Abstract
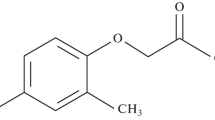
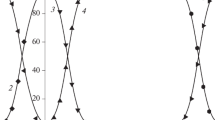
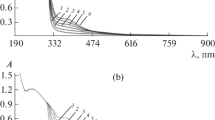
Pentachlorophenol (PCP) and astrafloxin FF (AF), a polymethine dye, were shown to form an ionic associate (IA), which could be rather perfectly extracted by different aromatic hydrocarbons. A maximum extraction of the ionic associate was attained at pH 8–12, being in quite a good agreement with the data obtained by calculating the distribution diagrams of corresponding dye and PCP forms. The distribution diagrams of these forms were calculated and constructed by using the MarvinScetch software. The effect of the dye concentration on the absorbance of the toluene extracts of PCP–AF ionic associates was studied. The PCP recovery attained a maximum at a dye concentration of (1.6–2.8) × 10–4 M. Extraction equilibrium was established for 50–60 s. The stoichiometry of the PCP–AF ionic associate was studied by the spectrophotometric methods of isomolar series and equilibrium shift, and the ratio of components was 1 : 1. The scheme of the formation and extraction of this ionic associate was proposed. The conventional molar absorption coefficient of the ionic associate was 1.2 × 105. The calibration curve of the extract absorbance as a function of the PCP concentration could be described by the linear equation А = 0.0121 + 0.0622c within a PCP concentration range of 1.2–60.3 μg/cm3. The PCP detection limit calculated by the 3s-criterion (n = 5, Р = 0.95) was 1.08 μg/cm3. The intralaboratory disperancy of the calibrating plot for PCP analysis with astrafloxin was estimated by the Cochran test G. The calculated Cochran test (n = 5, P = 0.95) was smaller than its tabular value: Gcalcd = 0.27 < Gtab = 0.64 to argue for variance homogeneity. A method for the extraction photometric analysis of pentachlorophenol in water and bottom sediments was developed.


Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Muino, M.A.F. and Lazano, J.S., Mass spectrometric determination of pentachlorophenol in honey, Anal. Chim. Acta, 1991, vol. 247, pp. 121–123.
US EPA. Pentaclorphenol carcinogenicity summary table, AWBERC Library, Cincinnati, OH, 1990, p. 17.
MUK 4.1.2479-09: Control Methods. Chemical Factors: Determination of Pentachlorophenol in Foods, Moscow, 2009.
Pentachlorphenol and its salts and esters: Joint TAO Junep procramme for the operation of the prior informed consent: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, United Nations Environment Programme, Rome, Geneva, 1991 (Amended 1996), pp. 49–62.
Fedorov, L.A., Dioksiny kak ekologicheskaya opasnost’: retrospektiva i perspektivy (Dioxins as an Environmental Hazard: Retrospective and Prospects), Moscow, 1993.
Leblance, Y.G., Gibert, R., and Hubert, J., Determination of pentachlorophenol and its oil solvent in wood pole samples by SFE and GC with postcolumn flow splitting for simultaneous detection of the species, Anal. Chem., 1999, vol. 71, pp. 78–85.
Meyer, A. and Kleibohmer, W., Determination of pentachlorophenol in leather using supercritical fluid extraction with in situ derivatization, J. Chromatogr. A., 1995, vol. 718, pp. 131–139.
Mapes, J.P., McKenzie, K.D., McClelland, L.R., Movassaghi, S., Reddy, R.A., Allen, R.L., and Friedman, S.B., Penta RIScTM soil—A rapid, on-site screening test for pentachlorophenol in soil, Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 1992, vol. 49, pp. 334–341.
Reigner, B.G., Rigod, J.F., and Tozer, L.N., Simultaneous assay of pentachlorophenol and its metabolite, tetrachlorohydroquinone, by gas chromatography without derivatization, J. Chromatogr. Biomed. Appl., 1990, vol. 533, pp. 111–124.
Butter, W. and Fooken, C., Simultaneous determination of pentachlorophenol and neutral organochlorine compounds in human milk, Fresenius’ J. Anal. Chem., 1990, vol. 336, pp. 511–514.
Butter, W., Determination of pentachlorophenol (PCP) in human serum and urine using triethylsulfonium hydroxide for pyrolytic ethylation, Fresenius’ J. Anal. Chem., 1987, vol. 326, pp. 449–452.
Gremaud, E. and Turesky, R.J., Rapid analytical methods to measure pentachlorophenol in wood, J. Agric. Food Chem., 1997, vol. 45, pp. 1229–1233.
Tayal, A., Das, L., and Kaur, I., Biodegradation of pentachlorophenol (PCP) by white rot fungal strains screened from local sources and its estimation by high-performance liquid chromatography, Biomed. Chromatogr., 1999, vol. 3, pp. 220–212.
Sherma, J. and McGinnis, S.C., Determination of pentachlorophenol and cymiazole in water and honey by C-18 solid phase extraction and quantitative HPTLC, J. Liquid Chromatogr., 1995, vol. 18, pp. 755–761.
Perrez, M., Barrios, C., Saelzer, R., Vega, M., and Villegas, R., Determination of pentachlorophenol by high performance thin layer chromatography, J. High Resolut. Chromatogr., 1989, vol. 12, pp. 419–421.
Andres, M.D., Canas, B., Izquierdo, R.C., Polo, L.M., and Alarcón, P., Transient changes of mobile phase in the high-performance liquid chromatographic separation of priority pollutant phenols, J. Chromatogr. A, 1990, vol. 507, pp. 399–402.
Ying Liu, Bei Wen, and Xiao-Quan Shan, Determination of pentachlorophenol in wastewater irrigated soils and incubated earthworms, Talanta., 2006, vol. 69, pp. 1254–1259.
Hanrahan, G., Patil, D.G., and Wang, J., Electrochemical sensors for environmental monitoring: design, development and applications, J. Environ. Monit., 2004, vol. 6, pp. 657–664.
Kormosh, Zh., Hunka, I., and Bazel, Ya., Extraction and spectrophotometric determination of diclofenac in pharmaceuticals, J. Chin. Chem. Soc., 2008, vol. 55, pp. 356–361. https://doi.org/10.1002/jccs.200800052
Lur’e, Yu.Yu., Spravochnik po analiticheskoi khimii (Handbook on Analytical Chemistry), Moscow: Khimiya, 1989.
CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, Boca Raton: CRC, 2010, 90th ed., pp. 5–30.
Kormosh, Z.A. and Tolmachev, A.A., State of polymethine (styryl and carbocyanine) indolium derivatives in aqueous solution and their analytical properties, J. Anal. Chem., 2002, vol. 57, pp. 118–124. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014091218429
Kormosh, Zh., Bazel, Ya., and Tolmachov, A., The state and chemical-analytical properties of certain polymethyne dyes in aqueous solutions, Acta Chim. Slov., 2002, vol. 49, pp. 795–804. http://acta-arhiv.chem-soc.si/49/49-4-795.pdf.
MarvinSketch 21.11.0/(c)1998–2022, ChemAxon. https://chemaxon.com.
Dvorkin, V.I., Metrologiya i obespechenie kachestva kolichestvennogo khimicheskogo analiza (Metrology and Quality Assurance for Quantitative Chemical Analysis), Moscow: Khimiya, 2001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interests.
Additional information
Translated by E. Glushachenkova
About this article
Cite this article
Zholt Kormosh, Olena Matskiv Photometric Analysis of Pentachlorophenol in Water by Extraction with Astrafloxin. J. Water Chem. Technol. 44, 169–174 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1063455X22030079
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1063455X22030079