Abstract
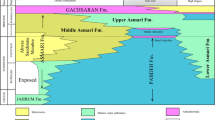
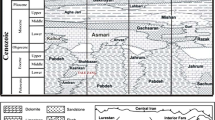
The presence of trace fossils and their diversity in Miocene deposits of western Makran accretionary prism (SE Iran) was the center of this research. The trace fossil contents of Cheraghsuz and Sardasht (with Middle Miocene in age) and Gowharan (with Early Miocene in age) stratigraphic sections were analyzed. The recognized specimens of the Cheraghsuz section are Gordia isp., Helminthopsis hieroglyphica, Helminthopsis abeli, Helminthorhaphe flexsuosa, Paleodictyon maximum, and Spirorhaphe involuta. The Sardasht section is composed of Gordia isp., Helminthopsis hieroglyphica, Helminthopsis abeli, Helminthorhaphe flexsuosa, Paleodictyon maximum, Paleodictyon majus, Paleodictyon isp., Spirorhaphe involuta, Helicolithus isp., Helicorhaphe tortilis, and Neonereites isp.. In the Gowharan section, some gastropod trails, a giant and very well-preserved Archaeonassa-like ichnogenus, and ripple marks were observed. Majority of the recognized trace fossils are of the graphoglyptid group. The trace fossil contents of Cheraghsuz and Sardasht sections are compatible with Nereites ichnofacies; as graphoglyptids are thought to be indicative of oligotrophic conditions, the trace-producers are filter-feeder organisms that normally tend to take suspended nutrient materials in the water column, but due to lower sedimentation rate, the nutrient content is concentrated on the superficial part of the substrate; accordingly, the trace-makers prefer grazing and moving on the surface sediment to take their food. However, the exceptionally preserved trace fossils in Gowharan section should be formed in a tidal flat environment. In relation to the floor, it has recorded at least three shapes, including bi-lobed, uni-lobed and submerged forms. In addition, it could be observed that different trace fossils may be created by a single animal and different animals may create the same trace fossils.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi N (2000) Palaeoichnology, lithostratigraphy and sedimentary environments of roksha and “vaziri” units (miocene) in nikshahr-ghasr ghand areas (Makran): [dissertation]. University of Shahid Beheshti, Tehran, p 350 (in Persian)
Abbasi N, Yarahmadzahi H, Nakhjiri S, Jalali A, Hafezi Moghadas H (2020) Paleoecological evaluation of the graphoglyptids of the eocene flysch deposits, West of khash, Southeast iran, regarding the event sedimentation. Iranian J Geolo 14(54):93–109 (In Persian)
Aceñolaza FG, Buatois LA (1993) Nonmarine perigondwanic trace fossils fromthe late Paleozoic of Argentina. Ichnos 2:183–201
Acenolaza GF, Gutierrez-Marco JC. (1998) Helminthopsis abeli Ksiazkiewicz, un icnofosil del ordovicico superior de la Zona Centroiberica Espanola. Geogaceta 7–10
Aghanabati A (2004) Geology of Iran. Geological survey of Iran publications, Tehran, p 586 (in Persian)
Alavi M (2004) Regional stratigraphy of the zagros fold-thrust belt of Iran and its proforeland evolution. Am J Sci 304:1–20
Azpeitia-Moros F (1933) Datos para el estudio paleontólogico del Flysch de la Costa Cantábrica y de algunos otros puntos de España. Boletin Del Instituto Geológico y Minero De España 53:1–65
Bayet-Goll A, Neto de Carvalho C, Moussavi-Harami R, Mahboubi A, Nasiri Y (2014) Depositional environments and ichnology of the deep-marine succession of the amiran formation (upper maastrichtian–paleocene), Lurestan Province, zagros fold-thrust belt Iran. Palaeogeogr, Palaeoclimatol, Palaeoecol 401:13–42
Bayet-Goll A, Neto de Carvalho C, Mahmudy-Gharaei MH, Nadaf R (2015) Ichnology and sedimentology of a shallow marine Upper Cretaceous depositional system (neyzar formation, Kopet-Dagh, Iran): palaeoceanographic influence on ichnodiversity. Cretac Res 56:628–646
Bayet-Goll A, Daraei M (2017) Ichnotaxonomy of trace fossil of the Upper Triassic Nayband Formation, Tabas Block. Central Iran. Geopersia 7(2):199–218
Berberian M, King GCP (1981) Towards a Paleogeography and tectonic evolution of Iran. Can J Earth Sci 18:210–265
Bertling M, Braddy SJ, Bromley RG, Demathieu GR, Genise J, Mikulas R, Nielsen JK, Nielsen KSS, Rindsberg AK, Schlirf M, Uchman A (2006) Names for trace fossils: a uniform approach. Lethaia 39:265–286
Bhargava ON, Bassi UK (1988) Trace Fossils from the palaeozoic-mesozoic sequence of spiti-kinnaur (himachal himalaya) with comments on palaeoenvironmental control on their frequency. J Geol Soc India 32(3):227–238
Bouma AH (1962) Sedimentology of some flysch deposits. Elsevier, Amsterdam, p 168
Bromley RG (1996) Trace fossils: biology, taphonomy, and applications. Chapman and Hall, London, p 361
Buatois LA, Mángano MG (2002) Trace fossils from carboniferous floodplain deposits in western Argentina: implications for ichnofacies models of continental environments. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 183:71–86
Buatois LA, Mángano MG (2011) Ichnology: organism-substrate interactions in space and time. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, p 358
Buatois LA, Mángano MG (2013) Ichnodiversity and ichnodisparity: significance and caveats. Lethaia 46:281–292
Buatois LA, Mángano MG, Maples CG, Lanier WP (1998) Ichnology of an upper carboniferous fluvio-estuarine paleovalley: the tonganoxie sandstone, buildex quarry, eastern kansas. J Paleolimnol 72:152–180
Buatois LA, Wisshak M, Wilson MA, Mángano MG (2017) Categories of architectural designs in trace fossils: a measure of ichnodisparity. Earth-Sci Rev 164:102–181
Buckman JO (1994) Archaeonassa fenton and fenton 1937 reviewed. Ichnos 3:185–192
Burg JP, Bernoulli D, Dolati A, Muller C, Smit J, Spezzaferri S. (2011) Stratigraphy and Structure of the Iranian Makran. AAPG International Conference and Exhibition in, Milan, Italy, p 23–26
Cabrera MIL, Olivro EB, Carmona NB, Ponce JJ (2008) Cenozoic trace fossils of the cruziana, zoophycos and nereites ichnofacies from the fuegian andes, Argentina. Ameghiniana 45:377–392
Callow RHT, McIlory D, Kneller B, Dykstra M (2013) Ichnology of late cretaceous turbidites from the rosario formation, Baja California, Mexico. Ichnos 20:1–14
Crimes TP (1987) Trace fossils and correlation of the late precambrian and early cambrian strata. Geol Mag 124:97–119
Crimes TP, Germs GJB (1982) Trace fossils from the namp group (precambrian-cambrian) of southeast Africa (Namibia). J Paleontol 56:890–970
Crimes TP, McCall GJH (1995) A diverse ichnofauna from eocene-miocene rocks of the makran range (S.E. Iran). Ichnos 3:231–258
Dolati A (2010) Stratigraphy, structural geology and low-temperature thermochronology across the Makran accretionary wedge in Iran: [dissertation]. Swiss institute of technology, Zurich, p 310
Eichwald E. (1868) Lethaea rossica ou paléontologie de la Russie. Décrite et figurée, Atlas. Stuttgart: E. Schweizerbart 1657
Ekdale AA (1980) Graphoglyptid burrows in modem deep-sea sediment. Science 207:304–306
Ekdale AA, Pemberton SG, Bromley RG (1984) Ichnology: trace fossils in sedimentology and stratigraphy. SEPM Short Course, Tulsa, p 317
Emmons E (1844) The taconic system based on observations in New-York, Massachusetts, Maine, Vermont, and Rhode-Island. Caroll and Cook, Albany, p 68
Falcon NL (1974) An outline of the geology of the Iranian Makran. Geogr J 140:284–291
Fan RY, Gong YM (2015) Ichnological and sedimentological features of the hongguleleng formation (devonian–carboniferous transition) from the western junggar NW, China. Palaeogeogr, Palaeoclimatol, Palaeoecol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2015.12.009
Fan RY, Gong YM (2017) Recent progress and focuses of ichnology: outline of the 14th international ichnofabric workshop. J Palaeogeogr 6(4):359–369 (00132)
Fan RY, Uchman A, Gong YM (2017) From morphology to behaviour: quantitative morphological study of the trace fossil Helminthorhaphe. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2017.08.013(inpress)
Fenton CL, Fenton MA (1937) Archaeonassa: cambrian snail trail and burrow. Am Midl Nat 18:454–456
Fillion D, Pickerill RK (1990) Ichnology of the upper cambrian? To lower ordovician bell island and wabana groups of eastern newfoundland, Canada. Palaeontogr Can 7:1–119
Fuchs T (1895) Studien u¨ber fucoiden und hieroglyphen: denkschriften der kaiserlichen akademie der wissenschaften wien. Mathematisch—Naturwissenschaftliche Klasse 62:369–448
Fürsich FT, Taheri J, Wilmsen M (2007) New occurrences of the trace fossil Paleodictyon in shallow marine environments: examples from the Triassic-Jurassic of Iran. Palaios 22:408–416
Gaigalas A, Uchman A (2004) Trace fossils from upper pleistocene varved clays S of Kaunas, Lithuania. Geologija 45:16–26
Geyer G, Uchman A (1995) Ichnofossil assemblages from the nama groip (neoproterozoic–lower cambrian) in namibia and the proterozoic-cambrian boundary problem revisited. Beringeria Spec Issue 2:175–202
Ghaedi M, Mousavi N, Yazdi M. (2008) Scrutiny and biozonation of permiam-triassic boundary in benarizeh area, north of Abadeh: 2nd Symposium of Iranian Paleontological Society, 27–29 May 2008, Islamic Azad University of Khorasgan, p 93–96
Ghaedi M, Johnson K, Yazdi M (2016) Paleoenvironmental conditions of early miocene corals, western Makran Iran. Arabian J Geosci 9:1–20
Ghaedi M, Yazdi M (2016) Bioerosion in the Miocene Coral fauna, Bashagard area, Western Makran Basin. Iranian J Paleontology 4(1): 45–64 (In Persian, with English abstract).
Ghorbani M (2019) Lithostratigraphy of Iran. Springer Nature, Switzerland, p 296
Gibson GG (1989) Trace fossils from late precambrian carolina slate belt South-Central North Carolina. J Paleontol 63(1):1–10
Greb SF, Chesnut Jr., Donald R. (1994) Paleoecology of an estuarine sequence in the breathitt formation (pennsylvanian), central appalachian Basin. Palaios 9 4 388-402
Hantzschel W. (1975) Trace fossils and problematica. In: Teichert C (ed). Treatise on invertebrate paleontology, Part W. miscellanea, supplement I. lawrence USA. Geological Society of America, Boulder. University of Kansas Press, Kansas, p 1–269
Heer O. (1877) Flora Fossilis Helvetiae Die vorweltiliche Flora der Schweiz. J Würster and Comp. Zurich. 182
Heydari E, Hassanzadeh J, Wade WJ, Ghazi AM (2003) Permian-Triassic boundary interval in the abadeh section of Iran with implications for the mass extinction: part 1 sedimentology. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 193:405–423
Hofmann HJ (1990) Computer simulation of trace fossils with random patterns and the use of goniograms. Ichnos 1:15–22
Hofmann HJ, Patel IM (1989) Trace fossils from the type “etchemian series” (lower cambrian ratcliffe brook formation), saint john area, New Brunswick, Canada. Geol Mag 126:139–157
Howard J III, Hatten, (1976) Lebensspuren Produced by Insect Wings. J Paleontol 50(5):833–840
Huber H (1978) Geological map of Iran, 1:1,000,000, with explanatory note. National Iranian Oil Company Exploration and Production Affairs, Tehran
Jenkens RJF (1995) The Problems and potential of using animal fossils and trace fossils in terminal protrozoic biostratigraphy. Precambr Res 73:51–69
Jensen S. (2003) The protrozoic and earliest camberian trace fossil record; patterns, problems and perspectives. Integr Comp Biol 219–228
Keighley DG (1996) The stratigraphy, sedimentology, and ichnology of Mabou Group and Cumberland Group strata (Middle Carboniferous) of western Cape Breton Island, Nova Scotia, eastern Canada: [Dissertation]. University of New Brunswick, Fredericton, p 705
Keighley DG, Pickerril RK (1997) Systematic ichnology of the mabou and cumberland groups (carboniferous) of Western Cape Breton Island, eastern Canada, 1: burrows, pits, trails, and coprolites. Atlantic Geol 33:181–215
Kern JP (1980) Origin of trace fossils in polish carpathians flysch. Lethaia 13:347–723
Kilibarda Z, Schassburger A (2018) A diverse deep-sea trace fossil assemblage from the adriatic flysch formation (middle Eocene–MiddleMiocene) Montenegro (Central Mediterranean). Palaeogeogr, Palaeoclimatol, Palaeoecol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2018.06.023
Knaust D (2012) Trace-fossil systematics. In: Dirk K, Bromley RG (eds) Trace fossils as indicators of sedimentary environments, developments in sedimentology, vol 64. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 79–101
Książkiewicz M (1961) On some problematic organic traces from the flysch of the polish carpathians (part II) (In Polish, English summary). Kwart Geol 5:882–890
Ksiazkiewicz M (1970) Observations on the ichnofauna of the polish carpathians. In: Crimes TP, Harper JC (eds) Trace fossils geological journal, special issue. Seel House Press, Liverpool, pp 283–322
Ksiazkiewicz M (1977) Trace fossils in the flysch of the polish carpathians. Palaeontologica Polonica 36:1–200
Lan ZW, Chen ZQ (2010) Paleodictyon from a nearshore paleoenvironmental setting in the guadalupian (middle permian) of the carnarvon basin, Western Australia. Aust J Earth Sci 57:453–467
Li Y, Lu Z, Wang D (1997) Continental trace fossils and sedimentary environments in Liaohe Basin. Petroleum Industry Press, Beijing (in Chinese, with English Abstract)
Luo M, George AD, Chen ZQ (2016) Sedimentology and ichnology of two lower triassic sections in South China: implications for the biotic recovery from the end-permian mass extinction. Global Planet Change 144:198–212
Luo M, Shi GR, Buatois LA, Chen ZQ (2019) Trace fossil as proxy for biotic recovery after the end-permian mass extinction: a critical review. Earth Sci Rev. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.103059
Luo M, Shi GR, Hu S, Benton MJ, Chen ZQ, Huang J, Zhang Q, Zhou C, Wen W (2017) Early Middle Triassic trace fossils from the Luoping Biota, southwestern China: evidence of recovery from mass extinction. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2017.11.028
Maceachern JA, Bann KL, Pemberton SG, Gingras MK (2007) The ichnofacies paradigm: high resolution paleoenvironmental interpretation of the rock record. In: Maceachern JA, Bann KL, Gingras MK, Pemberton SG (eds) Applied ichnology SEPM short course notes. Society for Sedimentary Geology, Tulsa, pp 27–64
Maillard G (1887) Considerations sur les fossils decrits comme algue. Societe Paleontologique De La Suisse, Memoire 14:1–40
Marenco KN, Hagadorn JW (2018) Big bedding planes: outcrop size and spatial heterogeneity influence trace fossil analyses. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2018.08.008
McCall GJH (1983) Melanges of the Makran, Southeastern Iran. In: McCall GJH (ed) Ophiolitic and related melanges benchmark papers in geology, Stroudsburg. Hutchinson and Ross, Pennsylvania, pp 292–299
McCall GJH (1985) Area report, east iran project, area no. 1, North Makran and South Baluchistan (with two 1:500,000 maps). Geol Surv Iran Rep 57:634
McCall GJH, Kidd RGW (1982) The Makran, Southeastem Iran: the anatomy of a convergent plate margin active from the cretaceous to present. In: Legget JK (ed) Trench-forearc geology: sedimentation and tectonics on modern and ancient active plate margins. Geological Society of London Special Publications, Oxford (Blackwell Scientific Publications), Oxford, pp 387–397
McCall GJH, Simonian GO (1986) The Makran project: a case history. Prospecting in Desert Terrains, London, pp 31–42
McCall J, Rosen B, Darrell J (1994) Carbonate deposition in accretionary prism settings: early miocene coral limestones and corals of the Makran mountain range in Southern Iran. Facies 31:141–178
McCann T (1994) A nereites ichnofacies from the ordovician-silurian welsh basin. Ichnos 3:39–56
McIlroy D (2004) Some ichnological concepts, methodologies, applications and frontiers. In: McIlroy D (ed) The application of ichnology to palaeoenvironmental and stratigraphic analysis, special publication, vol 228. The Geological Society of London, Bath, pp 3–27
McIlory D (2008) Ichnological analysis: the common ground between ichnofacies workers and ichnofabric analysis. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 270:332–338
Melchor RN, Bedatou E, Verde M, Loope D (2015) Contributions of ichnology to palaeoecology, palaeogeography, and sedimentology a special issue related to the second latin-american symposium on ichnology (SLIC 2013). Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology xxx 2015:xxx–xxx
Mohammadi E (2020) Sedimentary facies and depositional environments of the oligocene–early miocene marine qom formation, central iran back-arc basin, Iran (northeastern margin of the Tethyan Seaway). Carbonates Evaporites 35:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-020-00553-0 (Article number 20)
Mohammadi E (2021) Sedimentary facies and paleoenvironmental interpretation of the oligocene larger-benthic-foraminifera-dominated qom Formation in the northeastern margin of the Tethyan Seaway. Palaeoworld 30:356–372
Mohammadi E (2022) Foraminiferal biozonation, biostratigraphy and trans-basinal correlation of the oligo-miocene Qom Formation, Iran (northeastern margin of the Tethyan Seaway). Article accepted for publication, Palaeoworld
Mohammadi E, Hasanzadeh-Dastgerdi M, Ghaedi M, Dehghan R, Safari A, Vaziri-Moghaddam H, Baizidi C, Vaziri M, Sfidari E (2013) The Tethyan Seaway iranian plate oligo-miocene deposits (the qom formation): distribution of rupelian (early oligocene) and evaporate deposits as evidences for timing and trending of opening and closure of the Tethyan Seaway. Carbonates Evaporites 28:321–345
Mohammadi E, Safari A, Vaziri-Moghaddam H, Vaziri MR, Ghaedi M (2011) Microfacies analysis and paleoenviornmental interpretation of the qom formation, south of the Kashan, central Iran. Carbonates Evaporites 26:255–271
Mohammadi E, Vaziri MR, Dastanpour M (2015) Biostratigraphy of the nummulitids and lepidocyclinids bearing qom formation based on larger benthic foraminifera (sanandaj–sirjan fore-arc basin and Central Iran back-arc basin, Iran). Arab J Geosci 8:403–423
Monaco P (2008) Taphonomic features of paleodictyon and other graphoglyptid trace fossils in oligo-miocene thin-bedded turbidites, Northern Apennines, Italy. Palaios 23:667–682
Murchison RI (1850) Memoria sulla struttura geologica delle Alpi, delle Appenini e dei Carpazi: Stamperia granucale., Firenze, p 528
Narbonne GM, Aitken JD (1990) Ediacaran fossils from the sekwi brook area, mackenzie mountains, northwestern Canada. Paleontology 33:890–970
Nielsen JK, Gormus M, Uysal K, Kanbur S (2012) Ichnology of the miocene güneyce formation (Southwest Turkey): oxygenation and sedimentation dynamics. Turkish Journal of Earth Sciences 21:391–405
Paranjape AR, Kulkarni KG, Kale AS. (2014) Sea level changes in the upper aptian-lower/middle(?) Turonian sequence of Cauvery Basin, India—an ichnological perspective. Cretac Res xxx, 1–14.
Pattinson SAJ (2005) Storm-influenced prodelta turbidite complex in the lower kenilworth member at hatch mesa, book cliffs, Utah, USA: implications for shallow marine facies models. J Sediment Res 75:420–439
Peruzzi DG. (1880) Osservazioni sui generi Paleodictyon e Paleomeandron dei terreni cretacei ed eocenici dell'Appennino sett. e centrale. Atti della Societŕ Toscana di Scienze Naturali Residente in Pisa, Memorie 5: 3–8
Peterson LW, Rudzinskas KK (1982) Explanatory text of the taherui quadrangle map 1:250000. Geological Survey of Iran, Tehran
Pickerill RK, Mitchell SF (1999) The graphoglyptid trace fossil Spirorhaphe involuta (de Stefani 1895) from eastern Jamaica. J Geol Soc Jam 33:13–16
Pickerill RK, Romano M, Melendez B (1984) Arenig trace fossils from Salamanca area, western Spain. Geol J 19:249–269
Reichert J. (2007) A metallogenetic model for carbonate-hosted nonsulphide zinc deposits based on observations of Mehdi Abad and Irankuh, Central and Southwestern Iran. Unpublished PhD Thesis, Martin Luther University, p 304
Rodriguez-Tovar FJ, Uchman A, Payros A, Orue-Etxebarria X, Apellaniz E, Molina E (2010) Sea-level dynamics and palaeoecological factors affecting trace fossil distribution in eocene turbiditic deposits (gorrondatxe section, N Spain). Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 285:50–65
Savrda CE, Bottjer DJ, Gorsline DS (1984) Development of a comprehensive oxygen-deficient marine biofacies model: evidence from Santa Monica, San Pedro and Santa Barbara Basins, California continental borderland. Am Asso Petrol Geol Bull 68:1179–1192
Savrda CE (2007) Trace fossils and marine benthic oxygenation. In: Miller PW III (ed) Trace fossils concepts, problems. Elsevier, pp 149–158
Seilacher A (1960) Lebensspuren als leitfossilien. Geol Rundsch 49:41–50
Seilacher A (1962) Form und funktion des trilobiten-daktylus. Paläont Z 36:218–227
Seilacher A. (1977) Pattern analysis of Paleodictyon and related trace fossils. In: Crimes TP, Harper JC (Eds), Trace Fossils 2, vol 9. Geological Journal Special Issue, p 289–334
Seilacher A (2007) Trace fossil analysis. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, p 226
Shufeng Y, Chengzao J, Hanlin C, Guoqi W, Xiaogan C, Dong J, Ancheng X, Shaojie G (2002) Tectonic evolution of tethyan tectonic feld, formation of Northern Margin basin and explorative perspective of natural gas in Tarim Basin. Chin Sci Bull 47:34–41
Solórzano EJ, Buatois LA, Rodríguez WJ, Mángano MG (2017) From freshwater to fully marine: exploring animal-substrate interactions along a salinity gradient (miocene oficina formation of Venezuela). Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2017.05.028
Stampfli GM (2000) Tethyan oceans. In: Bozkurt E, Winchester JA, Piper JDA (eds) Tectonics and magmatism in Turkey and surrounding area. Geological Society of London, Special Publication, pp 1–23
Stampfli GM, Borel GD (2002) A plate tectonic model for the paleozoic and mesozoic constrained by dynamic plate boundaries and restored synthetic oceanic isochrones. Earth Planet Sci Lett 196:17–33
Stefani CD. (1895) Aperçu géologique et description paléontologique de l’île de Karpathos. In: Stefani CD, Forsyth Major CJ, Barbey W (Eds), Karpathos. Étude géologique, paléontologique et botanique, Lausanne, p 1–28
Stöcklin J (1968) Structural history and tectonics of Iran: a review. Am Asso Petrol Geol Bull 52(7):1229–1258
Uchman A (1995) Taxonomy and palaeoecology of flysch trace fossils: the marnosoarenacea formation and associated facies (Miocene, Northern Apennines, Italy). Beringeria 15:1–115
Uchman A (1998) Taxonomy and ethology of flysch trace fossils: revision of the Marian Ksiazkiewicz collection and studies of complementary material. Ann Soc Geol Pol 68:105–218
Uchman A (2003) Trends in diversity, frequency and complexity of graphoglyptid trace fossils: evolutionary and palaeoenvironmental aspects. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 192:123–142
Uchman A, Wetzel A (2011) Deep-sea ichnology: the relationships between depositional environment and endobenthic organisms. In: Huneke H, Mulder T (eds) Deep-sea sediments developments in sedimentology. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 517–556
Urash RG, Savrda CE (2017) Ichnology of an eocene shallow marine passive margin condensed section, eastern Gulf coastal plain, Alabama, USA. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 471:58–70
Vaziri SH, Fursich FT (2007) Middle to upper triassic deep-water trace fossils from the ashin formation, Nakhlak area, Central Iran. J Sci, Islamic Repoblic Iran 18:253–268
Vaziri Moghaddam H, Taheri A. (2003) Study of ichnofossils and ichnofacies of the upper ordovician in west of Shahrud (Dehmolla). Earth Sci (Persian) 50–49
Villegas-Martín J, Netto RG, Correa Lavina EL, Rojas-Consuegra R (2014) Ichnofabrics of the capdevila formation (early eocene) in the Los Palacios Basin (western Cuba): Paleoenvironmental and paleoecological implications. J S Am Earth Sci 56:214–227
Wang Y, Lin JP, Zhao YL, Orr PJ (2009) Palaeoecology of the trace fossil gordia and its interaction with nonmineralizing taxa from the early Middle Cambrian Kaili Biota, Guizhou province, South China. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 277:141–148
Wetzel A (2000) Giant Paleodictyon in eocene flysch. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 160:171–178
Wetzel A, Bromley RG (1996) Re-evaluation of the ichnogenus helminthopsis—a new look at the type material. Palaeontology 39:1–19
Wetzel A, Uchman A (2001) Sequential colonization of muddy turbidites: examples from eocene beloveza formation, carpathians, poland. Palaeogeography, palaeoclimatology, palaeoecology 168:171–186
Wignall PB (1993) Distinguishing between oxygen and substrate control in fossil benthic assemblages. J Geol Soc London 150:193–196
Yang SP (1994) Trace fossils from Early-Middle Cambrian Kaili Formation of Taijiang, Guizhou. Acta Palaeontol Sin 33:350–358 (in Chinese, with English Abstract)
Yochelson EL, Fedonkin MA (1997) The type specimens (Middle Cambrian) of the trace fossil archaeonassa fenton and fenton. Can J Earth Sci 34:1210–1219
Zhang LJ, Buatois LA, Mángano MG, Gong YM, Feng QL, Qi YA, Luo M, Zhang X (2018) Uppermost permian trace fossils along a shelf to slope transect in South China and their implications for oceanic redox evolution and extinction pattern. Global Planet Change. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2018.05.008
Zhao XM, Tong JN, Yao HZ, Niu ZJ, Luo M, Huang YF, Song HJ (2015) Early triassic trace fossils from the three gorges area of South China: implications for the recovery of benthic ecosystems following the permian-triassic extinction. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 429:100–116
Acknowledgements
Dr. Richard Callow are thanked for their useful suggestion and constructive comments. As the first author, I am grateful too for the advice of Dr. Jordi M. de Gibert who unfortunately passed away in 2012. This work is financially supported by the University of Isfahan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghaedi, M., Yazdi, M., Mohammadi, E. et al. Ichnological analysis of the Miocene marine deposits of Makran (SE Iran): implication for paleoenvironmental interpretations. Carbonates Evaporites 37, 51 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-022-00798-x
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-022-00798-x