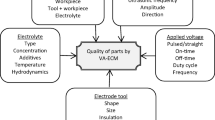
Abstract
The frequent occurrence of inherent abnormal discharges with the progress of machining in resistance–capacitance (RC) based micro-electrical discharge machining (µEDM) affects the product quality and material removal rate (MRR). This work presents a data acquisition-based analysis to address these alterations by exploring the nature of discharge pulses of vibration-assisted µEDM process variants. A cost-effective vibrating spindle attachment is developed for preliminary testing of vibration assistance to the controlled RC-based µEDM and reverse-µEDM processes. Micro-grooves of 5 mm \(\times\) 500 µm \(\times\) 500 µm and arrayed micro-rods with an aspect ratio of 20 with a diameter of 0.1 mm were fabricated using µED-milling and reverse-µEDM, respectively. Two different frequencies, 100 and 150 Hz, are used in vibration-assisted machining, leading to a maximum 57% reduction in machining time. The discharge pulses acquired during the machining showed a significant decrease in the arcing phenomenon that helps to understand the variation in MRR, surface finish, and overcut.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
U.S. Yadav and V. Yadava, Experimental investigation on electrical discharge drilling of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy. Mach. Sci. Technol., 19 (Oct 2015) 515–535. https://doi.org/10.1080/10910344.2015.1085316.
Y. Qin et al., Micro-manufacturing: research, technology outcomes and development issues. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 47 (2010) 821–837. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-009-2411-2.
S.H. Huang, F.Y. Huang and B.H. Yan, Fracture strength analysis of micro WC-shaft manufactured by micro-electro-discharge machining. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 26 (2005) 68–77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-003-1974-6.
J.S. Soni, Microanalysis of debris formed during rotary EDM of titanium alloy (Ti 6A1 4V) and die steel (T 215 Cr12). Wear, 177 (1994) 71–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1648(94)90119-8.
B.-H. Yan, G.-W. Chang, J.-H. Chang and R.-T. Hsu, Improving electrical discharge machined surfaces using magnetic abrasive finishing. Mach. Sci. Technol., 8 (Dec 2004) 103–118. https://doi.org/10.1081/MST-120034246.
B.M. Schumacher, About the role of debris in the gap during electrical discharge machining. CIRP Ann. - Manuf. Technol., 39 (1990) 197–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0007-8506(07)61034-8.
T. Endo, T. Tsujimoto and K. Mitsui, Study of vibration-assisted micro-EDM-The effect of vibration on machining time and stability of discharge. Precis. Eng., 32 (2008) 269–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precisioneng.2007.09.003.
T. Muthuramalingam and B. Mohan, A review on influence of electrical process parameters in EDM process. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng., 15 (2015) 87–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acme.2014.02.009.
M.Y. Tsai, C.S. Fang and M.H. Yen, Vibration-assisted electrical discharge machining of grooves in a titanium alloy (Ti-6A-4V). Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 97 (2018) 297–304. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-1904-2.
D.R. Unune and H.S. Mali, Experimental investigation on low-frequency vibration-assisted µ-ED milling of Inconel 718. Mater. Manuf. Process., 33 (2018) 964–976. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2017.1388516.
G.S. Prihandana, M. Mahardika, M. Hamdi, Y.S. Wong and K. Mitsui, Effect of micro-powder suspension and ultrasonic vibration of dielectric fluid in micro-EDM processes-Taguchi approach. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf., 49 (2009) 1035–1041. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2009.06.014.
W. Zhao, Z. Wang, S. Di, G. Chi and H. Wei, Ultrasonic and electric discharge machining to deep and small hole on titanium alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol., 120 (2002) 101–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(01)01149-9.
T. Bartkowiak and C.A. Brown, A Characterization of process-surface texture interactions in micro-electrical discharge machining using multiscale curvature tensor analysis. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng., 140 (May 2017) 021013. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4037601.
J.H. Zhang, T.C. Lee, W.S. Lau and X. Ai, Spark erosion with ultrasonic frequency. J. Mater. Process. Technol., 68 (1997) 83–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(96)02545-9.
D. Kremer, C. Lhiaubet and A. Moisan, A study of the effect of synchronizing ultrasonic vibrations with pulses in EDM. CIRP Ann. - Manuf. Technol., 40 (1991) 211–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0007-8506(07)61970-2.
H. Tong, Y. Li and Y. Wang, Experimental research on vibration assisted EDM of micro-structures with non-circular cross-section. J. Mater. Process. Technol., 208 (2008) 289–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2007.12.126.
R. Garn, A. Schubert and H. Zeidler, Analysis of the effect of vibrations on the micro-EDM process at the workpiece surface. Precis. Eng., 35 (2011) 364–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precisioneng.2010.09.015.
Y.C. Lin, F.P. Chuang, A.C. Wang and H.M. Chow, Machining characteristics of hybrid EDM with ultrasonic vibration and assisted magnetic force. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., 15 (2014) 1143–1149. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-014-0449-z.
S.A. Mastud, N.S. Kothari, R.K. Singh, J. Samuel and S.S. Joshi, Analysis of Debris motion in vibration assisted reverse micro electrical discharge machining. J Micro Nano-Manuf (2014). https://doi.org/10.1115/msec2014-4157.
S.A. Mastud, N.S. Kothari, R.K. Singh and S.S. Joshi, Modeling debris motion in vibration assisted reverse micro electrical discharge machining process (R-MEDM). J. Microelectromechanical Syst., 24 (2015) 661–676. https://doi.org/10.1109/JMEMS.2014.2343227.
T. Shitara, K. Fujita and J. Yan, Direct observation of discharging phenomena in vibration-assisted micro-electrical discharge machining. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 108 (2020) 1125–1138. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00170-019-04877-7.
W. Chang et al., Experimental research on the MRR of ultrasonic vibration aided electric discharge milling of ceramic materials using deionized water as processing medium. Mach. Sci. Technol., 24 (2020) 136–150. https://doi.org/10.1080/10910344.2019.1669165.
A. Schubert, N. Wolf, H. Zeidler and J. Schneider, “Indirect approach to ultrasonic superposition in micro-EDM,” ASME 2011 International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference, Vol. 1. Corvallis, Oregon, USA. June 13–17, 2011, pp. 427–434, 2011, https://doi.org/10.1115/msec2011-50240.
M.S. Mollik, T. Saleh, K.A. Bin Md Nor and M.S.M. Ali, A machine learning-based classification model to identify the effectiveness of vibration for μEDM. Alexandria Eng J (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.AEJ.2021.12.048.
D.R. Unune and H.S. Mali, Dimensional accuracy and surface quality of micro-channels with low-frequency vibration assistance in micro-electro-discharge milling. Adv. Mater. Process. Technol. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/2374068X.2020.1835008.
S.K. Singh and H.S. Mali, Workpiece dependency exploration & probabilistic nonparametric modelling of vibration-assisted hybrid micro-EDM process. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. (Feb 2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/S13369-022-06616-9.
N. Sabyrov, M.P. Jahan, A. Bilal and A. Perveen, Ultrasonic vibration assisted electro-discharge machining (EDM)-An overview. Materials (Basel) (Jan 2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030522.
H. Kishore, C.K. Nirala and A. Agrawal, Feasibility demonstration of µEDM for fabrication of arrayed micro pin-fins of complex cross-sections. Manuf. Lett., 23 (Jan 2020) 14–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mfglet.2019.11.005.
E. Uhlmann and D.C. Domingos, Investigations on vibration-assisted EDM-machining of seal slots in high-temperature resistant materials for turbine components -Part II. Procedia CIRP, 42 (2016) 334–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2016.02.179.
Q. Xing, Z. Yao and Q. Zhang, Effects of processing parameters on processing performances of ultrasonic vibration-assisted micro-EDM. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 112 (Jan 2021) 71–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00170-020-06357-9.
T.B. Thoe, D.K. Aspinwall and N. Killey, Combined ultrasonic and electrical discharge machining of ceramic coated nickel alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol., 92–93 (1999) 323–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(99)00117-X.
M. M. Sundaram, S. Billa and K. P. Rajurkar, “Generation of High Aspect Ratio Micro Holes by a Hybrid Micromachining Process,” ASME 2007 International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference. Atlanta, Georgia, USA. October 15–18, pp. 243–248, 2007, https://doi.org/10.1115/msec2007-31078.
A. Schubert, H. Zeidler, M.H. Oschätzchen, J. Schneider and M. Hahn, Enhancing micro-EDM using ultrasonic vibration and approaches for machining of nonconducting ceramics. Strojniški Vestn J Mech Eng (2013). https://doi.org/10.5545/sv-jme.2012.442.
B. Ghosh, R. K. Jain, and S. Majumder, “Control of voltage signal for piezoelectric actuator towards micro manipulation,” Int. Conf. Commun. Signal Process. ICCSP 2013 - Proc., pp. 922–926, 2013, https://doi.org/10.1109/iccsp.2013.6577191.
H. Kishore, R. Nadda, C.K. Nirala and A. Agrawal, Modelling and simulation based surface characterization of reverse- µEDM fabricated micro pin-fins. Procedia CIRP, 81 (2019) 1230–1235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2019.03.299.
D.R. Unune, C.K. Nirala and H.S. Mali, Accuracy and quality of micro-holes in vibration assisted micro-electro-discharge drilling of Inconel 718. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed., 135 (2019) 424–437. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MEASUREMENT.2018.11.067.
M. Goiogana, J.A. Sarasua, J.M. Ramos, L. Echavarri and I. Cascón, Pulsed ultrasonic assisted electrical discharge machining for finishing operations. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf., 109 (2016) 87–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2016.07.005.
C.K. Nirala and P. Saha, Evaluation of μEDM-drilling and μEDM-dressing performances based on online monitoring of discharge gap conditions. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 85 (2016) 1995–2012. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-7934-0.
C.K. Nirala, D.R. Unune and H.K. Sankhla, Virtual signal-based pulse discrimination in micro-electro-discharge machining. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng., 139 (2017) 094501. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4037108.
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Indian Institute of Technology Ropar for providing financial support under the ISIRD Grant No. (F. No. 9-282/2017IITRPR/705) to carry out this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Raza, S., Nadda, R. & Nirala, C.K. Discharge Pulse Analysis Based Machining Responses in Vibration Assisted µEDM Processes. MAPAN 37, 777–792 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12647-022-00591-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12647-022-00591-0