Abstract
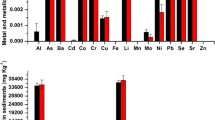
Six potential toxic metals (PTMs) in water-sediment-submerged macrophyte systems were investigated in six shallow lakes in Changsha City, Central China. The mean metal concentrations in the surface and interstitial water were in the order of Cu>As>Zn>Cr>Pb>Cd and As>Cu>Zn>Cr>Pb>Cd, respectively. Both surface and interstitial water were not polluted, except the interstitial water of Yue Lake with slight pollution (PN=1.93). The mean metal concentration was in the order of Zn>Cr>As>Cu>Pb>Cd in the sediments. The concentration of As in all urban shallow lakes exceeded 25 mg kg‒1, and Cd in Meixi Lake and Xianjia Lake also exceeded 0.3 mg kg‒1. The sediments were slight to severe pollution in the studied urban shallow lakes. Among the submerged macrophytes, the concentrations of PTMs were decreased in the order of Vallisneria natans (Lour.) Hara > Myriophyllum verticillatum L. > Centella asiatica (L.) Urban > Potamogeton crispus L. Zn was the most accumulated in all the submerged macrophytes, and the highest bioaccumulation factor (BAF) of Zn was 43.0 in V. natans. V. natans also exhibited relatively high BAFs of 4.6, 2.4, and 4.7 for Cu, As, and Pb, compared with other submerged macrophytes. The translocation factor (TF) of As was no more than 0.3 in all submerged macrophytes. The TFs of the other metals were dependent on the plant species. For most studied metals (As, Pb, Zn, and Cd), significant positive correlations were identified between submerged macrophytes and their surrounding water/sediments (P<0.05). These results indicated that the potential use of native submerged macrophytes, especially for V. natans, for PTM removal from urban shallow lakes is worth further exploration.











Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data used in this manuscript is included in the text.
References
Ali H, Khan E, Sajad MA (2013) Phytoremediation of heavy metals–concepts and applications. Chemosphere 91(7):869–881
Arnason JG, Fletcher BA (2003) A 40+ year record of Cd, Hg, Pb, and U deposition in sediments of Patroon Reservoir, Albany Country, NY, USA. Environ Pollut 123(3):383–391
Gale NL, Adams CD, Wixson BG, Loftin KA, Huang YW (2004) Lead, zinc, copper, and cadmium in fish and sediments from the big river and flat river creek of missouri’s old lead belt. Environ Geochem Health 26(1):37–49
Hu X, Wang C, Zou L (2011) Characteristics of heavy metals and Pb isotopic signatures in sediment cores collected from typical urban shallow lakes in Nanjing China. J Environ Manag 92(3):742–748
Hwang DW, Kim PJ, Kim SG, Sun CI, Koh BS, Ryu SO, Kim TH (2019) Spatial distribution and pollution assessment of metals in intertidal sediments Korea. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(19):19379–19388
Ji X, Dahlgren RA, Zhang M (2016) Comparison of seven water quality assessment methods for the characterization and management of highly impaired river systems. Environ Monit Assess 188(1):15
Karageorgis AP, Sioulas AI, Anagnostou CL (2002) Use of surface sediments in Pagassitikos gulf, Greece, to detect anthropogenic influence. Geo-Mar L 21(4):200–211
Keskinkan O (2005) Investigation of heavy metal removal by a submerged aquatic plant (Myriophyllum spicatum) in a batch system. Asian J Chem 17(3):1507–1517
Keskinkan O, Goksu MZ, Basibuyuk M, Forster CF (2004) Heavy metal adsorption properties of a submerged aquatic plant (Ceratophyllum demersum). Bioresour Technol 92(2):197–200
Kolawole TO, Olatunji AS, Jimoh MT, Fajemila OT (2018) Heavy metal contamination and ecological risk assessment in soils and sediments of an industrial area in southwestern Nigeria. J Health Pollut 8(19):180906
Li Y, Liu H, Zhou H, Ma W, Han Q, Diao X, Xue Q (2015) Concentration distribution and potential health risk of heavy metals in Mactra veneriformis from Bohai Bay China. Mar Pollut Bull 97(1–2):528–534
Li K, Wang J, Li K, Hu S, Huang Y (2017) Research and evaluation of water pollution in Lake Wabu Basin, Huaihe Catchment. J Environ Sci 29(1):143–150
Li B, Gu B, Yang Z, Zhang T (2018) The role of submerged macrophytes in phytoremediation of arsenic from contaminated water: a case study on Vallisneria natans (Lour.) Hara. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 165:224–231
Li D, Wang J, Pi J, Yu J, Zhang T (2019) Biota-sediment metal accumulation and human health risk assessment of freshwater bivalve corbicula fluminea in Dongting Lake, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:14951–14961
Liu H, Li L, Yin C, Shan B (2008) Fraction distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Moshui Lake. J Environ Sci 20(4):390–397
Liu B, Zhang W, Chi G (2019) Distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in sediment from Bohai Bay China. Minerals 9(2):111
Loska K, Wiechuła D, Pelczar J (2005) Application of enrichment factor to assessment of zinc enrichment/depletion in farming soils. Commun Soil Sci Pl Anal 36(9–10):1117–1128
Lu X, Wang L, Lei K, Huang J, Zhai Y (2009) Contamination assessment of copper, lead, zinc, manganese and nickel in street dust of Baoji, NW China. J Hazard Mater 161(2–3):1058–1062
Luo Y, Nie X, Li X, Dai Z, Xu T, Huang Y (2017) Distribution and emission flux estimation of phosphorus in the sediment and interstitial water of Xiangxi River. J Environ Sci 38(6):2345–2354
Ma L, Yang Z, Kong Q, Wang L (2017) Extraction and determination of arsenic species in leafy vegetables: method development and application. Food Chem 217:524–530
Matanzas N, Afif E, Díaz TE, Gallego JR (2021) Phytoremediation potential of native herbaceous plant species growing on a paradigmatic brownfield site. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 232:290
Monferran MV, Pignata ML, Wunderlin DA (2012) Enhanced phytoextraction of chromium by the aquatic macrophyte Potamogeton pusillus in presence of copper. Environ Pollut 161:15–22
Rajeshkumar S, Liu Y, Zhang X, Ravikumar B, Bai G, Li X (2018) Studies on seasonal pollution of heavy metals in water, sediment, fish and oyster from the Meiliang Bay of Taihu Lake in China. Chemosphere 191:626–638
Sadiq R, Husain T, Bose N, Veitch B (2003) Distribution of heavy metals in sediment pore water due to offshore discharges: an ecological risk assessment. Environ Model Softw 18(5):451–461
Srivastava A, Jain VK (2007) Size distribution and source identification of total suspended particulate matter and associated heavy metals in the urban atmosphere of Delhi. Chemosphere 68(3):579–589
Sun Q, Gao F, Chen Z, Wang Y, Li D (2019) The content and pollution evaluation of heavy metals in surface seawater in Dalian Bay. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci 227(6):062021
Wang S, Diao X, He L (2015) Effects of algal bloom formation, outbreak, and extinction on heavy metal fractionation in the surficial sediments of Chaohu Lake. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(18):14269–14279
Xing W, Wu H, Hao B, Huang W, Liu G (2013) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals by submerged macrophytes: looking for hyperaccumulators in eutrophic lakes. Environ Sci Technol 47(9):4695–4703
Xu F, Yang Z, Chen B, Zhao Y (2013) Impact of submerged plants on ecosystem health of the plant-dominated Baiyangdian Lake. China Ecol Model 252(167):175
Xue P, Yan C (2011) Arsenic accumulation and translocation in the submerged macrophyte hydrilla verticillata (Lf) royle. Chemosphere 85(7):1176–1181
Xue P, Zhao Q, Wang Y, Geng L, Chen M, Wang X, Wang D (2018) Distribution characteristics of heavy metals in sediment-submerged macrophyte-water systems of Lake Baiyangdian. J Lake Sci 30(6):1525–1536
Yu H, Li T, Liu Y, Ma L (2019) Spatial distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contamination in urban soil of China. Chemosphere 230:498–509
Zhang G, Pan Z, Hou X, Wang X, Li X (2014) Distribution and bioaccumulation of heavy metals in food web of Nansi Lake China. Environ Earth Sci 73(5):2429–2439
Zhu X, Shan B, Tang W (2016) Heavy metal in sediments of Ziya River in northern China: distribution, potential risks, and source apportionment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(23):23511–23521
Funding
This study was supported by the Hunan Provincial Key Research and Development Program (2022NK3060).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CJ contributed to writing—original draft. TZ contributed to writing—review and editing. ZY contributed to supervision. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Asaeda Takashi.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, C., Zhang, T. & Yang, Z. Risk assessment of potential toxic metal pollution in water-sediment-submerged macrophyte systems: a case study of urban shallow lakes in Central China. Aquat Ecol 56, 1001–1017 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10452-022-09972-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10452-022-09972-8