Abstract
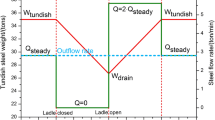
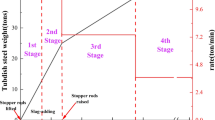
In this study, the materials used in turbulence inhibitors were identified, inhibitors were precisely designed, and the stress on turbulence inhibitors during the most demanding stage in the tundish operation cycle, i.e., the opening stage, was investigated. The fluid fields of the ladle and tundish during the opening stage of the tundish were simulated with a volume of fluid (VOF) model, and a dynamic analysis of the turbulence inhibitor during this stage was conducted using a fluid-transient structure coupling model. A square turbulence inhibitor with eaves in a Chinese steel mill was studied with the models. The fluid field of the tundish was confirmed by comparison with a water model. According to the model simulation, the average output of the ladle increased linearly with increasing depth of molten steel in the ladle. During the opening stage of the tundish, the opening stream from the ladle pushed the walls of the turbulence inhibitor outward, and the corners of the eave in the turbulence inhibitor were stress concentration points that bore the maximum stress. The maximum stress increased rapidly with increasing depth of molten steel in the ladle. A turbulence inhibitor with a height of 180 mm had the greatest maximum stress at 0.38 mPa. The maximum stress in the turbulence inhibitor decreased with increasing eave width. The maximum stress in the Al2O3 turbulence inhibitor was greater than that in the MgO turbulence inhibitor. The material strength and height of splashing of molten steel determined the maximum stress in the turbulence inhibitor. The splashing and falling of molten steel caused vibrations in the turbulence inhibitor, and these vibrations notably decreased the tensile stress of the materials in the turbulence inhibitor.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Chang, X. Cao, Z. Zou, et al.: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2016, vol. 47B(5), pp. 2732–43.
S. Chang, Cao, et al.: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2018, vol. 49B(3), pp. 953–57.
S. Chang, Z. Zou, B. Li, et al.: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2022, vol. 53B, pp. 526–36.
S. Chang, Z. Zou, J. Liu, et al.: Powder Technol., 2021, vol. 387, pp. 125–35.
S.P. Patil and N.N. Viswanathan: Trans. Indian Inst. Met., 2021, vol. 74(2), pp. 369–79.
Y. Jin, X.S. Dong, F. Yang, et al.: Metals, 2018, vol. 8(8), p. 611.
D.Y. Sheng and P.G. Jonsson: Materials, 2021, vol. 14(8), p. 1906.
P. Lin, Y. Jin, F. Yang, et al.: Metals, 2020, vol. 10(5), p. 691.
Q. Wang, Y. Liu, A. Huang, et al.: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2020, vol. 51B(1), pp. 276–92.
A. Ma, S. Chatterjee, and K. Chattopadhyay: ISIJ Int., 2019, vol. 637, pp. 1287–94.
Q. Fang, H. Zhang, R. Luo, et al.: J. Market. Res., 2020, vol. 9(1), pp. 347–63.
Y. Jin, C. Ye, X. Luo, et al.: High Temp. Mater. Process. (London), 2017, vol. 36(5), pp. 541–50.
D.Y. Sheng and D.F. Chen: Metals, 2021, vol. 11(5), p. 796.
Q. Wang, C. Tan, and A. Huang: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2021, vol. 52B(3), pp. 1344–56.
B.L. Zhang, F.H. Liu, R. Zhu, et al.: Materials, 2020, vol. 13(22), p. 5129.
X.G. Ai, D. Han, S.L. Li, et al.: J. Iron. Steel Res. Int., 2020, vol. 27(5), pp. 1035–44.
M.I.H. Siddiqui, A. Maurya, F. Asiri, et al.: VW Appl. Sci., 2021, vol. 3(1), pp. 92–103.
Q. Wang, C. Tan, A. Huang, et al.: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2021, vol. 52B(6), pp. 1–11.
M. Siddiqui and P.K. Jha: Steel Res. Int., 2015, vol. 86(7), pp. 799–807.
S. Garcia-Hernandez, R.D. Morales, J. Barreto, et al.: Steel Res. Int., 2016, vol. 87(9), pp. 1154–67.
C.M. Fan and W.S. Hwang: Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn., 2000, vol. 40(11), pp. 1105–14.
K. Takahashi, M. Ando, and T. Ishii: Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn., 2014, vol. 54(2), pp. 304–10.
Z. Hua, R. Luo, Q. Fang, et al.: Metals, 2018, vol. 8(2), p. 146.
H. Cheng, C. Fang, and J. Cheng: J. Hydrodyn. Ser. B, 2011, vol. 05, pp. 637–42.
J. Wu, S. Zheng, C. Wang, et al.: Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2020, vol. 107(2), pp. 4055–68.
X. Han, W. Lin, A. Qiu, et al.: J. Mar. Sci. Technol., 2019, vol. 15(6), pp. 622–39.
S. Samadi, S. Jin, D. Gruber, et al.: Int. J. Mech. Sci., 2021, vol. 197(4), pp. 1–9.
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51874215 and 51974213).
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all the authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, P., Jin, Y., Gan, F. et al. Study of the Impact of Opening Streams on Turbulence Inhibitors in Tundishes. Metall Mater Trans B 53, 3159–3169 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-022-02595-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-022-02595-2