Abstract
In this study, 9 remaining water components of Madian River in the Baraftab were considered. Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average modeling techniques are considered appropriate in creating and predicting components. SO42–, Na + and SAR show a declining fashion despite the different properties of brilliant water, which show an increasing lightness. However, practicing a delay to the position of the style desk was sure that the time group was ready for painting. Similarly, the time group study suggests that there is an unfamiliar location increase mode for all components except SO42–, Na + , and SAR. EC, Cl–, Ca2 + , Mg2 + and HCO3– show an increasing style, which is suggested to reduce the prominent water within the area. Depend on the sphere revisions, the extreme successful and relative population density, rising the use of artificial frameworks, departure city effluents and mainstream of rural manure in conservative method via streams, inopportune plans of burial litters, dispersal of nonsenses and disorders in floor waters and watercourses which later influx via streams are taken into deliberation because the important reasons of water brilliant worsening. Agronomic effluents and livestock are different causes that pollute floor water. Also, the water hazard outstanding worsening is rising because of extreme public boom with inside the area and green changes are energetic with inside the zone to exclude you larger ecological devastation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Water high-satisfactory is a main condition of lifestyles because of its straight impact on anthropological health. Very satisfactory water can be damaged by geological structure, salinity, over-harvesting of groundwater, municipal and domestic wastewater to floor streams, in addition to crop drainage and a wide variety of chemical compounds. (Derakhshannia et al. 2020; Fatahi Nafchi et al. 2021; Ostad-Ali-Askari et al. 2017a; Golian et al. 2020; Ostad-Ali-Askari et al. 2018b; Tsakiris and Alexakis 2012). A variety of strategies and procedures are applied to assess and predict high water satisfaction. Also, most of the water software along with SWAT, QUAL2K and MIKE-eleven use excellent equipment to evaluate the high satisfactory currents. Time group evaluation is one of the useful strategies that can be implemented in modeling and predicting water satisfaction (Abdollahi et al. 2021; Nafchi et al. 2021, 2022; Fattahi Nafchi et al. 2022; Ostad-Ali-Askari et al. 2021a; Chang 1988). Time group examines are beneficial in expertise and studying the method of various phenomena. It is likewise beneficial in producing beyond observations forecasting the destiny values primarily Depend totally at the beyond memory (Madani 2021). Time group consists of a string of records over the years with an identical c program language period among all records. The c program language period may be described as daily, weekly, month-to-month in addition to every year time steps. Time group study is used in selection in many operating systems and hydrological tactics. Time group assessment in hydrology has the most significant purpose: 1. Understanding and transcribing random tools of a hydrological system and 2. Estimating fate standards for the system (Pirnazar et al. 2018; Salehi Hafshejani et al. 2019; Talebmorad et al. 2021; Javadinejad et al. 2018, 2019a, b, 2021; Ostad-Ali-Askar et al. 2018a, 2019, 2020a; Kumar 2021). One of the most important issues in applied hydrology is water quality. Because the main activities of hydrology in order to supply water for drinking, agriculture or industry, each of which in terms of quality must have certain quality characteristics and criteria, and if such water supply is not possible, these activities are practically ineffective (Eslamian et al. 2018a; Eslamian et al. 2018b; Talebmorad et al. 2020; Fan 2020). Today, water quality studies are becoming more widespread and include issues related to surface and groundwater pollution (Cheng 2021). Water quality modeling is used to simulate changes in pollutants in the environment (Stansfield 2001). Concentrations of pollutants in the environment may increase or decrease due to various mechanisms that the fate of pollutants depends on the result of interactions between the mass and their transport processes, all these changes are the subject of water quality modeling (McKerchar 1974). Models include equations, relationships, and observational evaluation data that are used to explain the behavior of natural systems under different conditions and can have the ability to provide the best management option given specific time conditions and economic conditions (Shayannejad et al. 2022; Ostad-Ali-Askari et al. 2017b, 2020b, 2021b, c; Ostad-Ali-Askari 2022a, b; Raeisi Vanani et al. 2017; Pregun 2022). Madian River, which supplies water to Lorestan gardens in Ziwadar area of Poldakhtar city, Madian River is one of the important tributaries of Kashkan river, which originates from Kuhdasht city and several springs are drained along the water flow path. Due to the decrease in rainfall and the negative balance of the Kuhdasht plain, the flow of mares in the river has drastically decreased and the orchards of Ziodar figs have faced severe water shortages on the eve of the irrigation season. Ziwadar area of Poldakhtar city does not have the capacity to develop new gardens in the current situation (Nafsin 2021). Considering the damages that are left every year due to floods and inundation of rivers, the study and determination of the flood zone of rivers has been considered for a long time (Xue 2021). Various factors can be influential in determining the flood zone, including parameters related to the morphology of the river. Among the parameters related to morphology affecting the bed bottom of rivers, the form of rivers in terms of alluvial and mountainous has a geostructural form that will be different according to each state of the river flood zone (Schäfer, 2021).
Applied time-series analysis
ARIMA modes can reproduce the main statistical traits of a hydrological time group (autoregressive, incorporated, transferring average). ARIMA modes were used to observe river runoff and discharge (Kurunç et al. 2005), lake water area (Sheng and Chen 2011), sediment production (Hanh et al. 2010) and first water-rate (Ahmad et al. 2001; Lehmann & Rode 2001; Faruk 2010; Durdu 2010; Khalil Arya and Zhang 2015). Automated correlation modes have been used in several studies of flow analysis (Thomas and Fiering 1962). McKarchar and Delleur (1974) took the first step in using time groups in hydrology using self-regulated integrated moving averages. They applied seasonal modeling correctly to examine the seasonal properties of flow components. Time group modeling is in determining and predicting the sample of month-to-month flow and management of green combined water resources (Jalal Kamali 2006). It is widely used for predicted hydrological variables that include rainfall and discharge in addition to floods. (Komornık et al. 2006; Damle and Yalcin 2007). Many investigations have centered on water first-rate components, a Brief evaluation of that is referred to as follow. Many studies have focused on first-class water components, a brief evaluation of which is as follows.
Applied time series analysis on surface water quality
Hirsch et al. (1982) developed new strategies for examining month-to-month micro-water information for uniform traits. Temporal adjustments in micro-water components including pH, alkalinity, general phosphorus and nitrate concentration were also investigated using the Niagara Information Group. (El-Shaarawi et al. 1983). Yu et al. (1993) analyzed the micro-water data of Arkansas, Verdigris, and Neosho floors in addition to the Walnut River Basin to examine traits in 17 main materials using four unique nonparametric strategies. High circulatory states and leaky data from Plynlimon, Mid Wales were investigated using the Kendall Seasonal Test (Robson & Neil 1996). Gangyan et al. (2002) investigated the temporal sediment load traits of the Yangtze River the use of the turning factor test, Kendall’s rank correlation test. Gangyan et al. (2002) using the spin factor test, studied the temporal sediment load characteristics of the Yangtze and River the Kendall rank correlation test. Jassby et al. (2003) in Lake Tahoe, USA developed an advanced timeline version for Secchi intensity. Panda et al. (2011) studied sediment load traits of a tropical river basin in India.
Applied time series analysis on groundwater quality
Time group assessment has been performed in the best groundwater modeling in separate areas. Chang (1988) proposed a modeling approach consisting of examining the homogeneity of records and selecting a first-class version for use by the water loss group to use a random process. One study considered the best groundwater settings due to human exercise, using time group assessments of the best water records correctly from 1964 to 1965. Loftis (1996) reviewed global agricultural and urban surveys, supply factors, and unsafe groundwater near and local groundwater at best around the world, including a few snapshots. Lee and Lee (2003) evaluated and quantified the potential for groundwater depletion in the Seoul Business District, Korea. Various studies have been conducted on the water temperature time group (Kim et al. 2005) best performed the time group assessment to investigate the impact of tides on groundwater in the coastal region of Korea. Also, temporal variability of turbidity, dissolved oxygen, conductivity, temperature and fluorescence with decreasing Mekong River as the use of time group assessment was examined. (Irvine et al. 2011). The best water modeling plays an important role in the best water control and conservation. (Singh et al. 2004; Chenini and Khemiri 2009; Fang et al. 2010; Su et al. 2011; Prasad et al. 2014; Seth et al. 2013; Parmar and Bhardwaj 2014). The use of time group study in aquatic assets shows the performance and efficiency of this method due to the random nature of hydrological processes. It examines the ambitions to use this technique in the best water study. In the gift review, the best components of the Madian river water at Baraftab station have been examined. The technique and survey area are presented in the next section.
Materials and methods
The study area
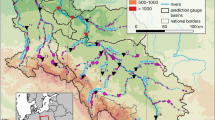
The study site is located in west of Iran in the Kuhdasht region. Figure 1 shows the study site in Iran. This river station is located at 47°48ʹE and 33°18ʹN minutes north. The area of the basin is about 1108 square kilometers, which is located in the Kashkan basin of Karkheh basin. The time sequence of 9 components of water quality such as TDS, EC, HCO3-, Cl-, SO42-, Ca2 + , Mg2 + , Na + and SAR of the Baraftab station in Madian river was measured in this research (Figs. 1, 3 and 6).
Methodology
The perception and knowledge of ARIMA modeling was confirmed in the characteristic survey. (Pankratz 1983; Vandaele 1983; Box and Jenkins 1976). The history of this method is temporarily provided. Autoregression (AR) modes suppose the values of the Depend variable, Zt, as the regression property of the previous values, Zt − 1, Zt − 2 … Zt − n. An AR version of order 1 (i.e., AR version (1)) is defined as an Eq. 1:
where Zt and Zt-1 show the mismatch from the mean, Φ1 is the first-order AR coefficient and defines the effect of the unit extrusion on Zt-1 on Zt, and αt is white noise.
The αt principles are usually chosen and expected to be neutral with zero proposed cost and normal variance cost. The cost of variance for a fixed, high-quality Zt version is limited (Vandaele 1983) and |Φ1| to meet these conditions must be much less than 1. Higher order AR modes are possible, just like multiple regressions; for this case, the absolute cost of each AR coefficient must be much less than 1. Moving Average (MA) modes cover the beyond random fluctuations to capture the time sequence.: An MA version of order 1 (ie MA version (1)) may be expressed as an Eq. 2:
where θ1 is the MA coefficient and random shocks (white sound) (αt) are usually distributed and neutrally expected to change at the proposed zero cost and fixed cost. Values greater than 1 indicate that similar descriptions inside the transverse have a greater effect on Zt than recent new observations that are not always plausible in a hydrological time group. A higher order of MA modes is possible. Similar to AR version coefficients, the absolute cost of each MA coefficient must be much less than 1. Because saving a time group is so important, modeling it may be possible to use a hybrid version (ARMA) instead of a regular AR or MA version from time to time. Also, showing a time group with ARMA version (1,1) is more economical than evaluating with AR version (3), as this version requires fewer component estimates. Mixing modes is possible due to the fact that they are theoretically represented as natural modes AR or MA with infinite order. (Vandaele 1983). A hybrid version can provide more flexibility in explaining the consequences of interaction between processes. (Salas et al. 1980). The primary purpose of time group assessment is to identify seasonal styles and/or trends over time. Most of the time, the hydrological time group shows an everyday seasonal sample that may be removed by standardizing the records for the offer and the seasonal standard. Information and modeling of the form of correlation with within the time group is also another goal of time group analysis. Basic areas with ARIMA modeling include: (1) version identification, (2) estimating version orders, and (3) version validation using routine testing. The impacts are prepared with inside the subsequent section. Rivers are one of the most important dynamic ecosystems and awareness of temporal and spatial changes in river water quality is very important. Madian River, which supplies water to the famous black fig orchards of Lorestan in Ziwadar area of Poldakhtar city, added: Madian River, one of the important tributaries of Kashkan River, originates from Koohdasht city and several springs are drained along it. Due to the decrease in rainfall and the negative balance of Koohdasht plain, the flow of mares in the river has drastically decreased and ziodar fig orchards have faced severe water shortages on the eve of the irrigation season. The flow of Madian in the river has decreased by 73% compared to the same period of the previous year and has decreased by 95% compared to the average long-term statistics (about 61 years) (Kim 2021).
Results and discussion
In this view, 9 excellent components of water are examined. With a delay, the records became a finite table time group. In the second a degree MINITAB 14 changes to apply in this view to examine that group nine times. The ACF and PACF of time group have been plotted at the second one degree. The ACF and PACF time groups are plotted quadratically. After specifying the ACF and PACF whenever a group considers the order of the version first. Then four values were applied to study the effects of group technology and the recommended modes and 35 record-time groups were generated. Depending on the four values, a pleasant version is considered for each time a group of 35 records and those modes are applied to predict the five time group values. These four values were R2, AIC, RMSE and VE% (Karamouz and Araghinejad 2015). The cost of AIC is estimated through the Eq. 3:
where σ is the same old fault of the remains. n is the design size. p and p represent AR and MA, respectively. The VE% fee is also programmed using the Eq. 4:
where yt and ŷt represent the values created and assumed, respectively, and n is the size of the outline. In predicting the next level, the best water components are finished. The consequences are confirmed by the inside of the next fig. Pre-defined metrics (AIC, RMSE, and VE%) were applied at this level to represent the performance of each form in predicting the cost of records. Figure 2 shows the uniform time group of the best water records for the TDS component and the predicted values for five consecutive years. The TDS standard group shows that this component has an extraordinary mode, which has been removed and verified with kilometers as shown in Table 1 (Fig. 2). The results show that the form is able to model the time set well. However, there is an increasing style for source values for five consecutive years that is not consistently indistinguishable from the predicted years. For an additional component, since the miles are from Fig. 3, the EC time group examines an increasing mode that has been omitted in the second level. Then the use of a good version was predicted for five years. Table 2 also shows the results of the model selection and fine-tuning (Fig. 4). The projected values for five consecutive years are also specified in this figure. Similar to the previous components, HCO3- examines the increasing gradient and modeling is done after removing the mode. Table 3 shows the modeling implications for this component. The uniform Cl-time group is provided in Fig. 5. The predicted values of this component are also confirmed in this figure. The implications show that the selected version, confirmed in Table 4, is able to model the group well. Figure 6 proves the old group similar to SO42-. SO42 group modeling became a skill in a reliable group without removing fashion. The projected values are also confirmed in this figure for five years. The consequences of the era and good competition are shown in Table 5. Also, the same old Ca2 + group is prepared in Fig. 7, and the predicted values of this component are specified on this figure. The implications of Table 6 show that the selected version created in Table 6 is able to model the group well. Figure 8 shows the same old group of Mg2 + .Fig. 8 shows that the group observes a growing fashion. Modeling of the Mg2 + group was performed after removing the fashion, which is also provided in this figure. Table 7 shows that the selected form can model the group well.
Figure 9 specifies over-all group of Na + . The figure shows that the group is done in a downward fashion. The modeling for the Na + group became final after the mod was removed, which is fine-tuned in this figure. The characteristics show that the selected form, created in Table 8, is able to accurately model the group. Finally, Fig. 10 proves the total SAR group. SAR group modeling was performed after removing the mode, which is also prepared in this figure. Table 9 shows that the selected form is able to modeling the group well.
The results of forecasting
Table 10 shows the forecast properties for the 9 components. Also, time group of HCO3-, Cl-, SO42 + , Ca + , Mg2 + , Na + , SAR, TDS and EC are specified in Fig. 11.
The last five years of time group display the forecasted values for components.
Conclusion
In this study, 9 special water components of Madian River in Baraftab were considered. ARIMA modeling method is suitable for constructing and predicting components. SO42–, Na + and SAR show a depressing fashion, yet the extraordinarily diverse water properties, which show an increasing style. However, the use of a delay to the limited time group position of the light table was prepared for portraits. Examination of the set-time set also shows that there may be an unusual place-increasing style for all components for SO42–, Na + , and SAR. EC, Cl–, Ca2 + , Mg2 + and HCO3– show an increasing style which is a suggestion for worsening of super-monopolized water. The water that eventually enters through the streams is examined as one of the main reasons for the excellent deterioration of water depending on sectoral surveys (JCE 2005), sharp increase in relative population density, increase in artificial frameworks input, municipal wastewater discharge, and conservative pastoral sewage popularity through rivers, problematic international disturbance schemes, water dispersion, and drive dispersion. Crop waste and livestock are different causes of contaminating floor water. Similarly, a sudden increase in water is increasing due to a sharp increase in population within the plot, and green changes within the plot are critical except for additional ecological loss. In statistical analysis of water quality variables, determining the relationships between these variables is one of the important issues. In this study, focal correlation analysis and principal component analysis were used to find the relationships between variables and determine the main variables determining water quality, respectively. Cluster analysis method was also used to classify the studied stations. The results showed that there is a significant relationship between the two categories of physical and chemical variables of the river, which are mostly due to man-made resources. Also, the results of principal component analysis showed that the main variables determining the quality of river water are EC, temperature, SAR, SO4, pH and DO, which are often caused by industrial and human pollutants. The results of cluster analysis for classification of stations showed that they are in the same category in terms of similarity of water quality variables. Therefore, urban areas and human pollutants have had a significant impact on the classification of stations.
Water quality could be an around the world issue which influences human creatures lives on a very basic level. Water shortage is heightening in result of quality weakening. Diverse variables such as population increase, economic advancement and water contamination may well be considered as the roots of the issue. The think about and estimating of water quality is essential to avoid genuine water quality deteriorations in future. Distinctive strategies have been utilized to foresee and gauge the quality of water. It appears that the quality of water is falling apart based on an expanding drift for the larger part of parameters and needs genuine administrative activities. Water contamination is one of the foremost vital natural issues which the world faces. Widespread issue of water lack and shortage of secure and sound water require the examination of problem. Water contamination, from a neighborhood stream and bowl to territorial water pollution, from single to complex contamination, from surface water to groundwater, has been a genuine restriction to sustainable economic development. Water quality may well be influenced by saltiness, overdraw of ground water, urban and household wastewater entrance into surface streams as well as rural waste. The reason of most water quality and stream thinks about is to point out the data and necessary information to oversee water assets as well as their use, control and advancement. Time and cash are spared through these studies and future advancement of water assets becomes inexpensive. The most goals of water quality modeling may well be to: infer cause and impact connections, distinguish impacts of toxin sources, survey fundamental levels of observing, assess arranging and administration choices, center on additional observing and administration destinations and evaluate and assess future water quality conditions. Time arrangement examination is one of the valuable strategies which are connected in water quality modeling and determining.
Data availability
Some or all data, models, or code that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Abdollahi S, Madadi M, Ostad-Ali-Askari K (2021) Monitoring and investigating dust phenomenon on using remote sensing science geographical information system and statistical methods. Appl Water Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-021-01419-z
Ahmad S, Khan IH, Parida BP (2001) Performance of stochastic approaches for forecasting river water quality. Water Res 35:4261–4266. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00167-1
Box GEP, Jenkins GM (1976) Time series analysis, forecasting and control, 1st edn. Holden-Day, Toronto
Chang TJ (1988) Stochastic forecast of water losses. J Irrig Drain Eng 114:558–558. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9437(1988)114:3(547)
Cheng B, Zhang Y, Zhang X (2021) Spatiotemporal analysis and prediction of water quality in the Han river by an integrated nonparametric diagnosis approach. J Clean Prod 328:129583
Chenini I, Khemiri S (2009) Evaluation of ground water quality applying multiple linear regression and structural equation modeling. Int J Environ Sci Technol 6:509–519
Damle C, Yalcin A (2007) Flood prediction applying time series data mining. J Hydrol 333:305–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2006.09.001
Derakhshannia M, Dalvand S, Asakereh B, Ostad Ali Askari K (2020) Corrosion and deposition in Karoon River Iran based on hydrometric stations. Int J Hydrol Sci Technol 10(4):334. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJHST.2020.108264
Durdu ÖF (2010) Stochastic approaches for time series forecasting of boron: a case study of Western Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 169:687–701. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-1208-y
El-Shaarawi AH, Esterby SR, Kuntz KW (1983) A statistical evaluation of trends in the water quality of the Niagara river. J Gt Lakes Res 9:234–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0380-1330(83)71892-7
Eslamian S et al (2018a) Saturation. In: Bobrowsky P, Marker B (eds) Encyclopedia of Engineering Geology. Encyclopedia of Earth Sciences Series. Springer, Cham, Denmark. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-12127-7_251-1
Eslamian S, et al (2018b) Water. In: Bobrowsky P, Marker B (eds) Encyclopedia of Engineering Geology. Encyclopedia of Earth Sciences Series. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-12127-7_295-1
Fan C, Chen KH, Ya-Zhen Huang YZ (2020) Model-based carrying capacity investigation and its application to total maximum daily load (TMDL) establishment for river water quality management: a case study in Taiwan. J Clean Prod 291:125251
Fang H, Wang X, Lou L, Zhou Z, Wu J (2010) Spatial variation and source apportionment of water pollution in Qiantang river (China) applying statistical techniques. Water Res 44:1562–1572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.11.003
Faruk DÖ (2010) A hybrid neural network and ARIMA model for water quality time series prediction. Eng Appl Artif Intell 23:586–594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2009.09.015
Fattahi Nafchi R, Raeisi Vanani H, Noori Pashaee K, Samadi Brojeni H, Ostad-Ali-Askari K (2022) Investigation on the effect of inclined crest step pool on scouring protection in erodible river beds. Nat Hazards 110(3):1495–1505. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-021-04999-w
Fatahi Nafchi R, Yaghoobi P, Reaisi Vanani H, Ostad-Ali-Askari K, Nouri J, Maghsoudlou B (2021) Eco-hydrologic stability zonation of dams and power plants using the combined models of SMCE and CEQUALW2. Appl Water Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-021-01427-z
Gangyan Z, Goel NK, Bhatt VK (2002) Stochastic modelling of the sediment load of the upper Yangtze River (China). Hydrol Sci J 47:S93–S105. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626660209493025
Golian M, Katibeh H, Singh VP, Ostad-Ali-Askari K, Rostami HT (2020) Prediction of tunnelling impact on flow rates of adjacent extraction water wells. Q J Eng Geol Hydrogeol 53(2):236–251. https://doi.org/10.1144/qjegh2019-055
Hanh PTM, Anh NV, Ba DT, Sthiannopkao S, Kim KW (2010) Analysis of variation and relation of climate, hydrology and water quality in the lower Mekong river. Water Sci Technol 62:1587–1594. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2010.449
Hirsch RM, Slack JR, Smith RA (1982) Techniques of trend analysis for monthly water quality data. Water Resour Res 18:107–121. https://doi.org/10.1029/WR018i001p00107
Irvine KN, Richey JE, Holtgrieve GW, Sarkkula J, Sampson M (2011) Spatial and temporal variability of turbidity, dissolved oxygen, conductivity, temperature and fluorescence in the lower Mekong river-Tonle sap system identified applying continuous monitoring. Int J River Basin Manag 9:151–168. https://doi.org/10.1080/15715124.2011.621430
Jalal Kamali N (2006). Forecasting the variations of inflow to Jiroft dam applying time series theories. In: Proceedings of the 6th international seminar on river engineering, (SRE’ 06), Shahid Chamran University, Ahvaz
Jassby AD, Reuter JE, Goldman CR (2003) Determining long-term water quality change in the presence of climate variability: lake Tahoe (U.S.A.). Can J Fish Aquat Sci 60:1452–1461. https://doi.org/10.1139/f03-127
Javadinejad S, Eslamian S, Ostad Ali Askari K (2019a) Investigation of monthly and seasonal changes of methane gas with respect to climate change using satellite data. Appl Water Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-019-1067-9
Javadinejad S, Eslamian S, Ostad-Ali-Askari K, Mirramazani SM, Zadeh LA, Samimi M (2018) Embankments. In: Bobrowsky P, Marker B (eds) Encyclopedia of Engineering Geology. Encyclopedia of Earth Sciences Series. Springer, Cham, Denmark. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-12127-7_105-1
Javadinejad S, Ostad Ali Askari K, Jafary F (2019b) Using simulation model to determine the regulation and to optimize the quantity of chlorine injection in water distribution networks. Model Earth Syst Environ 5(3):1015–1023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-019-00587-x
Javadinejad S, Eslamian S, Ostad Ali Askari K (2021) The analysis of the most important climatic parameters affecting performance of crop variability in a changing climate. Int J Hydrol Sci Technol 11(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJHST.2021.112651
JCE (2005) Integrated program of adaptation to climate study. JamAb Consulting Engineers, Karkheh Watershed
Karamouz M, Araghinejad SH (2015) Advanced hydrology. Amir Kabir University of Technology (Poly Technics), Tehran
Khalil Arya F, Zhang L (2015) Time series analysis of water quality components at Stillaguamish river applying order series method. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 29:227–239. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00477-014-0907-2
Kim JH, Lee J, Cheong TJ, Kim RH, Koh DC et al (2005) Use of time series analysis for the identification of tidal impact on groundwater in the coastal area of Kimje. Korea J Hydrol 300:188–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2004.06.004/
Kim S, Kwon YS, Cho KH (2021) Developing a cloud-based toolbox for sensitivity analysis of a water quality model. Environmental Modelling & Software. 24 April 2021
Komornık JM, Komornıkova R, Mesiar D, Szokeova J, Szolgay J (2006) Comparison of forecasting performance of nonlinear models of hydrological time series. Phys. Chem Earth Parts a/b/c 31:1127–1145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2006.05.006
Kumar A, Pandey R (2021) Long term trend analysis and suitability of water quality of River Ganga at Himalayan hills of Uttarakhand India. Environ Technol Innov 22:101405
Kurunç A, Yürekli K, Çevik O (2005) Performance of two stochastic approaches for forecasting water quality and streamflow data from Yeşilιrmak River. Turkey Environ Model Softw 20:1195–1200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2004.11.001
Lee J, Lee K (2003) Viability of natural attenuation in a petroleum-contaminated shallow sandy aquifer. Environ Pollut 126:201–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(03)00187-8
Lehmann A, Rode M (2001) Long-term behavior and cross-correlation water quality analysis of the river Elbe. Germany Water Res 35:2153–2160. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00488-7
Loftis JC (1996) Trends in groundwater quality. Hydrol Process 10:335–355. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1099-1085(199602)10:2%3c335::AID-HYP359%3e3.0.CO;2-T
Madani M, Seth R, McCrimmon C (2021) Microbial modelling of Lake St. Clair: impact of local tributaries on the shoreline water quality. Ecol Model 458:109709
McKerchar AI, Delleur LW (1974) Application of seasonal parametric linear stochastic models to monthly flow data. J Water Resour Res 10:246–255. https://doi.org/10.1029/WR010i002p00246
Nafchi RF, Samadi-Boroujeni H, Raeisi Vanani H, Ostad-Ali-Askari K, Brojeni MK (2021) Laboratory investigation on erosion threshold shear stress of cohesive sediment in Karkheh Dam. Environ Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09984-x
Nafchi RF, Yaghoobi P, Reaisi Vanani H, Ostad-Ali-Askari K, Nouri J, Maghsoudlou B (2022) Correction to: Eco-hydrologic stability zonation of dams and power plants using the combined models of SMCE and CEQUALW2. Appl Water Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-021-01563-6
Nafsin N, Jin Li J (2021) Using CANARY event detection software for water quality analysis in the Milwaukee river. J Hydro-Environ Res 38:117–128
Ostad-Ali-Askari K (2022a) Developing an optimal design model of furrow irrigation based on the minimum cost and maximum irrigation efficiency. Appl Water Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-022-01646-y
Ostad-Ali-Askari K (2022b) Management of risks substances and sustainable development. Appl Water Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-021-01562-7
Ostad-Ali-Askari K, Ghorbanizadeh Kharazi H, Shayannejad M, Zareian MJ (2019) Effect of management strategies on reducing negative impacts of climate change on water resources of the Isfahan-Borkhar aquifer using MODFLOW. River Res Appl 35(6):611–631. https://doi.org/10.1002/rra.3463
Ostad-Ali-Askari K, Ghorbanizadeh Kharazi H, Shayannejad M, Zareian MJ (2020a) Effect of Climate Change on Precipitation Patterns in an Arid Region Using GCM Models: Case Study of Isfahan-Borkhar Plain. Nat Hazards Rev 21(2):04020006. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)NH.1527-6996.0000367
Ostad-Ali-Askari K, Shayan M (2021b) Subsurface drain spacing in the unsteady conditions by HYDRUS-3D and artificial neural networks. Arab J Geosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-08336-0
Ostad-Ali-Askari K, Shayannejad M (2020b) Impermanent changes investigation of shape factors of the volumetric balance model for water development in surface irrigation. Model Earth Syst Environ 6(3):1573–1580. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-020-00771-4
Ostad-Ali-Askari K, Shayannejad M (2021a) Quantity and quality modelling of groundwater to manage water resources in Isfahan-Borkhar Aquifer. Environ Dev Sustain 23(11):15943–15959. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01323-1
Ostad-Ali-Askari K, Shayannejad M (2021c) Computation of subsurface drain spacing in the unsteady conditions using Artificial Neural Networks (ANN). Appl Water Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-020-01356-3
Ostad Ali Askari K, Shayannejad M, Eslamian S, Navabpour B (2018b) Comparison of solutions of Saint-Venant equations by characteristics and finite difference methods for unsteady flow analysis in open channel. Int J Hydrol Sci Technol 8(3):229. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJHST.2018.093569
Ostad-Ali-Askari K, Shayannejad M, Eslamian S, Zamani F, Shojaei N, Navabpour B, Majidifar Z, Sadri A, Ghasemi-Siani Z, Nourozi H, Vafaei O, Homayouni SMA (2017b) Chapter No. 18: Deficit irrigation: optimization models. In: Management of drought and water scarcity. Handbook of Drought and Water Scarcity, 1st Edn, vol 3, pp 373–389. Taylor & Francis Publisher, Imprint: CRC Press. eBook ISBN: 9781315226774
Ostad-Ali-Askari K, Shayannejad M, Ghorbanizadeh-Kharazi H (2017a) Artificial neural network for modeling nitrate pollution of groundwater in marginal area of Zayandeh-rood River Isfahan Iran. KSCE J Civ Eng 21(1):134–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-016-0572-8
Ostad-Ali-Askar K, Su R, Liu L (2018a) Water resources and climate change. J Water and Clim Change 9(2):239. https://doi.org/10.2166/wcc.2018.999
Panda DK, Kumar A, Mohanty S (2011) Recent trends in sediment load of the tropical (Peninsular) river basins of India. Glob Planet Change 75:108–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2010.10.012
Pankratz A (1983) Forecasting with Univariate box-Jenkins models: concepts and cases, 1st edn. Wiley, New York
Parmar KS, Bhardwaj R (2014) Water quality management applying statistical analysis and time-series prediction model. Appl Water Sci 4:425–434. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-014-0159-9
Pirnazar M, Hasheminasab H, Karimi AZ, Ostad Ali Askari K, Ghasemi Z, Haeri Hamedani M, Mohri Esfahani E, Eslamian S (2018) The evaluation of the usage of the fuzzy algorithms in increasing the accuracy of the extracted land use maps. Int J Global Environ Issues 17(4):307. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJGENVI.2018.095063
Prasad B, Kumari P, Bano S, Kumari S (2014) Ground water quality evaluation near mining area and development of heavy metal pollution index. Appl Water Sci 4:11–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-013-0126-x
Pregun CZ (2022) Dynamics of self-regulatory processes in a lowland river due to seasonal changes in certain hydro-ecological and water quality factors. Ecol Eng 78:106595
Raeisi Vanani H, Shayannejad M, Soltani Tudeshki AR, Ostad-Ali-Askari K, Eslamian S, Mohri-Esfahani E, Haeri-Hamedani M, Jabbari H (2017) Development of a new method for determination of infiltration coefficients in furrow irrigation with natural non-uniformity of slope. Sustain Water Resour Manage 3(2):163–169. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-017-0091-x
Robson AJ, Neal C (1996) Water quality trends at an upland site in Wales, UK, (1983–1993). Hydrol Process 10:183–203. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1099-1085(199602)10:2%3c183::AID-HYP356%3e3.0.CO;2-8
Salas JD, Delleure JW, Yevjevich VD, Lane WL (1980) Applied modeling of hydrologic time series. Water Resources Publications, Littleton CO
Salehi Hafshejani S, Shayannejad M, Samadi Broujeni H, Zarraty AR, Soltani B, Mohri Esfahani E, Haeiri Hamedani M, Eslamian S, Ostad Ali Askari K (2019) Determination of the height of the vertical filter for heterogeneous Earth dams with vertical clay core. Int J Hydrol Sci Technol 9(3):221. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJHST.2019.102315
Schäfer B, Heppell M, Beck C (2021) Fluctuations of water quality time series in rivers follow superstatistics. Science 24(8):102881
Seth R, Singh P, Mohan M, Singh R, Aswal RS (2013) Monitoring of phenolic compounds and surfactants in water of Ganga Canal, Haridwar (India). Appl Water Sci 3:717–720. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-013-0116-z
Shayannejad M, Ghobadi M, Ostad-Ali-Askari K (2022) Modeling of Surface Flow and Infiltration During Surface Irrigation Advance Based on Numerical Solution of Saint–Venant Equations Using Preissmann's Scheme. Pure Appl Geophys 179(3):1103–1113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-022-02962-9
Sheng H, Chen YQ (2011) FARIMA with stable innovations model of Great Salt Lake elevation time series. Signal Process 91:553–561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sigpro.2010.01.023
Singh KP, Malik A, Mohan D, Sinha S (2004) Multivariate statistical techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality of Gomti River (India)–a case study. Water Res 38:3980–3992. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2004.06.011
Stansfield B (2001) Impacts of sampling frequency and laboratory detection limits on the determination of time series water quality trends. N Z J Marine Freshw Res 35:1071–1075. https://doi.org/10.1080/00288330.2001.9517064
Su S, Li D, Zhang Q, Xiao R, Huang F et al (2011) Temporal trend and source apportionment of water pollution in diverse functional zones of Qiantang River. China Water Res 45:1781–1795. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.11.030
Talebmorad H, Abedi Koupai J, Eslamian S, Mousavi SF, Akhavan S, Ostad Ali Askari K, Singh VP (2021) Evaluation of the impact of climate change on reference crop evapotranspiration in Hamedan-Bahar plain. Int J Hydrol Sci Technol 11(3):333. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJHST.2021.114554
Talebmorad H, Ahmadnejad A, Eslamian S, Ostad Ali Askari K, Singh VP (2020) Evaluation of uncertainty in evapotranspiration values by FAO56-Penman-Monteith and Hargreaves-Samani methods. Int J Hydrol Sci Technol 10(2):135. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJHST.2020.106481
Thomas HA, Fiering MB (1962) Mathematical synthesis of stream flow sequences for the analysis of river basin by simulation, 1st edn. Harward University Press, Cambridge, p 751
Tsakiris G, Alexakis D (2012) Water quality models: an overview. Eur Water 37:33–46
Vandaele W (1983) Applied time series and Box-Jenkins models, 1st edn. Academic Press Inc, New York
Xue B, Zhang H, Shrestha S (2021) Modeling water quantity and quality for a typical agricultural plain basin of northern China by a coupled model. Sci Total Environ 790:148139
Yu YS, Zou SC, Whittemore D (1993) Non-parametric trend analysis of water quality data of rivers in Kansas. J Hydrol 150:61–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(93)90156-4
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Funding information is not applicable. No funding was received. No grants were received. “The author(s) received no specific funding for this work.”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors designed the study, collected data, wrote the manuscript and revised it.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The present study and ethical aspect was approved by Department of Irrigation, College of Agriculture, Isfahan University of Technology (IUT), Isfahan 8415683111, Iran.
Consent to participate
All authors designed the study, collected data, wrote the manuscript and revised it.
Consent to publish
All authors agree to publish this manuscript. There is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Ghashghaie, M., Eslami, H. & Ostad-Ali-Askari, K. Applications of time series analysis to investigate components of Madiyan-rood river water quality. Appl Water Sci 12, 202 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-022-01693-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-022-01693-5