Abstract
Introduction
The use of tourniquets and bipolar sealers are effective methods of hemostasis during total knee arthroplasty (TKA). However, their effect on perioperative patient outcomes is unknown. The purpose of this study is to compare the efficacy of tourniquet-less, tourniquet-less with use of a bipolar sealer, and tourniquet use on postoperative pain and surgical outcomes following TKA.
Methods
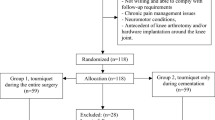
A retrospective study of prospectively collected data of 120 primary TKA cases was conducted at an urban academic hospital. Primary outcomes were visual analog scale (VAS) scores and opioid consumption (in morphine milligram equivalents). Demographics, length of stay (LOS), perioperative complications, and change in Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score (ΔKOOS) were also collected. Patients were divided into cohorts based on the use of tourniquet-less with bipolar sealer (TRLB) (n = 40), tourniquet (TR) (n = 40), or tourniquet-less (TRL) (n = 40).
Results
There were no differences in demographic data between each cohort. TRLB, TR and TRL had similar LOS (2.68 ± 1.63 vs 2.29 ± 1.27 vs 2.36 ± 1.42 days; p = 0.472) and VAS pain score on postoperative day 1 (4.68 vs 3.74 vs 3.63; p = 0.209). There were also no differences in opioid consumption at 2 weeks (p = 0.903), 1 month (p = 0.973), 3 months (p = 0.983), or 5 months (p = 0.983) post-operatively. TRLB and TR had comparable improvement in ΔKOOS from baseline to 12 weeks post-operatively (Δ16.58 ± 8.47 vs Δ23.92 ± 14.60; p = 0.254). Compared to the ΔKOOS of TRL (Δ5.19 ± 2.59), TRLB and TR had clinically and statistically greater ΔKOOS improvements (p = 0.009; p = 0.001). The TRL cohort also had a higher readmission rate than TRLB and TR (15% vs 0% vs 5%, p = 0.025).
Conclusion
Our findings demonstrate that both bipolar sealer and tourniquet use in TKA are associated with similar postoperative pain levels and LOS in comparison to tourniquet-less only TKA. However, bipolar sealer and tourniquet use may lead to better longer term improvement such as greater PRO score improvement and fewer readmissions.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data used in this study are from the authors’ institution and are available from the corresponding author, RS, upon reasonable request.
References
Stokes, M. E., Ye, X., Shah, M., Mercaldi, K., Reynolds, M. W., Rupnow, M. F. T., et al. (2011). Impact of bleeding-related complications and/or blood product transfusions on hospital costs in inpatient surgical patients. BMC Health Services Research. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6963-11-135
Park, J. H., Rasouli, M. R., Mortazavi, S. M. J., Tokarski, A. T., Maltenfort, M. G., & Parvizi, J. (2013). Predictors of perioperative blood loss in total joint arthroplasty. J Bone Jt Surg Ser A. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.L.01335
Hart, A., Khalil, J. A., Carli, A., Huk, O., Zukor, D., & Antoniou, J. (2014). Blood transfusion in primary total hip and knee arthroplasty. Incidence, risk factors, and thirty-day complication rates. J Bone Jt Surg Am. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.N.00077
Cai, D. F., Fan, Q. H., Zhong, H. H., Peng, S., & Song, H. (2019). The effects of tourniquet use on blood loss in primary total knee arthroplasty for patients with osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-019-1422-4
Huang, Z., Ma, J., Shen, B., Yang, J., Zhou, Z., Kang, P., et al. (2015). Use of a bipolar blood-sealing system during total joint arthroplasty. Orthopedics. https://doi.org/10.3928/01477447-20151119-07
Liu, Y., Si, H., Zeng, Y., Li, M., Xie, H., & Shen, B. (2020). More pain and slower functional recovery when a tourniquet is used during total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sport Traumatol Arthrosc. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-019-05617-w
Ajnin, S., & Fernandes, R. (2020). Reduced length of stay and faster recovery after total knee arthroplasty without the use of tourniquet. J Clin Orthop Trauma. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcot.2019.08.016
Zeh, A., Messer, J., Davis, J., Vasarhelyi, A., & Wohlrab, D. (2010). The aquamantys system-an alternative to reduce blood loss in primary total hip arthroplasty? Journal of Arthroplasty. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2009.10.008
Kamath, A. F., Austin, D. C., Derman, P. B., Clement, R. C., Garino, J. P., & Lee, G. C. (2014). Saline-coupled bipolar sealing in simultaneous bilateral total knee arthroplasty. Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery. https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2014.6.3.298
Pfeiffer, M., Bräutigam, H., Draws, D., & Sigg, A. (2005). A new bipolar blood sealing system embedded in perioperative strategies vs. a conventional regimen for total knee arthroplasty: Results of a matched-pair study. German Medical Science, 3:Doc10
Marulanda, G.A., Ragland, P.S., Seyler, T.M., & Mont, M.A. (2005). Reductions in blood loss with use of a bipolar sealer for hemostasis in primary total knee arthroplasty. Surgical Technology International, 14, 281–286
Pasqualotto, S., Demey, G., Dejour, D., Michelet, A., Nover, L., & Saffarini, M. (2020). Bipolar sealers do not improve blood loss or functional outcomes of primary total knee arthroplasty. The Journal of Knee Surgery. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0038-1676516
Marulanda, G.A., Krebs, V.E., Bierbaum, B.E., et al (2009). Hemostasis using a bipolar sealer in primary unilateral total knee arthroplasty. American Journal of Orthopedics (Belle Mead NJ), 38, E179-83
Li, H-Z., Li, X-Q., Zhao, G-Z., et al (2017). The efficacy of bipolar sealer for blood loss control after total knee arthroplasty: A meta-analysis. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine, 10, 1778–1787
Wen, L. J., Shuo, M. Y., & Kun, X. L. (2019). Postoperative pain management in total knee arthroplasty. Orthopaedic Surgery, 11, 755–761. https://doi.org/10.1111/os.12535
Dowell, D., Haegerich, T. M., & Chou, R. (2016). CDC guideline for prescribing opioids for chronic pain-United States, 2016. Journal of the American Medical Association, 315, 1624–1645. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2016.1464
Lappin, R. (2016). CDC issues new opioid prescribing guideline. Emergency Medicine, 48, 150–151. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.rr6501e1er
Chen, X., Yang, W., & Wang, X. (2019). Is bipolar sealer superior than standard electrocautery for blood loss control after primary total knee arthroplasty: A meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 98,e17762. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000017762
Goel, R., Rondon, A.J., Sydnor, K., et al (2019). Tourniquet Use Does Not Affect Functional Outcomes or Pain after Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Prospective, Double-Blinded, Randomized Controlled Trial. The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery American Volume, 101, 1821–1828. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.19.00146
McCarthy, D. E., Hu, S.Y., & Abdulkarim, A. (2019). Does Tourniquet Use in TKA Increase Postoperative Pain? A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research, 477, 547–558. https://doi.org/10.1097/CORR.0000000000000572
Goel, R., Rondon, A. J., Sydnor, K., et al. (2019). Tourniquet use does not affect functional outcomes or pain after total knee arthroplasty: a prospective, double-blinded, randomized controlled trial. J Bone Jt Surg Am, 101, 1821–1828. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.19.00146
Zak, S. G., Yeroushalmi, D., Long, W. J., Meftah, M., Schnaser, E., & Schwarzkopf, R. (2021). Does the use of a tourniquet influence outcomes in total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Arthroplasty. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2021.02.068
Hung, M., Bounsanga, J., Voss, M. W., & Saltzman, C. L. (2018). Establishing minimum clinically important difference values for the patient-reported outcomes measurement information system physical function, hip disability and osteoarthritis outcome score for joint reconstruction, and knee injury and osteoarthritis outcome score for joint reconstruction in orthopaedics. World J Orthop, 9(3), 41–49. https://doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v9.i3.41
Gandek, B., Roos, E. M., Franklin, P. D., & Ware, J. E. (2019). A 12-item short form of the Knee injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score (KOOS-12): tests of reliability, validity and responsiveness. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage, 27, 762–770. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JOCA.2019.01.011
Eckhard, L., Munir, S., Wood, D., et al. (2021). The KOOS-12 shortform shows no ceiling effect, good responsiveness and construct validity compared to standard outcome measures after total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surgery, Sports Traumatology, Arthroscopy, 29, 608–615. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00167-020-05904-X
Funding
There is no funding source for this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mr. SZ: writing original draft, writing review and editing. Mr. NM: writing—review and editing. Ms. CS: formal analysis and investigation. Dr. JS: conceptualization, writing—review and editing. Dr. RS: supervision, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
One of more authors is a paid consultant for Horizon Pharma, Intelijoint and Smith & Nephew; receives royalties from Smith & Nephew; own stock in Gauss surgical and Intelijoint; and received research support from Smith & Nephew.
Ethical Approval
This study has obtained all required IRB and ethical approval at our institution.
Informed Consent
This study is a retrospective review in which patients were subject to their normal standard of care. No individual data are included within this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zak, S.G., Muthusamy, N., Sicat, C. et al. Bipolar Sealers and Tourniquet Use Have Similar Outcomes in Total Knee Arthroplasty. JOIO 56, 1745–1750 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43465-022-00670-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43465-022-00670-z