Abstract
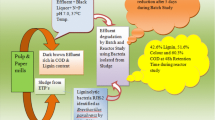
Sodium benzoate, the sodium salt of benzoic acid, is the first accepted and one of the widely used chemical preservatives in the food, cosmetic and, beverage industries. In recent past, soaring demand of packaged food resulted in increased industrialization and intensified use of chemical preservatives. The residual remains of these industries are discharged into their wastewater treatment plants (WWTP) and effluent treatment plants (ETP) thus concentrating the chemical preservatives in these treatment plants. This causes harmful effects on the growth of indigenous microbes in treatment plants and reduces the effectiveness of biological processes in secondary wastewater treatment. Therefore, it is necessary to degrade preservatives like sodium benzoate in the WWTP/ETP of industries. The ETP samples were collected from food processing industry for the isolation of sodium benzoate degrading aerobic bacteria. The microscopic analysis of the isolate with maximum ability to grow at a very high concentration of sodium benzoate (10 000 mg/L) showed it to be Gram-positive, endospore forming bacteria. The molecular characterization was done using 16S rDNA sequencing with universal primers and the isolate was identified as Bacillus subtilis DSSK1. The sequence was submitted to NCBI GenBank with accession number MT704505. The isolate was able to utilize sodium benzoate as the sole carbon and energy source. It was able to degrade 76% of sodium benzoate (10 000 mg/L) in 72 h. It was also able to produce hydrolytic and oxidative enzymes (cellulase, amylase, pectinase and laccase) which can help it to better survive in the food industry effluent rich in cellulose, starch, pectin, and lignin thus making it a promising candidate for industrial effluent treatment rich in benzoate.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Zengin, N., Yüzbasıoglu, D., Ünal, F., Yilmaz, S., and Aksoy, H., The evaluation of the genotoxicity of two food preservatives: Sodium benzoate and potassium benzoate, Food Chem. Toxicol., 2011, vol. 49, no. 4, pp. 763–769.
Jay, J.M., Modern Food Microbiology, Gaithersburg: Springer, 2000.
Davidson, P.M., Taylor, T.M., and Schmidt, S.E., Chemical preservatives and natural antimicrobial compounds, in Food Microbiology, Am. Soc. Microbiol., 2013.
Wibbertmann, A., Kielhorn, J., Koennecker, G., Mangelsdorf, I., and Melber, C., Concise international chemical assessment Document 26, Benzoic acid and Sodium benzoate, Geneva: World Health Organization, 2000, vol. 26, pp. 1–48.
Noorafshan, A., Erfanizadeh, M., and Karbalay-Doust, S., Stereological studies of the effects of sodium benzoate or ascorbic acid on rats' cerebellum, Saudi Med. J., 2014, vol. 35, no. 12, pp. 1494–1500.
Madeira, F., Park, Y.M., Lee, J., Buso, N., Gur, T., Madhusoodanan, N., Basutkar, P., Tivey, A.R., Potter, S.C., Finn, R.D., and Lopez, R., The EMBL-EBI search and sequence analysis tools APIs in 2019, Nucl. Acids Res., 2019, vol. 47, no. 1, pp. 636–641.
Kumar, S., Stecher, G., Li, M., Knyaz, C., and Tamura, K., MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms, Mol. Biol. Evol., 2018, vol. 35, no. 6, pp. 1547–1549.
Zaveri, P., Munshi, N., Vaidya, A., Jha, S., and Kumar, G.N., Functional microbial diversity dynamics in common effluent treatment plants of South Gujarat and hydrocarbon degradation, Can. J. Microbiol., 2015, vol. 61, no. 6, pp. 389–397.
Demirci, B.K., The relationship between some physicochemical, microbiological characteristics and electrical conductivity of milk stored at different temperature, Tekirdag Ziraat Fakultesi Dergisi, 2011, vol. 8, no. 2, pp. 13–21.
Qiu, Y.L., Sekiguchi, Y., Imachi, H., Kamagata, Y., Tseng, I.C., Cheng, S.S., Ohashi, A., and Harada, H., Sporotomaculum syntrophicum sp. nov., A novel anaerobic, syntrophic benzoate-degrading bacterium isolated from methanogenic sludge treating wastewater from terephthalate manufacturing, Arch. Microbiol., 2003, vol. 179, no. 4, pp. 242–249.
Thomas, L., Joseph, A., and Gottumukkala, L.D., Xylanase and cellulase systems of Clostridium sp.: An insight on molecular approaches for strain improvement, Bioresour. Technol., 2014, vol. 158, pp. 343–350.
Mohapatra, B.R., Banerjee, U.C., and Bapuji, M., Characterization of a fungal amylase from Mucor sp. associated with the marine sponge Spirastrella sp., J. Biotechnol., 1998, vol. 60, nos. 1–2, pp. 113–117.
Basheer, S., Rashid, N., Akram, M.S., and Akhtar, M., A highly stable laccase from Bacillus subtilis strain R5: Gene cloning and characterization, Biosci., Biotechnol., Biochem., 2019, vol. 83, no. 3, pp. 436–445.
Song, B., Palleroni, N.J., and Haggblom, M.M., Isolation and characterization of diverse halobenzoate-degrading denitrifying bacteria from soils and sediments, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2000, vol. 66, no. 8, pp. 3446–3453.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors in this manuscript contributed to the information communicated to the journal.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
About this article
Cite this article
Shweena Krishnani, Vineet, Tripathi, N.M. et al. Isolation and Identification of Benzoate Degrading Bacteria from Food Industry Effluent. J. Water Chem. Technol. 44, 191–197 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1063455X22030080
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1063455X22030080