Abstract
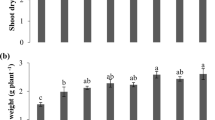
Transitioning the productive base to a more sustainable agriculture is one of the great challenges of our time. The current conflicts in Eastern Europe have had a major repercussion on the agricultural commodity market with restricted access and a massive cost increase for some fertilizers used in agriculture. This scenario has led to international concern about food shortages, whereby countries that depend on fertilizer imports need to find mechanisms and new technological paths to reduce their dependence on the international market. The use of crushed rock (soil remineralizers) associated with microorganisms is an important alternative in terms of cost reduction, lower impact on the environment and reduction of external dependence on agricultural inputs. The objective of this work was to evaluate the results of different types of inputs for soil fertilization (crushed rock – remineralizer, organic material and conventional – NPK), the production parameters of quinoa culture (Chenopodium quinoa) and this nutritional content of the crop. The experiment was carried out in a greenhouse and the data were subjected to analysis of variance, the Dunnett's test, complex contrasts, and multivariate analyses. The results showed significant increases in grain filling and quinoa yields, in soil fertility, and in the nutrient content of the aerial parts of plants treated with remineralizers. The treatments containing a mixture of remineralizers and organic compost were superior to those without these inputs, suggesting positive interaction among these sources. This approach may help toward adopting new technologies, especially with the current undersupply of soluble fertilizers. The use of local geological sources (crushed rock) has the capacity to reduce the dependence on imported fertilizers, thus helping to increase agri-food sovereignty in countries and adhering to the principles of agroecology at the local and global levels.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez, V. H. V., Roscoe, R., Kurihara, C. H., & Pereira, N. F. (2007). Enxofre. Fertil do Solo, 1, 595–644.
Anda, M., Shamshuddin, J., & Fauziah, C. I. (2015). Improving chemical properties of a highly weathered soil using finely ground basalt rocks. CATENA, 124, 147–161.
Badr, M. A. (2006). Efficiency of K-feldspar combined with organic materials and silicate dissolving bacteria on tomato yield. Journal of Applied Sciences Research, 2, 1191–1198.
Basak, B. B., Sarkar, B., & Naidu, R. (2021). Environmentally safe release of plant available potassium and micronutrients from organically amended rock mineral powder. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 43(9), 3273–3286.
Baptista, J.de C., Gray, N.C., Tarumoto, M. B., Singleton, I., McCann, S. M., & Manning, D. A. C (2022). Bacterial communities in soils as indicators of the potential of syenite as an agromineral. Pesquisa Agropecuária Brasileira10.1590/S1678-3921pab2022.v57.01414
Beerling, D. J., Kantzas, E. P., Lomas, M. R., Wade, P., Eufrasio, R. M., Renforth, P., Sarkar, B., Andrews, M. G., James, R. H., Pearce, C. R., Mercure, J. F., Pollitt, H., Holden, P. B., Edwards, N. R., Khanna, M., Koh, L., Quegan, S., Pidgeon, N. F., Janssens, I. A., … Banwart, S. A. (2020). Potential for large-scale CO2 removal via enhanced rock weathering with croplands. Nature, 583, 242–248.
Beerling, D. J., Leake, J. R., Long, S. P., Scoles, J. D., Ton, J., Nelson, P. N., Bird, M., Kantzas, E., Taylor, L. L., Sarkar, B., Kelland, M., Delucia, E., Kantola, I., Muller, C., Rau, G., & Hansen, J. (2018). Farming with crops and rocks to address global climate, food and soil security. Nature Plants, 4, 138–147.
Berg, A., & Banwart, S. A. (2000). Carbon dioxide mediated dissolution of Ca-feldspar: implications for silicate weathering. Chemical Geology, 163, 25–42.
Bergmann, M., Silveira, C. A. P., Bandeira, R., Bamberg, A., & Martinazzo., & R. Grecco, M. (2013). Basaltos amigdalóides à zeólitas da formação Serra Geral da Bacia do Paraná: potencial para uso agronômico. Congresso Brasileiro de Rochagem (2nd ed., pp. 168–180). New Jersey: Suprema.
Blanco, M. (2011). Supply of and access to key nutrients NPK for fertilizers for feeding the world in 2050 (p. 39p). Madrid (report): UPM.
Brazil, 2016. Normative Instruction No 05 Marc 10th, 2016. Available: https://www.gov.br/agricultura/pt-br/assuntos/insumos-agropecuarios/insumos-agricolas/fertilizantes/legislacao/in-05-_ingles.pdf
Caner, L., Radtke, L. M., Vignol-Lelarge, M. L., Inda, A. V., Bortoluzzi, E. C., & Mexias, A. S. (2014). Basalt and rhyo-dacite weathering and soil clay formation under subtropical climate in southern Brazil. Geoderma, 235, 100–112.
Carvalho, A. M. X. (2012). Rochagem e suas interações no ambiente solo: contribuições para aplicação em agroecossistemas sob manejo agroecológico. Tese de Doutorado, Universidade Federal de Viçosa. 116p. 2012. Available in: https://locus.ufv.br//handle/123456789/1631.
Carvalho, A. M. X., Cardoso, I. M., Theodoro, S. H., & Souza, M. E. P. (2018). Rochagem: o que se sabe sobre essa técnica. CARDOSO, IM; FÁVERO, C. Solos e agroecologia. Brasília: Embrapa, 101–128. Coleção Transição Agroecológica. 1ºed. Brasília, DF: Embrapa., 4, 101–111.
Carvalho, A. M. X., Mendes, F. Q., Mendes, F. Q., & Tavares, L. D. F. (2020). SPEED Stat: A free, intuitive, and minimalist spreadsheet program for statistical analyses of experiments. Crop Breed Appl Biotechnol, 20(3), e327420312.
Chiwona, A. G., Cortés, J. A., Gaulton, R. G., & Manning, D. A. C. (2020). Petrology and geochemistry of selected nepheline syenites from Malawi and their potential as alternative potash sources. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 164, 103769.
Churchman, G. J., Singh, M., Schapel, A., Sarkar, B., & Bolan, N. (2020). Clay minerals as the key to the sequestration of carbon in soils. Clays and Clay Miner, 68(2), 135–143.
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences (2nd ed., p. 474p). Academic Press.
Conagin, A. (2001). Tables for the calculation of the probability to be used in the modified Bonferroni’s test. Braz J Agric, 76, 71–83.
Dalmora, A. C., Ramos, C. G., Oliveira, M. L., Teixeira, E. C., Kautzmann, R. M., Taffarel, S. R., & Silva, L. F. (2016). Chemical characterization, nano-particle mineralogy and particle size distribution of basalt dust wastes. Science of the Total Environment, 539, 560–565.
Donagema, G. K., Campos, D. V. B., Calderano, S. B., Texeira, W. G., & Viana, J. H. M. (2011). Manual de Métodos de Análise de Solos (3rd ed.). Embrapa Solos.
Elhaissoufi, W., Barakat, G. C., & A., Zeroual, Y., & Bargaz, A. (2022). Phosphate bacterial solubilization: A key rhizosphere driving force enabling higher P use efficiency and crop productivity. Journal of Advanced Research, 38, 13–28.
Eshaghi, E., Nosrati, R., Owlia, P., Malboobi, M. A., Ghaseminejad, P., & Ganjali, M. R. (2019). Zinc solubilization characteristics of efficient siderophore-producing soil bacteria. Iranian J Microbiol, 11, 419–430.
FAO, 2018. The future of food and agriculture – Alternative pathways to 2050. Rome. 224
FAO, 2022. Information Note. The importance of Ukraine and the Russian Federation for global agricultural markets and the risks associated with the current conflict. https://www.fao.org/3/cb9013en/cb9013en.pdf
Frank, H. T., Gomes, M. E. B., & Formoso, M. L. L. (2009). Revisão da extensão areal e do volume da formação Serra Geral, Bacia do Paraná, América do Sul. Pesquisas em Geociências, 36, 49–57.
Gama-Rodrigues, A. C. D., Gama-Rodrigues, E. F. D., & Brito, E. C. D. (2007). Decomposição e liberação de nutrientes de resíduos culturais de plantas de cobertura em Argissolo Vermelho-Amarelo na região noroeste fluminense (RJ). Revista Brasileira de Ciência do Solo, 31, 1421–1428.
Hartmann, L. A. (2014). A história natural do Grupo Serra Geral desde o Cretáceo até o Recente. Ciência e Nat, 36, 173–182.
Hinsinger, P., Barros, O. N. F., Benedetti, M. F., Noack, Y., & Callot, G. (2001). Plant-induced weathering of a basaltic rock: Experimental evidence. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 65, 137–152.
IPCC, “Special Report on Climate Change and Land”, 2019: Summary for Policy Makers page 8. https://www.ipcc.ch/srccl/
Jacobson, T. K. B., & da Cunha Bustamante, M. M. (2019). Effects of nutrient addition on polyphenol and nutrient concentrations in leaves of woody species of a savanna woodland in Central Brazil. J Trop Ecolog, 35, 288–296.
Jarque, C. M., & Bera, A. K. (1980). Efficient tests for normality, homoscedasticity and serial independence of regression residuals. Economic Letters, 6, 255–259.
Kelemen, P. B., McQueen, N., Wilcox, J., Renforth, P., Dipple, G., & Vankeuren, A. P. (2020). Engineered carbon mineralization in ultramafic rocks for CO2 removal from air: Review and new insights. Chemical Geology, 550, 119628.
Kelland, M. E., Wade, P. W., Lewis, A. L., Taylor, L. L., Sarkar, B., Andrews, M. G., & Beerling, D. J. (2020). Increased yield and CO2 sequestration potential with the C4 cereal Sorghum bicolor cultivated in basaltic rock dust-amended agricultural soil. Global Change Biology, 26, 3658–3676.
Korchagin, J., Bortoluzzi, E. C., Moterle, D. F., Petry, C., & Caner, L. (2019a). Evidences of soil geochemistry and mineralogy changes caused by eucalyptus rhizosphere. CATENA, 175, 132–143.
Kronberg, B. I., Leonardos, O. H., & Fyfe, W. S. (1987). The use of ground rocks in laterite systems: an improvement to the use of conventional soluble fertilizers. Chemical Geology, 60, 361–370.
Korchagin, J., Caner, L., & Bortoluzzi, E. C. (2019b). Variability of amethyst mining waste: A mineralogical and geochemical approach to evaluate the potential use in agriculture. Journal of Cleaner Production, 210, 749–758.
Korhonen, J., Nuur, C., Feldmann, A., & Birkie, S. E. (2018). Circular economy as an essentially contested concept. Journal of Cleaner Production, 175, 544–552.
Lefebvre, D., Goglio, P., Williams, A., Manning, D. A., de Azevedo, A. C., Bergmann, M., & Smith, P. (2019). Assessing the potential of soil carbonation and enhanced weathering through Life Cycle Assessment: A case study for Sao Paulo State, Brazil. Journal of Cleaner Production, 233, 468–481.
Leonardos, O. H., Fyfe, W. S., & Kronberg, B. I. (1987). The use of ground rocks in laterite systems: An improvement to the use of conventional soluble fertilizers? Chemical Geology, 60, 361–370.
Leonardos, O. H., Theodoro, S. H., & Assad, M. L. (2000). Remineralization for sustainable agriculture: A tropical perspective from a Brazilian viewpoint. Nutr Cycl Agroecosystems, 56, 3–9.
Luján, A. M., Gomez, P., & Buckling, A. (2015). Siderophore cooperation of the bacterium Pseudomonas fluorescens in soil. Biology Letters, 11, 20140934.
Manning, D. A. C. (2010). Mineral sources of potassium for plant nutrition: a review. Agronomy for Sustainable Development, 30, 281–294.
Manning, D. A. C., Renforth, P., Lopez-Capel, E., Robertson, S., & Ghazireh, N. (2013). Carbonate precipitation in artificial soils produced from basaltic quarry fines and composts: An opportunity for passive carbon sequestration. Int J Greenh Gas Control, 17, 309–317.
Manning, D. A. C., & Theodoro, S. H. (2020). Enabling food security through use of local rocks and minerals. The Extractive Industries Soc, 7, 480–487.
Mbissik, A., Elghali, A., Ouabid, M., Raji, O., Bodinier, J. L., & El Messbahi, H. (2021). Alkali-Hydrothermal Treatment of K-Rich Igneous Rocks for Their Direct Use as Potassic Fertilizers. Minerals, 11, 140.
Melo, V. F., Uchôa, S. C. P., de Oliveira, F., & Dias Barbosa, G. F. (2012). Doses de basalto moído nas propriedades químicas de um Latossolo Amarelo distrófico da savana de Roraima. Acta Amazonica, 42(4), 471–476. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0044-59672012000400004
Mujica, A., & Jacobsen, S. (2006). La quinua (Chenopodium quinoa Willd) y sus parientes silvestres. In M. R. Moraes, B. Øllgaard, L. P. Kvist, F. Borchsenius, & H. Balslev (Eds.), Botánica Económica de los Andes Centrales (pp. 449–457). Universidad Mayor de San Andrés.
Ramos, C. G., Dalmora, A. C., Kautzmann, R. M., Hower, J., Dotto, G. L., & Oliveira, L. F. S. (2021). Sustainable release of macronutrients to black oat and maize crops from organically-altered dacite rock powder. Natural Resources Research, 30, 1941–1953.
Ramos, C. G., dos Santos, D., de Medeiros, L., Gomez, L. F., Oliveira, S., Schneider, I. A. H., & Kautzmann, R. M. (2020). Evaluation of soil re-mineralizer from by-product of volcanic rock mining: experimental proof using black oats and maize crops. Natural Resources Research, 29(3), 1583–1600. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-019-09529-x
Ramos, C. G., Hower, J. C., Blanco, E., Oliveira, M. L. S., & Theodoro, S. H. (2022). Possibilities of using silicate rock powder: an overview. Geoscience Frontiers, 13(1), 101185.
Ribeiro, A. C., Guimarães, P. T. G., & Alvarez, V. H. (1999). Recomendações para o uso de corretivos e fertilizantes em Minas Gerais – 5ª aproximação (p. 359p). New York: Viçosa.
Rosner, B. (1983). Percentage points for a generalized ESD many-outlier procedure. Technometrics, 25(2), 165–172.
Roy, E. D., Richards, P. D., Martinelli, L. A., Coletta, L. D., Lins, S. R. M., Vazquez, F. F., & Porder, S. (2016). The phosphorus cost of agricultural intensification in the tropics. Nat Plants, 2, 1–6.
Sarkar, B., Li, Y., & LÜ, G.I., Ali, A., YANG, J., & Yue-E. (2021). Influence of soil microorganisms and physicochemical properties on plant diversity in an arid desert of Western China. Journal of Forest Research, 32(6), 2645–2659.
Santos, H. G., Jacomine, P. K. T., Anjos, L. H. C., Oliveira, V. A., Lumbreras, J. F., Coelho, M. R., Almeida, J. A., Araújo Filho, J. C., Oliveira, J. B., & Cunha, T. J. F. (2018). Sistema Brasileiro de Classificação de Solos (5a ed., p. 356p). Brasília: Embrapa. Brasília.
Santos, L. F. D., Sodré, F. F., Martins, É. D. S., Figueiredo, C. C. D., & Busato, J. G. (2021). Effects of biotite syenite on the nutrient levels and electrical charges in a Brazilian Savanna Ferralsol. Agriculture Research in the Tropics, 51, https://www.revistas.ufg.br/pat/article/view/66691.
Setiawati, T. C., & Mutmainnah, L. (2016). Solubilization of potassium containing mineral by microorganisms from sugarcane rhizosphere. Agric Agric Sci Procedia, 9, 108–117.
Shamshuddi, N. J., & Anda, M. (2012). enhancing the productivity of ultisols and oxisols in malaysia using basalt and/or compost. Pedologist, 55, 382–391.
Silva, F. C. (2009). Manual de Análises Químicas de Solos, Plantas e Fertilizantes (2nd ed.). Embrapa Informação Tecnológica.
Soares, G. J. (2018). Influência da rochagem no desenvolvimento de sistemas agroflorestais e na captura de dióxido de carbono atmosférico. Mather Thesis, University of Brasília. 99p. https://repositorio.unb.br/handle/10482/33088?locale=en
Souza, M., & Alves, M. C. (2003). Propriedades químicas de um latossolo vermelho distrófico de cerrado sob diferentes usos e manejos. Revista Brasileira de Ciência do Solo, 27, 133–139.
Spehar, C. R., Rocha, J. E. D. S., & Santos, R. L. D. B. (2011). Desempenho agronômico e recomendações para cultivo de quinoa (BRS Syetetuba) no cerrado. Pesquisa Agropecuária Tropical, 41, 145–147.
Straaten, V. (2022). Distribution of agromineral resources in space and time – a global geological perspective. Pesquisa Agropecuária Brasileira, 57, 1453.
Tavares, L. D. F., de Carvalho, A. M. X., Camargo, L. G. B., Pereira, S. G. D. F., & Cardoso, I. M. (2018). Nutrients release from powder phonolite mediated by bioweathering actions. Int J Recycl Org Waste Agric, 7, 89–98.
Tchouankoue, J. P., Tchekambou, A. N. T., Angue, M. A., Ngansop, C., & Theodoro, S. H. (2015). Rock fertilizers as an alternative to conventional fertilizers: The use of basalt from the Cameroon volcanic line for maize farming on ferralitic soils. Geotherapy, 26, 445–458.
Theodoro, S. H. (2000). A Fertilização da Terra pela Terra: Uma Alternativa de Sustentabilidade para o Pequeno Produtor Rural. Doctoral Thesis, University of Brasília. 231p. https://repositorio.unb.br/handle/10482/20881.
Theodoro, S. H., & Leonardos, O. H. (2006). The use of rocks to improve Family agriculture in Brazil. Acad. Bras. de Cienc, 78, 721–730.
Theodoro, S. H., & Leonardos, O. H. (2015). Stonemeal: Principles, potential and perspective from Brazil. In T. J. Goreau, R. W. Larson, & J. Campe (Eds.), Geotherapy: Innovative Methods of Soil Fertility Restoration, Carbon Sequestration and Reversing CO2 Increase (pp. 403–418). CRC Press.
Theodoro, S. H., Leonardos, O. H., Rocha, E., Macedo, I., & Rego, K. G. (2013). Stonemeal of amazon soils with sediments from reservoirs: A case study of remineralization of the Tucuruí degraded land for agroforest reclamation. An. Acad. Bras de Cienc., 85, 23–34.
Theodoro, S. H., Medeiros, F. M., Ianniruberto, M., & Jacobson, T. K. B. (2021a). Soil remineralization and recovery of degraded areas: An experience in the tropical region. Journal of South American Earth Sciences, 107, 103014.
Theodoro, S. H., Sander, A., Burbano, D. F. M., & Almeida, G. R. (2021b). Rochas basálticas para rejuvenescer solos intemperizados. Revista Liberato, 22(37), 1–120.
UN/SDGs, 2020 The Sustainable Development Goals Report. https://doi.org/10.18356/d3229fb0-en
Tonello, M. S., Korchagin, J., & Bortoluzzi, E. C. (2021). Environmental agate mining impacts and potential use of agate residue in rangeland. Journal of Cleaner Production, 280, 124263.
Van Straaten, P. (2006). Farming with rocks and minerals: Challenges and opportunities. Acad. Bras. de Cienc., 78, 721–730.
Ventura, M., Scandellari, F., Bonora, E., & Tagliavini, M. (2010). Nutrient release during decomposition of leaf litter in a peach (Prunus persica L.) orchard. Nutr Cycl Agroecosystems, 87, 115–125.
Weerasuriya, T. J., Pushpakumara, S., & Cooray, P. I. (1993). Acidulated pegmatitic mica: a promising new multi-nutrient mineral fertilizer. Fertil Res, 34, 67–77.
Wezel, A., Bellon, S., Doré, T., Francis, C., Vallod, D., & David, C. (2009). Agroecology as a science, a movement and a practice: a review. Agron sustainable dev, 29(4), 503–515.
White, A. F., & Buss, H. L. (2013). Natural Weathering Rates of Silicate Minerals. In J. I. Drever (Ed.), Surface and Ground Water, Weathering and Soils, Treatise on Geochemistry (2nd ed.). New Jersey: Elsevier.
Yang, X., Long, Y., Sarkar, B., Li, Y., Lü, G., Ali, A., & Cao, Y. E. (2021). Influence of soil microorganisms and physicochemical properties on plant diversity in an arid desert of Western China. Journal of Forest Research, 32, 2645–2659.
Zhang, L., Gadd, G. M., & Li, Z. (2020). Microbial biomodification of clay minerals. Adv Appl Microbiol, Academic Press, 114, 111–139.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for the financial support of the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel—Brazil (CAPES). We extend our thanks to Pedreira Incopel Ltda. For donating of the materials derived from basaltic rocks.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Burbano, D.F.M., Theodoro, S.H., de Carvalho, A.M.X. et al. Crushed Volcanic Rock as Soil Remineralizer: A Strategy to Overcome the Global Fertilizer Crisis. Nat Resour Res 31, 2197–2210 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-022-10107-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-022-10107-x