Abstract
Background
Blood pressure (BP) monitoring following pediatric kidney transplantation is essential for optimizing graft perfusion. Differences between invasive BP and noninvasive BP (NIBP) measurements are sometimes considerable. We aimed to assess agreement between invasive BP and NIBP in pediatric patients after kidney transplantation and compare with measurements obtained by systolic Doppler with manual sphygmomanometer as a reference technique.
Methods
A prospective, observational cohort study, of children aged 18 years or younger, admitted immediately following kidney transplantation to the pediatric intensive care unit of a tertiary, university-affiliated medical center, between May 2019 and June 2021.
Results
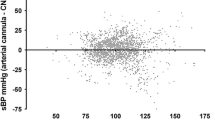
Eighty-two paired simultaneous measurements of invasive BP, NIBP, and Doppler BP in 18 patients were compared. Patients were significantly hypertensive, with mean systolic NIBP above the 95th percentile (96 ± 6%). Systolic invasive BP measurements were significantly higher than NIBP (149 ± 20 vs. 136 ± 15 mmHg, p < 0.001). Substantial differences (≥ 20 mmHg) were found in 23% (95% CI 15–34%). Similar disagreement was found between systolic invasive and Doppler BP (150 ± 23 and 137 ± 17 mmHg, respectively, p < 0.001). In contrast, systolic NIBP was in good agreement with Doppler BP (135 ± 17 and 138 ± 18, respectively, p = 0.27). A moderate to strong correlation was found between higher systolic invasive BP and the difference to systolic Doppler BP (Spearman's ρ = 0.63, p < 0.001).
Conclusions
In children immediately following kidney transplantation, clinically significant disagreement was found between invasive and noninvasive BP measurements. Invasive BP values were significantly higher than those obtained by Doppler. Better agreement was found between NIBP and Doppler. These issues should be considered when interpreting BP measurements in this sensitive patient population.
Graphical abstract
A higher resolution version of the Graphical abstract is available as Supplementary information




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chatterjee A, DePriest K, Blair R, Bowton D, Chin R (2010) Results of a survey of blood pressure monitoring by intensivists in critically ill patients: a preliminary study. Crit Care Med 38:2335–2338. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181fa057f
Goodwin A, Mazwi ML, Somer J, Schwartz SM, McEwan A, Eytan D (2021) Blood pressure in critically ill children: exploratory analyses of concurrent invasive and noninvasive measurements. Crit Care Explor 3:e0586. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCE.0000000000000586
Takci S, Yigit S, Korkmaz A, Yurdakök M (2012) Comparison between oscillometric and invasive blood pressure measurements in critically ill premature infants. Acta Paediatr 101:132–135. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1651-2227.2011.02458.x
Lehman LH, Saeed M, Talmor D, Mark R, Malhotra A (2013) Methods of blood pressure measurement in the ICU. Crit Care Med 41:34–40. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0b013e318265ea46
Ribezzo S, Spina E, Di Bartolomeo S, Sanson G (2014) Noninvasive techniques for blood pressure measurement are not a reliable alternative to direct measurement: a randomized crossover trial in ICU. Sci World J 2014:353628. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/353628
Meidert AS, Dolch ME, Mühlbauer K, Zwissler B, Klein M, Briegel J, Czerner S (2021) Oscillometric versus invasive blood pressure measurement in patients with shock: a prospective observational study in the emergency department. J Clin Monit Comput 35:387–393. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10877-020-00482-2
Zhou J, Elkhateeb O, Lee KS (2016) Comparison of non-invasive vs invasive blood pressure measurement in neonates undergoing therapeutic hypothermia for hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. J Perinatol 36:381–385. https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2015.198
Holt TR, Withington DE, Mitchell E (2011) Which pressure to believe? A comparison of direct arterial with indirect blood pressure measurement techniques in the pediatric intensive care unit. Pediatr Crit Care Med 12:e391-394. https://doi.org/10.1097/PCC.0b013e3182230f43
Fujii T, Nishiwaki K (2020) Comparing oscillometric noninvasive and invasive intra-arterial blood pressure monitoring in term neonates under general anesthesia: A retrospective study. Paediatr Anaesth 30:1396–1401. https://doi.org/10.1111/pan.14020
Cambiaso-Daniel J, Rontoyanni VG, Foncerrada G, Nguyen A, Capek KD, Wurzer P, Lee OJ, Hundeshagen G, Voigt CD, Branski LK, Finnerty CC, Herndon DN (2018) Correlation between invasive and noninvasive blood pressure measurements in severely burned children. Burns 44:1787–1791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.burns.2018.03.001
Severova-Andreevska G, Danilovska I, Sikole A, Popov Z, Ivanovski N (2019) Hypertension after Kidney Transplantation: Clinical Significance and Therapeutical Aspects. Open Access Maced J Med Sci 7:1241–1245. https://doi.org/10.3889/oamjms.2019.264
Stegall HF, Kardon MB, Kemmerer WT (1968) Indirect measurment of arterial blood pressure by Doppler ultrasonic sphygmomanometry. J Appl Physiol 25:793–798. https://doi.org/10.1152/jappl.1968.25.6.793
Hernandez A, Goldring D, Hartmann AF (1971) Measurement of blood pressure in infants and children by the Doppler ultrasonic technique. Pediatrics 48:788–794. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80133-7
National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group on High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents (2004) The fourth report on the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. Pediatrics 114(2 Suppl 4th Report):555–576. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.114.2.S2.555
Muntner P, Shimbo D, Carey RM, Charleston JB, Gaillard T, Misra S, Myers MG, Ogedegbe G, Schwart JE, Townsend RR, Urbina EM, Viera AJ, White WB, Wright JT Jr (2019) Measurement of blood pressure in humans: A scientific statement from the American heart association. Hypertension 73:e35–e66. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYP.0000000000000087
Gardner RM (1981) Direct blood pressure measurement–dynamic response requirements. Anesthesiology 54:227–236. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000542-198103000-00010
Kleinman B, Powell S, Kumar P, Gardner RM (1992) The fast flush test measures the dynamic response of the entire blood pressure monitoring system. Anesthesiology 77:1215–1220. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000542-199212000-00024
Romagnoli S, Ricci Z, Raffaele De Gaudio A (2012) Invasive arterial pressure. Pediatr Crit Care Med 13:248. https://doi.org/10.1097/PCC.0b013e3182389586
McGhee BH, Bridges EJ (2002) Monitoring arterial blood pressure: what you may not know. Crit Care Nurse 22(60–64):66. https://doi.org/10.4037/ccn2002.22.2.60
Bland JM, Altman DG (1986) Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1:307–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(86)90837-8
Joffe R, Duff J, Garcia Guerra G, Pugh J, Joffe AR (2016) The accuracy of blood pressure measured by arterial line and non-invasive cuff in critically ill children. Crit Care 20:177. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-016-1354-x
Marouane A, Cornelissen EAM, Nusmeier A, Bootsma-Robroeks CMHHT (2019) Oscillometric and intra-arterial blood pressure in children post-kidney transplantation: Is invasive blood pressure measurement always needed? Pediatr Transplant 23:e13309. https://doi.org/10.1111/petr.13309
Querfeld U (2004) The clinical significance of vascular calcification in young patients with end-stage renal disease. Pediatr Nephrol 19:478–484. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-004-1450-z
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
No funding was received for conducting this study. All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or nonfinancial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kaplan, E., Kadmon, G., Nahum, E. et al. Blood pressure monitoring following kidney transplantation in children: a comparison of invasive and noninvasive measurements using Doppler as a benchmark technique. Pediatr Nephrol 38, 1291–1298 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-022-05691-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-022-05691-2