field effects. Electronic and Magnetic Properties of Nanoscopic Systems. Braz. J. Phys. 36(3b), (2006). https://doi.org/10.1590/S0103-97332006000600017
N. Raigoza, A.L. Morales, A. Montes, N. Porras-Montenegro, C.A. Duque, Stress effects on shallow-donor impurity states in symmetrical GaAs/Al\(_x\)Ga\(_{1-x}\)As double quantum wells. Phys. Rev. B 69(045323), 1–8 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.69.045323
N. Raigoza, A.L. Morales, C.A. Duque, Effects of hydrostatic pressure on donor states in symmetrical GaAs-Ga\(_{0.7}\)Al\(_{0.3}\)As double quantum wells, Physica B 363, 262-270 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2005.03.031
E. Tangarife, C.A. Duque, Shallow-donor impurity in coupled GaAs/Ga\(_{1-x}\)Al\(_x\)As quantum well wires: Hydrostatic pressure and applied electric field effects. Phys. Stat. Sol. (B) 247, 1778–1785 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1002/pssb.200945519
C.M. Duque, M.G. Barseghyan, C.A. Duque, Donor impurity in vertically-coupled quantum-dots under hydrostatic pressure and applied electric field. Europ. Phys. J. B 73, 309–319 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2009-00433-7
J.J. Liu, M. Shen, S.W. Wang, The influence of compressive stress on shallow-donor impurity states in symmetric GaAs-Ga\(_{1-x}\)Al\(_x\)As double quantum dots. J. Appl. Phys. 101, 073703 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2717584
R. Arraoui, A. Sali, A. Ed-Dahmouny, M. Jaouane, A. Fakkahi, Polaronic mass and non-parabolicity effects on the photoionization cross section of an impurity in a double quantum dot, Superlattice Microst. 159, 107049 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SPMI.2021.107049
C.M. Duque, M.G. Barseghyan, C.A. Duque, Hydrogenic impurity binding energy in vertically coupled Ga\(_{1-x}\)Al\(_x\)As quantum-dots under hydrostatic pressure and applied electric field. Physica B 404, 5177–5180 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2009.08.292
M. Kirak, Y. Altinok, S. Yilmaz, The effects of the hydrostatic pressure and temperature on binding energy and optical properties of a donor impurity in a spherical quantum dot under external electric field. J. Lumin. 136, 415–421 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2012.12.026
S. Saha, J. Ganguly, A. Bera, M. Ghosh, Simultaneous influence of hydrostatic pressure and temperature on diamagnetic susceptibility of impurity doped quantum dots under the aegis of noise. Chem. Phys. 480, 17–22 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemphys.2016.10.012
G. Rezaei, S.F. Taghizadeh, A.A. Enshaeian, External electric field, hydrostatic pressure and temperature effects on the binding energy of an off-center hydrogenic impurity confined in a spherical Gaussian quantum dot. Physica E 44, 1562–1566 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physe.2012.03.028
H.O. Oyoko, C.A. Duque, N. Porras-Montenegro, Uniaxial stress dependence of the binding energy of shallow donor impurities in GaAs-(Ga, Al)As quantum dots. J. Apply. Phys. 90, 819–823 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1372976
O. Akankan, A study of the effect of spatial electric field on the binding energy and polarization of a donor impurity in a GaAs/AlAs tetragonal quantum dot (TQD). Superlattice Microst. 55, 45–52 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2012.11.014
G. Lamouche, Y. Lépine, Photoionization of semiconductor impurities in the presence of a static electric field. Phys. Rev. B 49, 13452 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevb.49.13452
S. Li, L. Shi, Z.W. Yan, Binding energies and photoionization cross-sections of donor impurities in GaN/Al\(_x\)Ga\(_{1-x}\)N spherical quantum dot under hydrostatic pressure. Mod. Phys. Let. B 34, 1–13 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0217984920501535
E. Tangarife, C.A. Duque, Simultaneous effects of hydrostatic pressure and electric field on impurity binding energy and polarizability in coupled InAs/GaAs quantum wires. Physica B 406, 952–956 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2010.12.035
Acknowledgements
CAD is grateful to the Colombian Agencies: CODI-Universidad de Antioquia (Estrategia de Sostenibilidad de la Universidad de Antioquia and projects “Propiedades magneto-ópticas y óptica no lineal en superredes de Grafeno”, “Estudio de propiedades ópticas en sistemas semiconductores de dimensiones nanoscópicas”, and “Propiedades de transporte, espintrónicas y térmicas en el sistema molecular ZincPorfirina”), and Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales-Universidad de Antioquia (CAD exclusive dedication project 2021-2022). CAD also acknowledges the financial support from El Patrimonio Autónomo Fondo Nacional de Financiamiento para la Ciencia, la Tecnología y la Innovación Francisco José de Caldas (project: CD 111580863338, CT FP80740-173-2019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The contributions of the authors are as follows: Ayoub Ed-Dahmouny and C. A. Duque: worked on the numerical calculations, in formal analysis, and writing of the manuscript. Ahmed Sali: proposed the problem and worked on the numerical calculations and writing of the manuscript. Najia Es-Sbai: worked on the numerical calculations, in formal analysis, and writing of the manuscript. Reda Arraoui: worked on the formal analysis and writing of the manuscript. Mohammed Jaouane, Abdelghani Fakkahi and Kamal El-Bakkari: worked on the numerical calculations and writing of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors do not have any financial and non-financial competing interests statement.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ed-Dahmouny, A., Sali, A., Es-Sbai, N. et al. Combined effects of hydrostatic pressure and electric field on the donor binding energy, polarizability, and photoionization cross-section in double GaAs/Ga\(_{1-x}\)Al\(_{x}\)As quantum dots. Eur. Phys. J. B 95, 136 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/s10051-022-00400-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/s10051-022-00400-2