Abstract
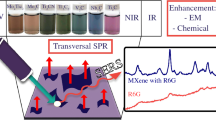
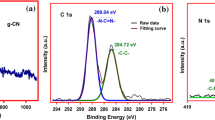
Recently, various semiconductor/metal composites have been developed to fabricate surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy substrates. However, low metal loading on semiconductors is still a challenge. In this study, cystine was introduced to increase the accumulation of gold nanoparticles on zinc oxide, owing to the biomineralization property of cystine. Morphological analysis revealed that the obtained ZnO/Au/cystine composite not only had a higher metal loading but also formed a porous structure, which is beneficial for Raman performance. Compared with ZnO/Au, the ZnO/Au/cystine substrate displayed a 40-fold enhancement in the Raman signal and a lower limit of detection (10−11 mol·L−1) in the detection of rhodamine 6G. Moreover, the substrate has favorable homogeneity and stability. Finally, ZnO/Au/cystine displayed excellent performance toward crystal violet and methylene blue in a test based on river water samples. This study provided a promising method to fabricate sensitive semiconductor/noble metal-based surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy substrates for Raman detection.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fan M, Andrade G F S, Brolo A G. A review on recent advances in the applications of surface-enhanced Raman scattering in analytical chemistry. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2020, 1097: 1–29
Neng J, Zhang Q, Sun P L. Application of surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy in fast detection of toxic and harmful substances in food. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 2020, 167: 112480
Zong C, Xu M, Xu L J, Wei T, Ma X, Zheng X S, Hu R, Ren B. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for bioanalysis: reliability and challenges. Chemical Reviews, 2018, 118(10): 4946–4980
Cialla May D, Zheng X S, Weber K, Popp J. Recent progress in surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for biological and biomedical applications: from cells to clinics. Chemical Society Reviews, 2017, 46(13): 3945–3961
Xu M L, Gao Y, Han X X, Zhao B. Detection of pesticide residues in food using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy: a review. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2017, 65(32): 6719–6726
Chakraborty A, Ghosh A, Barui A. Advances in surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for cancer diagnosis and staging. Journal of Raman Spectroscopy, 2020, 51(1): 7–36
Yang B, Wang Y, Guo S, Jin S, Park E, Chen L, Jung Y M. Charge transfer study for semiconductor and semiconductor/metal composites based on surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Bulletin of the Korean Chemical Society, 2021, 42(11): 1411–1418
Sharma B, Frontiera R R, Henry A I, Ringe E, Van Duyne R P. SERS: materials, applications, and the future. Materials Today, 2012, 15(1–2): 16–25
Itoh T, Yamamoto Y S. Recent topics on single-molecule fluctuation analysis using blinking in surface-enhanced resonance Raman scattering: clarification by the electromagnetic mechanism. Analyst (London), 2016, 141(17): 5000–5009
Yang M, Yu J, Lei F, Zhou H, Wei Y, Man B, Zhang C, Li C, Ren J, Yuan X. Synthesis of low-cost 3D-porous ZnO/Ag SERS-active substrate with ultrasensitive and repeatable detectability. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2018, 256: 268–275
Hsieh S, Lin P Y, Chu L Y. Improved performance of solution-phase surface-enhanced Raman scattering at Ag/CuO nanocomposite surfaces. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2014, 118(23): 12500–12505
Yang L, Wang W, Jiang H, Zhang Q, Shan H, Zhang M, Zhu K, Lv J, He G, Sun Z. Improved SERS performance of single-crystalline TiO2 nanosheet arrays with coexposed {001} and {101} facets decorated with Ag nanoparticles. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2017, 242: 932–939
Li P, Wang X, Zhang X, Zhang L, Yang X, Zhao B. Investigation of the charge-transfer between Ga-doped ZnO nanoparticles and molecules using surface-enhanced Raman scattering: doping induced band-gap shrinkage. Frontiers in Chemistry, 2019, 7: 144
Doan Q K, Nguyen M H, Sai C D, Pham V T, Mai H H, Pham N H, Bach T C, Nguyen V T, Nguyen T T, Ho K H, Tran T H. Enhanced optical properties of ZnO nanorods decorated with gold nanoparticles for self-cleaning surface enhanced Raman applications. Applied Surface Science, 2020, 505: 7
Liu Y, Ma H, Han X X, Zhao B. Metal-semiconductor heterostructures for surface-enhanced Raman scattering: synergistic contribution of plasmons and charge transfer. Materials Horizons, 2021, 8(2): 370–382
Han X X, Ji W, Zhao B, Ozaki Y. Semiconductor-enhanced Raman scattering: active nanomaterials and applications. Nanoscale, 2017, 9(15): 4847–4861
Yang B, Jin S, Guo S, Park Y, Chen L, Zhao B, Jung Y M. Recent development of SERS technology: semiconductor-based study. ACS Omega, 2019, 4(23): 20101–20108
Araújo A, Pimentel A, Oliveira M J, Mendes M J, Franco R, Fortunato E, Águas H, Martins R. Direct growth of plasmonic nanorod forests on paper substrates for low-cost flexible 3D SERS platforms. Flexible and Printed Electronics, 2017, 2(1): 014001
Pimentel A, Araújo A, Coelho B, Nunes D, Oliveira M, Mendes M, Águas H, Martins R, Fortunato E. 3D ZnO/Ag surface-enhanced Raman scattering on disposable and flexible cardboard platforms. Materials, 2017, 10(12): 1351
Kim W, Lee S H, Kim J H, Ahn Y J, Kim Y H, Yu J S, Choi S. Paper-based surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for diagnosing prenatal diseases in women. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(7): 7100–7108
Barbillon G, Graniel O, Bechelany M. Assembled Au/ZnO nano-urchins for SERS sensing of the pesticide thiram. Nanomaterials, 2021, 11(9): 2174
Graniel O, Iatsunskyi I, Coy E, Humbert C, Barbillon G, Michel T, Maurin D, Balme S, Miele P, Bechelany M. Au-covered hollow urchin-like ZnO nanostructures for surface-enhanced Raman scattering sensing. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2019, 7(47): 15066–15073
Dong S, Wang Y, Liu Z, Zhang W, Yi K, Zhang X, Zhang X, Jiang C, Yang S, Wang F, Xiao X. Beehive-inspired macroporous SERS probe for cancer detection through capturing and analyzing exosomes in plasma. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(4): 5136–5146
Liu K, Yuan C Q, Zou Q L, Xie Z C, Yan X H. Self-assembled zinc/cystine-based chloroplast mimics capable of photoenzymatic reactions for sustainable fuel synthesis. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2017, 56(27): 7876–7880
Guan M, Wang M, Qi W, Su R, He Z. Biomineralization-inspired copper-cystine nanoleaves capable of laccase-like catalysis for the colorimetric detection of epinephrine. Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering, 2020, 15(2): 310–318
Ejgenberg M, Mastai Y. Biomimetic crystallization of l-cystine hierarchical structures. Crystal Growth & Design, 2012, 12(10): 4995–5001
Moe O W. Kidney stones: pathophysiology and medical management. Lancet, 2006, 367(9507): 333–344
Jana N R, Gearheart L, Murphy C J. Seeding growth for size control of 5–40 nm diameter gold nanoparticles. Langmuir, 2001, 17(22): 6782–6786
Yang L L, Yang Y, Ma Y F, Li S, Wei Y Q, Huang Z R, Long N V. Fabrication of semiconductor ZnO nanostructures for versatile SERS application. Nanomaterials, 2017, 7(11): 398
Subramanian V, Wolf E E, Kamat P V. Green emission to probe photoinduced charging events in ZnO-Au nanoparticles. Charge distribution and fermi-level equilibration. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2003, 107(30): 7479–7485
Nuzzo R G, Fusco F A, Allara D L. Spontaneously organized molecular assemblies. 3. Preparation and properties of solution adsorbed monolayers of organic disulfides on gold surfaces. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1987, 109(8): 2358–2368
Nuzzo R G, Allara D L. Adsorption of bifunctional organic disulfides on gold surfaces. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1983, 105(13): 4481–4483
Nuzzo R G, Zegarski B R, Dubois L H. Fundamental studies of the chemisorption of organosulfur compounds on gold (111). Implications for molecular self-assembly on gold surfaces. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1987, 109(3): 733–740
Pal A K, Pagal S, Prashanth K, Chandra G K, Umapathy S, Mohan D B. Ag/ZnO/Au 3D hybrid structured reusable SERS substrate as highly sensitive platform for DNA detection. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2019, 279: 157–169
Bharadwaj S, Pandey A, Yagci B, Ozguz V, Qureshi A. Graphene nano-mesh-Ag-ZnO hybrid paper for sensitive SERS sensing and self-cleaning of organic pollutants. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 336: 445–455
Zhang J, Liu X, Wu S, Cao B, Zheng S. One-pot synthesis of Au-supported ZnO nanoplates with enhanced gas sensor performance. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2012, 169: 61–66
Ma Z F, Han H L. One-step synthesis of cystine-coated gold nanoparticles in aqueous solution. Colloids and Surfaces. A, Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2008, 317(1–3): 229–233
Di Felice R, Selloni A. Adsorption modes of cysteine on Au(111): thiolate, amino-thiolate, disulfide. Journal of Chemical Physics, 2004, 120(10): 4906–4914
Qi D, Lu L, Wang L, Zhang J. Improved SERS sensitivity on plasmon-free TiO2 photonic microarray by enhancing light-matter coupling. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2014, 136(28): 9886–9889
Macias Montero M, Pelaez R J, Rico V J, Saghi Z, Midgley P, Afonso C N, Gonzalez Elipe A R, Borras A. Laser treatment of Ag@ZnO nanorods as long-life-span SERS surfaces. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(4): 2331–2339
He X, Wang H, Li Z, Chen D, Liu J, Zhang Q. Ultrasensitive SERS detection of trinitrotoluene through capillarity-constructed reversible hot spots based on ZnO-Ag nanorod hybrids. Nanoscale, 2015, 7(18): 8619–8626
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 21621004 and 22178260), the Tianjin Development Program for Innovation and Entrepreneurship (2018), and the Cooperative Program of Technical Center of Gongbei Customs District of China (Grant No. 2020GKF-0281).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
11705_2022_2177_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Cystine-assisted accumulation of gold nanoparticles on ZnO to construct a sensitive surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy substrate
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, Q., Zeng, C., Huang, J. et al. Cystine-assisted accumulation of gold nanoparticles on ZnO to construct a sensitive surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy substrate. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 17, 15–23 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-022-2177-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-022-2177-8